Updated: 5/25/2022
Search engines have always been the easiest and most natural way to dig up information. Their “snappiness” gives users the impression that new data is immediately available, making them a pleasure to use.
However, vast amounts of data cannot be simply flattened into a single search index, similar to standard search engines, and instead requires the joint capabilities traditionally offered only by relational databases. With millions of downloads, Elastic Stack is one of the world’s most popular data management platforms.
Some of the biggest companies like Netflix, eBay, and Walmart, rely on Elasticsearch to monitor customer service operations, utilize advanced analytics, and reveal customer purchasing patterns.
In this article, we will give a comprehensive overview of Elastic stack, including what role it plays in analyzing data pipelines and how Softjourn has helped its clients to use it.
Core Elements of ELK Stack
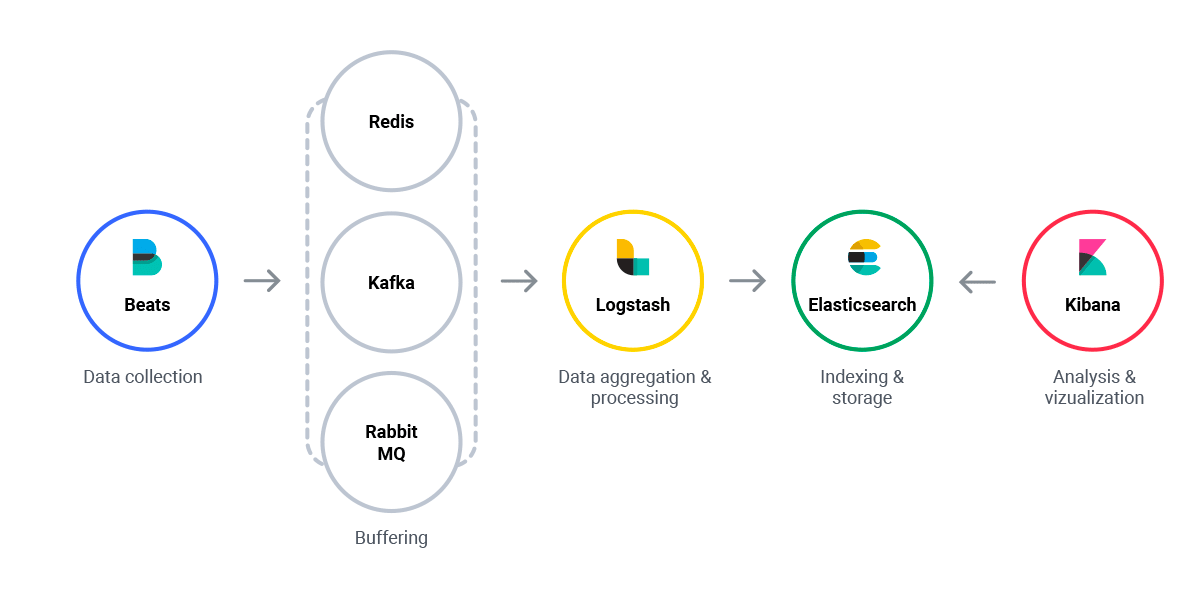
Elasticsearch is the central component of a set of open-source tools for data ingestion, storage, analysis, and visualization. With Logstash, a tool for collecting and processing logs, and Kibana, an interface for searching and visualizing data in ElasticSearch, the Elastic stack is being adapted more and more widely every day.
