In the dynamic world of startups and software innovation, the race to market is often a defining factor in success.
MVP, or Minimum Viable Product, has emerged as a pivotal strategy in this race, allowing businesses to launch products swiftly while ensuring they meet the core needs of their target audience.
One of the key aspects of any MVP, according to Forbs are it's value propositions. Once a company has most of the answers to questions about what product offers and how it solves a certain problem, it becomes easier to build an MVP.

What is MVP in Software Development?
In software development, MVP stands for Minimum Viable Product. It's a concept that refers to the most basic version of a product that allows a team to release it to the users with the minimum amount of work.
The primary goal of an MVP is to validate the product's core concept with the least effort, quickly gather user feedback, and iterate based on that feedback.
The Philosophy Behind Software MVP
Lean is known to be one of the most effective software development approaches as it focuses on ensuring fast product delivery. It's rooted in the Lean manufacturing process from the 1980s, but it progressed significantly, and it became a part of the Agile software development methodology.
Today, the MVP approach is rooted in the Lean Startup methodology, which emphasizes the importance of adapting and adjusting before any large sums of money or time are invested in software development.
By releasing an MVP, companies can test their hypotheses about the market, understand what resonates with users, and iterate based on real-world feedback. Especially when it comes to event or payment processing solutions, it's key to see how the users will react to a new product and where there's room for improvements.
According to an article in the Harward Business Review, a crucial aspect of product development lies in the differing perspectives on business models between startups and established companies. Startups actively seek to discover and refine their models through rapid iteration, whereas established companies often focus primarily on executing their existing models. 
Key Benefits of MVPs in Software Development
The advantages of embracing an MVP approach are multifaceted and pivotal for companies seeking to thrive in the dynamic landscape and stay competitive. We will focus on the four key benefits that can make all the difference and turn your solution into a user-centric powerhouse.
- Essential Features Only: The MVP should include only the core features that allow the product to be operational, omitting secondary or non-essential functionalities.
- Quick to Market: The aim is to release the product quickly to start gathering feedback as soon as possible.
- Feedback Loop: An MVP serves as a tool to understand user preferences, requirements, and potential areas of improvement.
- Foundational: MVP sets the foundation for future iterations of the product based on real-world insights.
