Updated: 4/14/2023
In the rapidly evolving landscape of blockchain technology, a groundbreaking innovation has emerged: smart contracts. These digital protocols, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code, have revolutionized how transactions and agreements are handled across various industries. For tech company leaders, understanding smart contracts is not just a matter of staying current; it's a strategic imperative.
Blockchain technology, known primarily for underpinning cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, offers far more than a secure digital currency platform. At its core, blockchain provides a decentralized, transparent, and immutable ledger system. Smart contracts leverage this technology to facilitate, verify, or enforce the negotiation or performance of a contract, thereby offering a level of efficiency, security, and trust previously unattainable in digital transactions.
The implications are profound for tech company CEOs and CTOs. Smart contracts can automate processes, reduce costs, and eliminate the need for intermediaries. But more than that, they offer an opportunity to innovate and disrupt traditional business models. As we dive deeper into smart contracts, we'll explore their types, use cases, and best practices, focusing on how they can be strategically employed in fintech and the entertainment industry, particularly in event ticketing.
According to Juniper's research1 blockchain will become critical for all financial institutions working to automate banking processes. Banks and financial institutions could save up to $27 billion annually by 2030 as compliance costs continue to rise in North American and European markets.
In this article, we examine why blockchain-based smart contracts are essential for the future of finance and how they can automate business processes.
What Is a Blockchain-Based Smart Contract?
In 1994, Nick Szabo proposed the idea of smart contracts:
"A smart contract is a computerized transaction protocol that executes the terms of a contract. The general objectives of smart contract design are to satisfy common contractual conditions (such as payment terms, liens, confidentiality, and even enforcement), minimize malicious and accidental exceptions, and minimize the need for trusted intermediaries."
Smart contracts are pieces of self-executing code on a blockchain. They can put the terms of an agreement in place automatically. This technology has immense potential to streamline any process that demands access to multiple databases and resource planning systems.
As for benefits, this level of automation ensures a reduced risk of error or contract manipulation. With a shared database running on a blockchain protocol, the smart contracts remove the need for third-party intermediaries as the contracts are automatically executed.
Understanding Smart Contracts
The Mechanics and Types of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts represent more than a technical novelty; they are a transformative tool for business operations. At their essence, smart contracts are self-executing contracts where the terms of the agreement are written into code and executed on a blockchain. They function as autonomous agents carrying out predefined instructions without intermediaries when certain conditions are met.
Types of Smart Contracts: Application logic contracts, smart legal contracts.
-
Ethereum Contracts:
- Description: Ethereum, often seen as the pioneer of smart contract technology, allows developers to create complex contracts that execute various functions.
- Key Features:
- Turing-complete language (Solidity) enables versatile contract designs.
- Decentralized Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) for execution.
- They are widely used for decentralized applications (dApps).
-
Chainlink Contracts:
- Description: Chainlink introduces an additional layer to smart contracts, allowing them to interact securely with external data sources and off-chain systems.
- Key Features:
- Oracles for real-world data integration.
- It has enhanced reliability and security for data-sensitive applications with the help of smart contracts stored on a blockchain.
-
Hyperledger Fabric Contracts:
- Description: Hyperledger Fabric offers a more private, permissioned approach to smart contracts, suitable for enterprise solutions.
- Key Features:
- Modular architecture for customizable business solutions.
- Strong privacy and confidentiality controls.
-
Other Contract Types:
- Other platforms like EOS, Tezos, and Cardano, which also offer unique features and capabilities for smart contracts, should be briefly mentioned.
Advantages in Business Operations:
- Automation and Efficiency: Smart contracts automate previously manual and time-consuming tasks, streamlining business processes.
- Trust and Transparency: The immutable nature of blockchain ensures that contract terms cannot be altered, fostering trust among parties.
- Cost Reduction: By eliminating intermediaries, smart contracts reduce transaction costs.
- Accuracy and Security: Automated execution minimizes human error and enhances security against fraud.