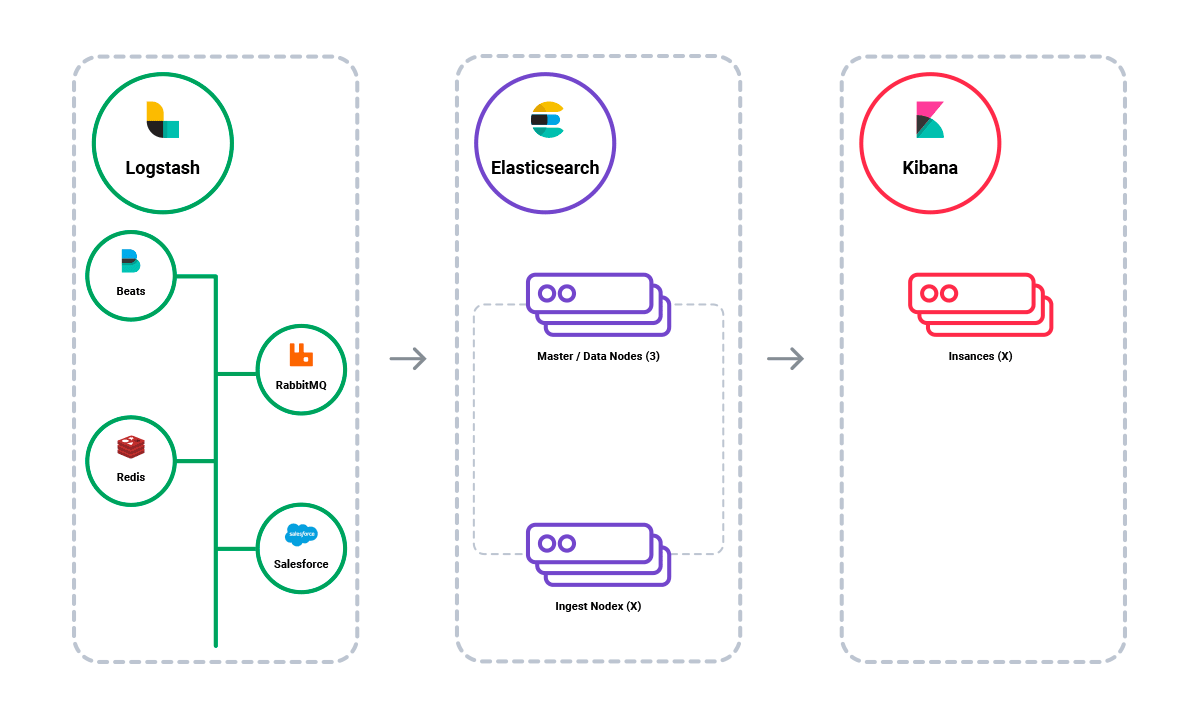
Logstash is a log aggregator that collects data and executes different enhancements and transformations to ship the data back to a supported output destination. It is a valuable tool for collecting, parsing and transporting logs for downstream use.
Elasticsearch is an open-source, full-text search and analysis engine based on Apache Lucene. ElasticSearch connects Logstash and Kibana, giving the ability to store logs in a highly scalable, durable and accessible manner.
Kibana works with Elasticsearch as a visualization tool that allows users to analyze data. Kibana is a web interface that can be used to search and view the logs that Logstash has indexed.
Beats collect different types of data to forward it to the stack. It contains and sends data from hundreds of thousands of machines and different systems to Logstash or Elasticsearch.
The Elastic stack, particularly Elasticsearch,, is already known and used by many developers. Hundreds of companies have successfully implemented this proven search engine and its connected tools. Other tools developed by Elastic are:
- Elastic Cloud — Hosts Elasticsearch clusters
- Machine Learning — Used to analyze data patterns
- APM — Application Performance Monitoring
- Swiftype —One-click site search
How is Elasticsearch used?
Elasticsearch is a distributed, RESTful search and analytics engine capable of solving a growing number of use cases. SInce its release in 2010, Elasticsearch quickly became and stayed popular for its use in log analytics, full-text search, security intelligence and business analytics.
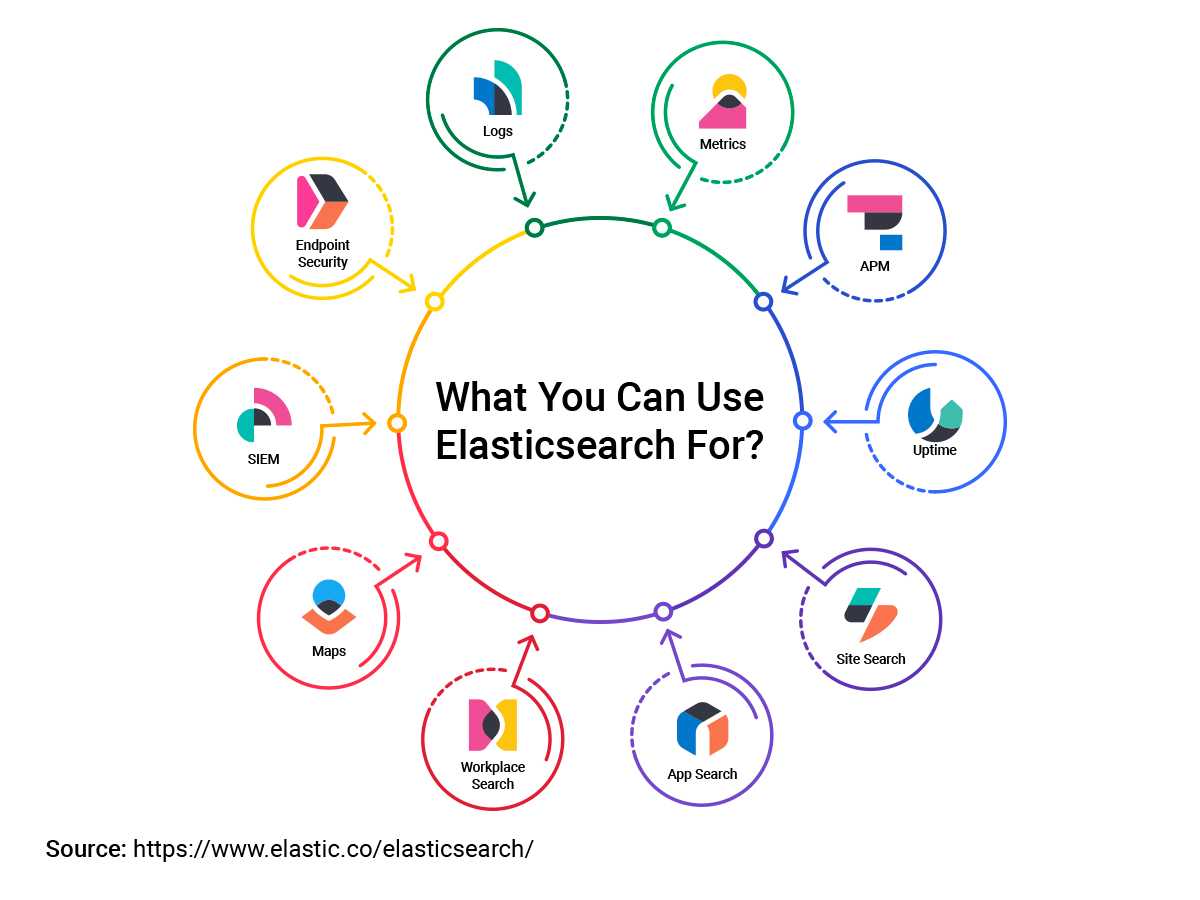
Elasticsearch is currently one of the best solutions for searching through reports because it uses a variety of filters and options. The speed and scalability of Elasticsearch can be used for many different actions and is commonly used for:
- Website searches
- Application searches
- Enterprise searches
- Logging
- Infrastructure metrics
- Container monitoring
- Application performance monitoring
- Security analytics
- Business analytics
Benefits of Using Elasticsearch
Performance. Elasticsearch offers simple REST-based APIs, schema-free JSON documents, and a simple HTTP interface that makes it an easy tool for building applications for various use-cases. It also can process large volumes of data and quickly find matches for different queries.