- Minimalistic Design: The MVP should have a simple and streamlined design focusing only on necessary features and avoiding any necessary complexity.
- Scalability: The MVP should prioritize user needs and preferences, enhancing their experience and addressing their pain points.
- Cost-effectiveness: Developing an MVP allows for cost reduction by avoiding the development of unnecessary features and functionalities.
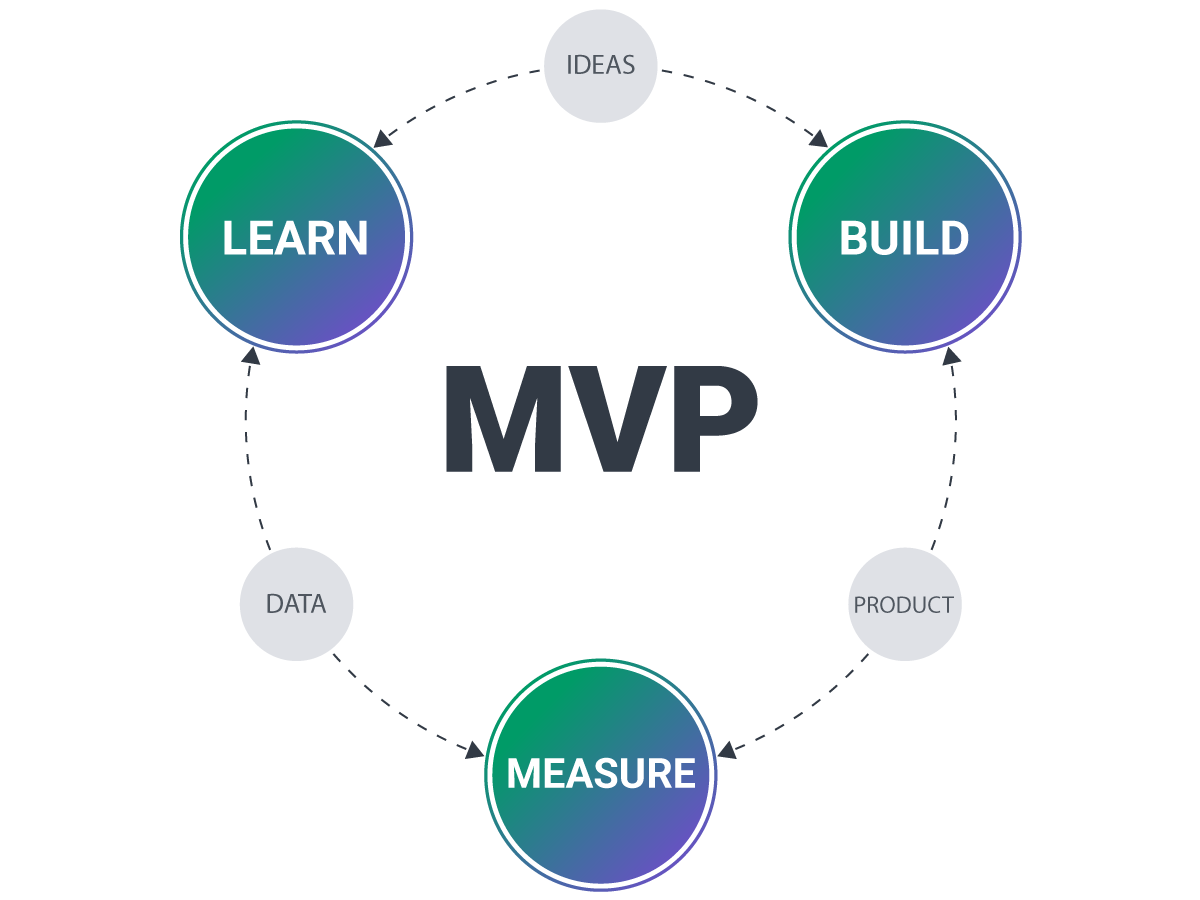
The Importance of Working on Software MVP
- Risk Reduction: By releasing a software MVP, companies can gauge the market's response before heavily investing in full-fledged product development.
- Cost-Effective: It reduces the initial development costs as only the core features are built. The development team focuses only on the key aspects of the products and ensures that they follow a proof of concept development roadmap.
- Faster Time to Market: Companies can launch their product faster, gaining a potential competitive advantage.
- User-Centric Development: Continuous feedback ensures that subsequent versions of the product are more in line with user needs and preferences.
Building an MVP: Key Steps
- Identify the Core Problem: Understand the primary problem the product aims to solve. This clarity is crucial in determining the MVP's features.
- Design and Prototype: Create a basic design or prototype of the solution. This step doesn't involve extensive development but provides a visual representation of the product.
- Develop Essential Features: Focus on building features that are absolutely necessary to solve the core problem.
- Launch and Gather Feedback: After developing an MVP, it's time to release it to a selected group or the broader market for gathering valuable feedback.
- Iterate: Based on the feedback received, make necessary changes and improvements to the final product idea.

Common Misconceptions
- MVP is a Half-Baked Product: Some believe MVP is a low-quality or incomplete product. In reality, an MVP should be a fully functional product but with a limited set of features.
- Only Startups Need MVPs: While startups frequently use MVPs to validate their business ideas, established companies also use them to test new product concepts.
Conclusion
MVP software development is more than just a development approach; it's a mindset. It's about understanding that in the world of software, learning and iterating based on real-world feedback is more valuable than launching a 'perfect' product.
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the principles of MVP development remain a guiding light, ensuring that businesses stay agile, adaptive, and user-centric.
For those interested in a deeper dive, "The Lean Startup" by Eric Ries is a must-read. It delves into the principles of MVP and how startups can leverage it for success. Online platforms like Coursera and Udemy also offer courses on MVP development, providing practical insights and methodologies.