Traditional vs. Smart Contracts
Understanding the benefits of smart contracts is closely connected to properly comprehending how blockchain works and what it brings to the table in finance.
Blockchain-based smart contracts contain the same level of detail as physical contracts. They can do something no conventional contract can do: perform tasks such as negotiating prices and monitoring inventory levels. This capability replaces expensive, manual effort with dynamic, automated tracking of supply chains, inventory levels, and expenses to reduce costs and maximize profits.
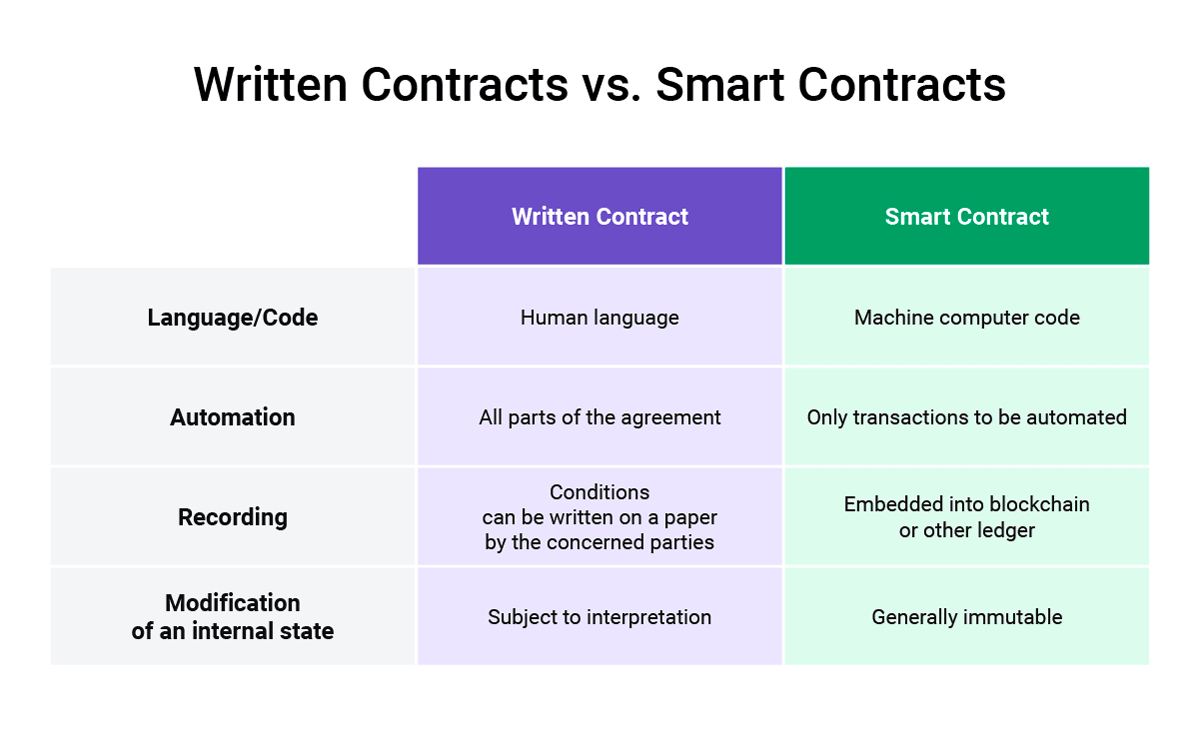
Source: Cointelegraph
How Do Smart Contracts Work
In more technical terms, creating a smart contract can be broken down into a few steps—first, a smart contract forms an agreement between two or more parties. Once established, the two sides can agree on conditions for the smart contract to be considered complete. The requirements are written into the smart contract, then encrypted and stored in the blockchain network.