Operation speed. Operations in Elasticsearch usually take less than a second to complete, whether it's reading or writing data. This makes it a useful tool for detecting system anomalies or application monitoring.
Variety of tools and plugins. Elasticsearch is integrated with Kibana, Beats and Logstash. It's also possible to use a number of open-source plugins alongside it, like language analyzers and suggesting tools.
Price. The open-source features are free to use under the Apache 2 license. Additional free features are available under the Elastic license.
Widely-used. Numerous developers around the world are using Elastic stack as its one of the best tools on the market.
News and Trends Regarding Elastic Stack
As one might expect from an extremely popular open-source project, the ELK Stack is constantly and frequently updated with new 7.x versions and useful features.
Elasticsearch
Elasticsearch 7.x is easier than ever to set up, since it now works with Java. With the new update, comes performance improvements, including a real memory circuit breaker, better search performance, and a 1-shard policy. In addition, a new cluster coordination layer makes Elasticsearch even more scalable and resilient.
Logstash
Logstash’s Java execution engine (announced as experimental in version 6.3) is enabled by default in version 7.x. By replacing the old Ruby execution engine, it now has improved performance and offers an entirely faster experience.
Kibana
Kibana is undergoing a major facelift. It will have new pages and will be updated with major usability improvements. The latest release comes with improved querying and filtering abilities.
Beats
Beats 7.x conforms with the Elastic Common Schema (ECS) — a new standard for field formatting. Metricbeat supports a new AWS module for pulling data from AWS CloudWatch, Kinesis and SQS. New modules were introduced in Filebeat and Auditbeat as well.
How Softjourn has Utilized Elasticsearch/ELK
"More Than Just 'Search': Harnessing Elasticsearch for Enhanced Decision-Making in Finance, Event Ticketing, and Media and Entertainment
Elasticsearch is an advanced, open-source, distributed search and analytics engine with immense potential for businesses across various sectors, particularly in industries where Softjourn has extensive experience, such as Finance, Event Ticketing, and Media and Entertainment.
