Embedded finance is no longer a futuristic concept—it’s a rapidly growing trend reshaping the way businesses and consumers interact with financial services.
From offering instant loans at checkout to streamlining payments within apps, embedded finance integrates traditional financial services directly into non-financial platforms, enabling faster, more seamless transactions.
However, implementing embedded finance solutions requires careful consideration of regulatory compliance, data security, and technological integration. Companies must navigate complex financial landscapes to ensure their embedded services meet legal standards and protect user information. Choosing the right technology partners and platforms is crucial for successful implementation.
In this article, we’ll explore embedded finance, its growing importance, and how it’s poised to transform industries ranging from e-commerce to transportation.
We will also explore the future of embedded finance, emphasizing key statistics and trends that position this market as one of the most promising growth areas in fintech.

What is Embedded Finance?
Embedded finance refers to the integration of financial services—such as payments, lending, or insurance—into non-financial platforms, applications, or services. This means that rather than needing to visit a traditional bank or financial institution, consumers can access these services directly at the point of need.
The beauty of embedded finance is its ability to make financial services available within the everyday apps and platforms people already use.
For example, when booking a flight online, you can now seamlessly purchase travel insurance during checkout, or split payments over time through buy-now-pay-later (BNPL) options.
Wayne Chang, co-founder of Digits, notes, “Companies that adopt embedded finance technologies are going to have an enormous competitive advantage over others in their market.”
This is because embedded finance simplifies the financial journey for consumers and helps businesses process transactions faster and more efficiently.
A Booming Market
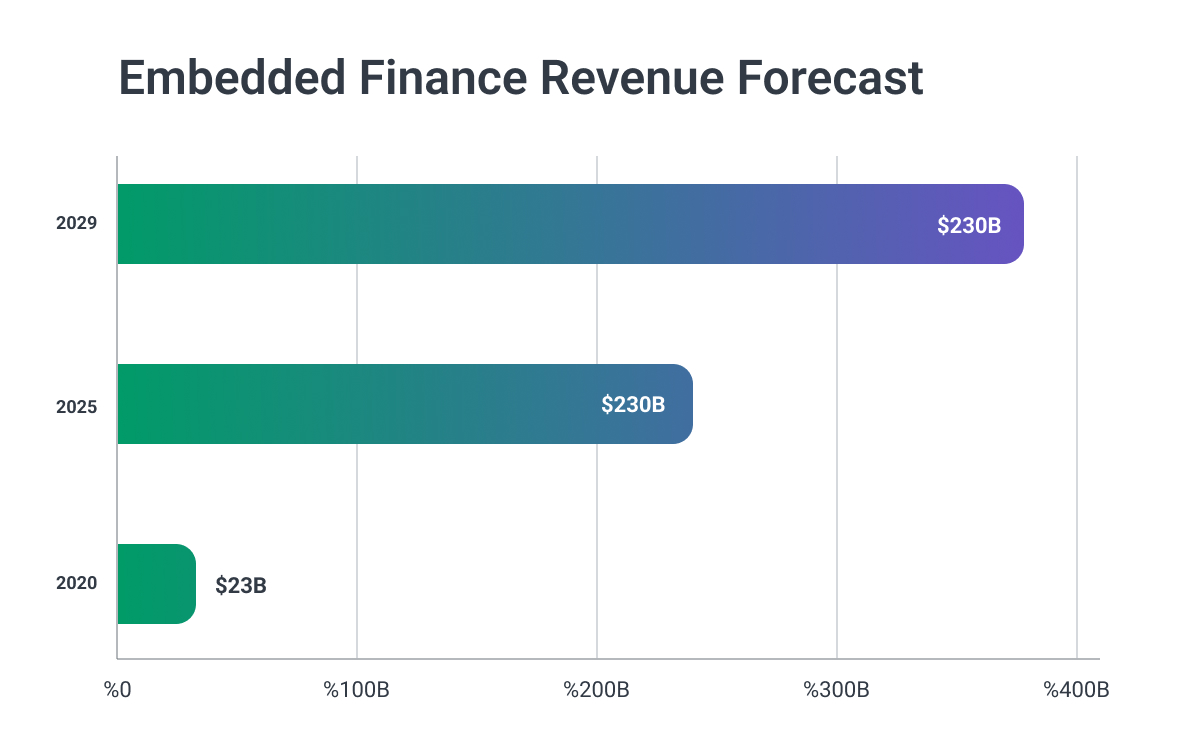
The embedded finance market is on a steep growth trajectory, with estimates suggesting it could reach a global value of $7 trillion within the next decade. This growth is driven by several factors, including advancements in API technology, changes in consumer behavior, and the increasing digitalization of commerce.
In 2020, embedded financial services generated $22.5 billion in revenue, and this figure is projected to soar to $384.8 billion by 2029—a nearly 17x increase.
According to Grand View Research, the market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 32.2% through 2030, further emphasizing the substantial opportunities for businesses and fintech providers alike.