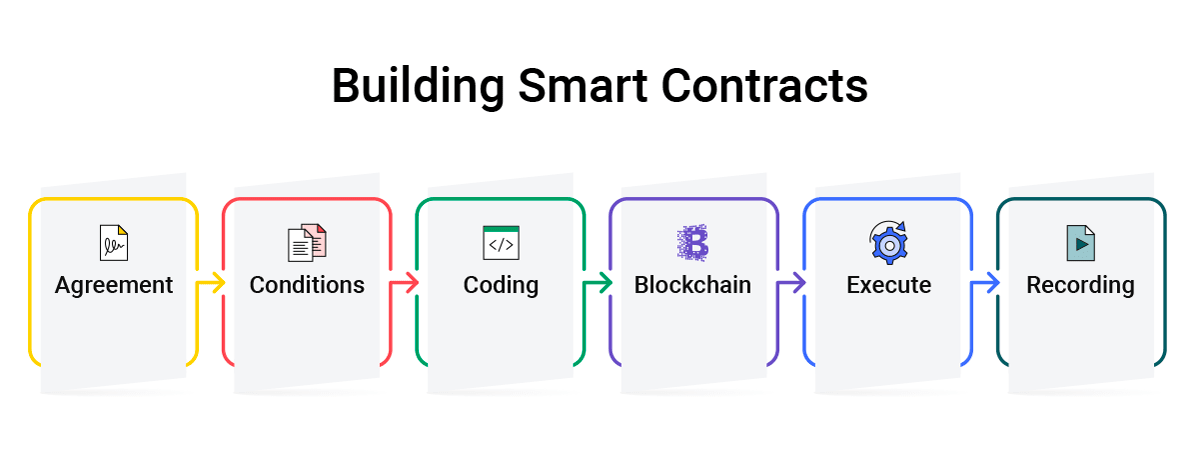
Once the contract is complete, the transaction is recorded on the blockchain. Then, all nodes would update their copy of the blockchain with this transaction, updating the new "state" of the network.
Smart contracts control the transfer of digital currencies or assets between parties. They define rules and conditions around an agreement, including penalties, and automatically enforce all contractual obligations.
Where smart contracts can be used:
- Banks and financial companies
- Health insurance policies
- Trade clearing and settlement
- Supply chains
- Trade finance
- Event industry
Benefits and Challenges of Using Blockchain-Enabled Contracts
Smart contracts can be a worthwhile option in environments where many transactions happen within a network and manual tasks must be performed for every application. Blockchain has become a type of shared database, as it provides a secure source of information and enables faster approvals and calculations with minimal errors.
Blockchain-based smart contracts come with many benefits:
High accuracy and reliability. Smart contracts can significantly increase the efficiency of various manual business processes.
Real-time updates. Automated transactions are quickly executed, and both parties can follow the contract's live status.
Reduced number of intermediaries. Standard contracts require intermediaries to ensure the validity of each transaction, but smart contracts don't need an arbitrator.
Lower cost. Smart contracts can significantly reduce dependency on human intermediaries and reduce the overall cost of the transaction.
Adaptability to different business models. Contracts are a fundamental part of business as they allow transactions to be performed as agreed upon, regardless of the industry.
Due to its early development stages, smart contract technology still needs to advance in certain aspects:
Processing speed and scalability. Currently, blockchains have issues with latency, as it takes time for a block of transactions to become a part of the ledger.
Dependence on programmers. Because all blockchain-based smart contracts are unchangeable, developers need to anticipate every case that might require changes in the contract.
Privacy. The code within smart contracts is visible to everyone in the network, and some applications cannot risk outside parties accessing their sensitive data.
High latency. Ethereum, the most popular blockchain technology for smart contracts, takes 17 seconds to add verified blocks to the ledger. This technology still needs improvement compared to milliseconds, which are standard for storing non-blockchain data.
When it's Time to Consider Using Smart Contracts
Industry leaders not focusing on the smart contract development or the overall development of blockchain technology should keep an eye on application logic contracts and evaluate how we can use this technology to make the process more efficient. Operations executives of big companies are already investing in smart contract projects to assess their efficiency.
Factors to look into if you are thinking about implementing smart contracts:
- Manual workflows
- Complex workflows
- Multiparty agreements
- Number of independent transactions
The Ethereum blockchain transforms conventional banking services through the implementation of smart contracts and DApps. Thus, smart contracts promote the Ethereum blockchain's benefits for attracting many crypto investments and payment transactions from crypto investors.