By leveraging Elasticsearch's capabilities to analyze, search, and store vast amounts of data in near real-time, Softjourn can unlock numerous opportunities to enhance its offerings and provide more excellent value to its clients.
Here are some use cases of Elasticsearch:
- Fraud Detection: Elasticsearch can be used to analyze and identify patterns in financial transactions, which helps detect fraudulent activities. Financial institutions can proactively prevent fraud and mitigate risks by quickly searching and analyzing large volumes of data.
- Risk Management: Elasticsearch can process and analyze risk-related data, such as credit scores, historical transactions, and market trends, allowing financial institutions to make informed decisions and manage risks more effectively.
- Portfolio Analysis: Elasticsearch can analyze and visualize large financial data sets, enabling portfolio managers to make better investment decisions based on trends, correlations, and other insights.
- Real-time Trading Analytics: Elasticsearch can process real-time market data and provide insights into trading patterns, helping traders and investment managers optimize their trading strategies.
- Personalized Recommendations: Elasticsearch can analyze user preferences and behavior to provide customized event recommendations, improving the user experience and increasing ticket sales.
- Real-time Inventory Management: Elasticsearch can handle large volumes of data in real-time, allowing event organizers to monitor ticket sales, manage inventory, and optimize pricing strategies.
- Search and Filtering: Elasticsearch can help users quickly search and filter through many events and tickets, allowing them to find the most relevant events and purchase tickets more efficiently.
- Data Analysis for Event Performance: Elasticsearch can analyze event data, such as attendance, ticket sales, and social media engagement, enabling event organizers to optimize their marketing efforts and improve future events.
- Content Search and Discovery: Elasticsearch can index and search through vast amounts of media content, such as articles, videos, and audio files, allowing users to find and discover relevant content quickly.
- Sentiment Analysis: Elasticsearch can analyze social media data, reviews, and comments to gauge audience sentiment and engagement, helping content creators and marketers better understand their target audience.
- Personalized Recommendations: Elasticsearch can analyze user behavior and preferences to provide personalized content recommendations, improving user engagement and increasing content consumption.
- Real-time Analytics: Elasticsearch can process and analyze large volumes of user data in real time, allowing media and entertainment companies to monitor content performance, engagement, and advertising effectiveness.
By tapping into Elasticsearch's diverse use cases in Softjourn's key industries, such as Finance, Event Ticketing, and Media and Entertainment, Softjourn can help its clients optimize their decision-making processes, improve user experiences, and stay ahead of the competition.
Elasticsearch's fast and accurate search capabilities, real-time analytics, and actionable insights can enable Softjourn to create innovative solutions that cater to the evolving needs of these industries and drive growth for both Softjourn and its clients.
Softjourn has and will continue to use the ELK stack in projects due to its speed and multifunctionality—plus the fact it all comes in one package! Here are some instances where Softjourn harnessed the power of Elasticsearch:
Creating an Application with Data-Tracking Capabilities
Our client, a leading provider of digital publishing and conversion solutions, turned to Softjourn with an idea for a solution that would track data packets sent from their existing applications and publications, and allow reports on that data to be viewed by authorized users.
We utilized ElasticSearch in order to search for all reports, filters and different options. This was a perfect starting point to gather the information we needed to build a stand-alone application for our client.
Building a Multi-Feature Interface
A client who specializes in digital publishing and conversion needed Softjourn’s help realizing their idea. They wanted a new interface that would receive tracking data from the client's existing technology and would allow users to view and export relational data.
Before writing the report application, Softjourn’s team started off by adjusting ElasticSearch, since it would eliminate the need to design for specific-use cases, the way some NoSQL databases require. This was a big win for us with our client. as it enabled our teams to iterate on solutions faster than would otherwise be possible.
Conclusion
In today’s competitive market, organizations cannot afford downtime or slow performance of their applications. Performance issues can damage a brand’s relationship to users, so engineers rely on different types of data generated by their applications and infrastructure.
Elasticsearch is a platform with many applications. Since 2010, it proved to be a robust set of products that successfully ingest and store data from various sources in various formats. New versions are providing users with new Elasticsearch features and changes to underlying data structures to ensure it responds to its user’s changing needs.
Softjourn continues to provide Elasticsearch consulting and implementation services and support clients interested in using the ELK tech stack.