Key Examples of Embedded Finance
Embedded finance takes many forms, with different use cases depending on the industry. Below are some of the most prominent examples:
Embedded Payments
This is perhaps the most common form of embedded finance. Companies like Uber, DoorDash, and Amazon enable customers to make payments directly within their apps, streamlining the transaction process.
According to Digits co-founder Sofiat Abdulrazaaq, “Embedded finance makes it quicker and simpler for consumers to check out,” eliminating the need to re-enter payment details and enhancing the user experience.
Embedded Lending
BNPL services are one of the most visible examples of embedded lending. Companies like Klarna and Affirm allow consumers to split payments into installments without leaving the merchant’s checkout page.
This not only improves the customer experience but also increases sales for businesses by making products more affordable through flexible payment options.

Embedded Insurance
Another growing sector is embedded insurance, where consumers can purchase coverage at the point of sale. Whether booking a flight or buying a new car, embedded insurance ensures customers can get the coverage they need instantly, without dealing with traditional insurance companies.
Embedded Banking
Some platforms, such as Shopify and Lyft, offer their own branded bank accounts and debit cards to users. This encourages loyalty and provides users with more convenient ways to access their earnings.
For instance, Lyft drivers can receive immediate payment after a ride through a dedicated account, eliminating the need to wait for weekly payouts.
Embedded Investing
Platforms like Robinhood and Cash App allow users to invest directly within their apps, offering an easy entry point into stock trading and cryptocurrency. Embedded investing democratizes access to financial markets by making investing as easy as spending money online.

How Embedded Finance Benefits Businesses and Consumers
For businesses, adopting embedded finance can lead to increased customer engagement, improved user experience, and additional revenue streams.
A report by Plaid found that 88% of companies that implement embedded finance solutions report higher customer engagement, while 85% say it helps them acquire new customers.
Embedded finance also provides businesses with valuable data about customer behavior, which can be used to personalize services and foster loyalty. For instance, fintech platforms that offer branded debit or credit cards can analyze spending habits and tailor rewards programs that align with customer preferences.
Consumers benefit from convenience and speed. By integrating financial services into platforms they already use, customers can complete transactions in fewer steps, making their interactions with businesses smoother and more efficient.
Embedded finance also reduces reliance on traditional financial institutions, which often have more cumbersome processes.

The Future of Embedded Finance
The embedded finance landscape is still evolving, but its impact on both financial services and non-financial industries is expected to deepen.
Experts predict that embedded finance will become a standard feature in sectors like healthcare, education, and real estate, as businesses increasingly integrate financial solutions into their service offerings.
Embedded finance also holds the potential to serve underbanked populations by offering financial services in more accessible, user-friendly ways.
According to Joris Hensen of Deutsche Bank, “Embedded finance can help foster economic growth by offering banking services through mobile wallets or microfinance options within supply chains,” thereby democratizing access to financial tools.
Final Word
As embedded finance continues to grow, it is transforming how businesses and consumers engage with financial services. By integrating payments, lending, insurance, and more directly into apps and platforms, embedded finance simplifies the user experience and unlocks new opportunities for businesses to enhance customer loyalty and revenue streams.
The future of embedded finance is bright, and companies that embrace this technology stand to benefit significantly in the coming years.
Whether through smoother payment processes, instant loan offerings, or personalized insurance options, embedded finance is proving to be a game-changer in the world of fintech and beyond.
Industry Updates
Retail FinTech VC Funding Drops in Q1 2025
Venture Capital investment in retail fintech fell nearly 38% in Q1 2025, totaling $1.9B, as concerns over tariffs, inflation, and IPO slowdowns outweighed optimism around AI and regulatory easing.
Seed-stage funding and valuations saw steep declines, while growth-stage deals remained afloat thanks to outliers like Klarna’s $12B valuation. With ongoing market uncertainty, restrained funding is expected to continue through mid-2025.
[Source: PitchBook via PYMNTS, May 2025]