Some use cases show the importance of smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps) on the Ethereum blockchain, such as multi-signature accounts, external agreements, storage, etc. Any crypto investor can start using smart contracts if there is an investment in Ethereum's native token, ETH.
Smart contracts offer banks and other financial institutions an opportunity to streamline trade clearing and replace this labor-intensive work with an automated system. They are helpful to financial institutions as they detect discrepancies in settlement systems. And a few Wall Street banks are currently testing settlement systems based on smart contracts.
Use Cases of Smart Contracts
Transforming Industries with Automated Agreements
Smart contracts are not just theoretical constructs; they have practical and impactful applications across various industries. The fintech and entertainment sectors, particularly event ticketing, offer compelling examples of how these digital contracts can revolutionize traditional practices.
1. Fintech Industry:
-
Streamlining Payments and Remittances:
- Smart contracts automate payment processes, reducing the time and cost associated with traditional bank transfers.
- They enable more efficient cross-border transactions, bypassing conventional banking systems and their associated fees.
-
Enhancing Loan and Mortgage Processes:
- Loan origination and servicing can be automated, with terms encoded in application logic contracts.
- Automated verification of compliance and creditworthiness speeds up approval processes, enhancing customer experience.
-
Improving Audit and Compliance Mechanisms:
- The transparent nature of blockchain aids in maintaining accurate records for auditing.
- Smart contracts can be programmed to ensure compliance with regulations automatically, reducing the risk of human error.
2. Entertainment Industry (Event Ticketing):
-
Counteracting Fraud in Ticket Sales:
- Each ticket can be uniquely represented as a smart contract on the blockchain, making counterfeiting virtually impossible.
- Smart contracts ensure tickets are sold and resold at predetermined prices, eliminating the risk of fraudulent markups.
-
Implementing Dynamic Pricing Models:
- Ticket prices can be programmed to vary based on demand, time, or other factors, maximizing revenue while ensuring fair access.
- Artists and event organizers can retain more control over pricing, benefiting from secondary sales directly.
-
Enhancing Customer Engagement and Loyalty Programs:
- Smart contracts can facilitate reward systems, where attending events or early ticket purchases yield benefits, enhancing customer loyalty.
- They enable more personalized interactions with fans, offering exclusive content or experiences based on ticket purchase history.
Other Notable Smart Contract Use Cases:
- Supply Chain Management: Enhancing transparency and efficiency.
- Real Estate: Simplifying property sales and lease agreements.
- Healthcare: Securing patient data and managing consent forms.
Best Practices in Implementing Smart Contracts
As CEOs and CTOs of tech companies consider integrating smart contracts into their operations, it's crucial to follow best practices to maximize their benefits while mitigating risks. Smart contract implementation involves technical, legal, and operational considerations.
1. Ensuring Code Quality and Security:
- Rigorous Testing: Before deployment, smart contracts should undergo extensive testing, including unit tests, integration tests, and stress tests, to ensure they function as intended under various conditions.
- Code Audits are crucial to smart contract development. Regular audits by independent security experts can identify vulnerabilities and suggest improvements, enhancing the security of the contracts.
- Bug Bounty Programs: Implementing bug bounty programs encourages ethical hackers to report vulnerabilities, further strengthening contract security.
2. Legal Considerations and Compliance:
- Understanding Regulatory Frameworks: Compliance with relevant laws and regulations, including those related to digital assets, is paramount. This may involve consulting with legal experts in blockchain technology.
- Clear Terms and Conditions: Smart contracts should have unambiguous terms that align with traditional legal contracts to avoid disputes and legal complications.
3. Effective Integration with Existing Systems:
- Interoperability: Smart contracts should be compatible with existing systems and platforms within the organization. This may require using middleware or APIs for seamless integration.
- Employee Training: Educating employees about smart contracts, functionalities, and benefits is crucial for effective adoption and usage.
4. Continuous Monitoring and Maintenance:
- Ongoing Management: Smart contracts, once deployed, should be continuously monitored for performance and compliance.
- Update Mechanisms: Developing mechanisms to update contracts in response to changing regulations, business needs, or discovered vulnerabilities is essential for long-term viability.
What is the Future of Smart Contracts
Blockchain-based contracts are undoubtedly moving the finance industry forward. Yet, without regulatory clarity, they cannot offer any law-supported guarantees.
As B2B cross-border payments stored on blockchain are set to increase in value from $122.2 million in 2020 to $1,8 billion in 2025, 2 the market for smart contracts will only keep expanding.
As technology continuously evolves, the landscape of smart contracts is poised for significant advancements. For tech leaders, staying ahead of these trends is vital for strategic planning and maintaining a competitive edge.
1. Advances in Technology:
- Scalability and Efficiency Improvements: Ongoing research in blockchain scalability, such as Layer 2 solutions and sharding, promises to enhance the efficiency and speed of smart contract transactions.
- Enhanced Security Protocols: As security concerns remain paramount, expect advancements in cryptographic techniques and consensus algorithms, further bolstering the security and reliability of smart contracts.
- Integration with AI and IoT: The convergence of smart contracts with AI and IoT opens up possibilities for more sophisticated, self-optimizing contracts that can interact intelligently with data and devices.
2. Expanding Industry Applications:
- Government and Public Sector: Smart contracts can bring automation and efficiency to governance systems, which could help enhance transparency in public spending.
- Insurance: Smart contracts can streamline operations in the insurance sector by automating claim processing and verification.
- Environmental Sustainability: Tokenization of carbon credits and automated compliance with environmental regulations are potential areas where smart contracts could significantly impact.
3. Legal and Regulatory Developments:
- Standardization of Smart Contract Protocols: Efforts towards standardizing smart contract protocols and languages could facilitate broader adoption and interoperability across different blockchain platforms.
- Regulatory Clarity: As governments and regulatory bodies become more familiar with blockchain technology, more explicit guidelines and frameworks for smart contracts can be expected, fostering a more conducive environment for innovation and adoption.
4. User Experience and Accessibility:
- Improved User Interfaces: Strides in developing more user-friendly interfaces for creating and managing smart contracts will make them more accessible to non-technical users.
- Education and Awareness: Increased educational initiatives will demystify smart contracts, leading to wider understanding and adoption among businesses and individuals.
Are you curious whether smart contracts would make your processes more efficient? Our experienced team is happy to answer any questions about this quickly-evolving finance technology, particularly regarding the use of smart contracts.
Conclusion
As we have navigated the intricate world of smart contracts, it's clear that these digital protocols are more than just a technological novelty; they are a pivotal component in the future of business and governance. For CEOs and CTOs at the helm of tech companies, the implications of smart contracts are profound and wide-reaching.
Smart contracts offer a blend of automation, security, and efficiency that can significantly enhance business operations. The applications are diverse and impactful, from streamlining financial transactions in the fintech sector to revolutionizing ticketing systems in the entertainment industry. However, integrating smart contracts into existing systems demands a thorough understanding, careful planning, and complete adherence to best practices to harness their potential fully.
Looking forward, the evolution of smart contracts will likely be marked by technological advancements, expanding industry applications, and an evolving legal landscape. Integrating smart contracts with emerging technologies like AI and IoT and the push towards more user-friendly interfaces will further broaden their appeal and utility.
For tech leaders, the call to action is clear: Stay ahead of the curve by understanding the current landscape of smart contracts, anticipating future trends, and preparing for them. Proactively adopting and thoughtfully implementing smart contracts could be a game-changer, offering a competitive edge in a rapidly changing digital world.
In conclusion, smart contracts stand at the forefront of the next wave of digital transformation. By embracing this technology, CEOs and CTOs can lead their organizations into a new era of efficiency, transparency, and innovation.





