Your company's most valuable digital asset might also be its biggest liability.
Every day, legacy systems across industries quietly power critical business operations—processing millions of transactions, storing decades of customer data, and executing complex business logic that took years to perfect. Yet these same systems are increasingly becoming digital anchors, dragging down performance, inflating costs, and blocking the very innovations that could drive competitive advantage.
Consider this: while your competitors launch new features in weeks, your development team spends months just maintaining code written when smartphones didn't exist. While fintech startups process payments in milliseconds, your financial transactions crawl through architecture designed for dial-up internet. While agile companies scale seamlessly to meet demand, your systems buckle under loads they were never designed to handle.
At Softjourn, we’ve helped companies modernize their software systems to stay competitive, scalable, and efficient. With years of experience in software development and consulting, we understand the challenges of maintaining legacy systems while adapting to new technologies.
In this guide, we explore software reengineering—what it is, when it’s needed, and how businesses can transform their applications for long-term success.
Key Benefits of Strategic Reengineering:
- Reduce maintenance costs by 40-60% while improving performance
- Enable digital transformation initiatives without system replacement
- Strengthen security posture and ensure regulatory compliance
- Improve scalability to support business growth
- High ROI over years when properly executed
What is Software Reengineering?
Software reengineering is the systematic process of analyzing, restructuring, and modernizing existing software systems to improve performance, maintainability, and business value without a complete rebuild. It helps organizations extend the lifespan of legacy applications, optimize costs, and align technology with evolving business needs.
Unlike simple maintenance or complete replacement, reengineering takes a strategic approach that preserves valuable business logic while modernizing the underlying architecture, technology stack, and user experience.
The Three-Phase Reengineering Process
Every successful software reengineering initiative follows a structured approach:
- Understanding the Current System: Comprehensive analysis of existing architecture, dependencies, and business requirements through reverse engineering
- Strategic Planning: Mapping out necessary modifications, identifying improvement opportunities, and selecting the optimal modernization approach
- Systematic Implementation: Removing outdated components, rewriting critical sections, and implementing modern architectural patterns
Reengineering vs. Other Approaches
| Approach | Code Changes | Architecture Changes | Data Impact | Timeline | Risk Level |
| Reengineering | Moderate | Selective | Preserved | 6-18 months | Medium |
| Refactoring | Minor | Minimal | None | 1-6 months | Low |
| Replacement | Complete | Complete | Migration required | 12-36 months | High |
| Maintenance | Patches only | None | None | Ongoing | Low |
Why Business Leaders & CTOs Should Care: The Hidden Costs of Legacy Systems
Many companies continue using outdated systems under the belief that "if it's working, why change it?" However, legacy systems carry significant hidden costs that compound over time:
Maintenance Costs: Can exceed the original development budget within the first decade, with costs escalating as systems age and skilled developers become scarce.
Security Vulnerabilities: Legacy systems become easy targets for cybercrime, with outdated security frameworks and discontinued vendor support creating compliance risks.
As businesses increasingly rely on interconnected systems and third-party integrations, legacy applications often become bottlenecks that prevent organizational growth.
Integration Barriers: Modern business relies heavily on third-party APIs and cloud services. Legacy systems often can't integrate effectively, requiring expensive custom solutions.
Missed Opportunities: Clinging to outdated technology prevents businesses from capitalizing on new market opportunities and digital transformation initiatives.
Strategic Business Drivers
- Reduces Technical Debt: Aging software accumulates inefficiencies that make maintenance increasingly expensive. Reengineering cleans up outdated code, reducing long-term operational costs.
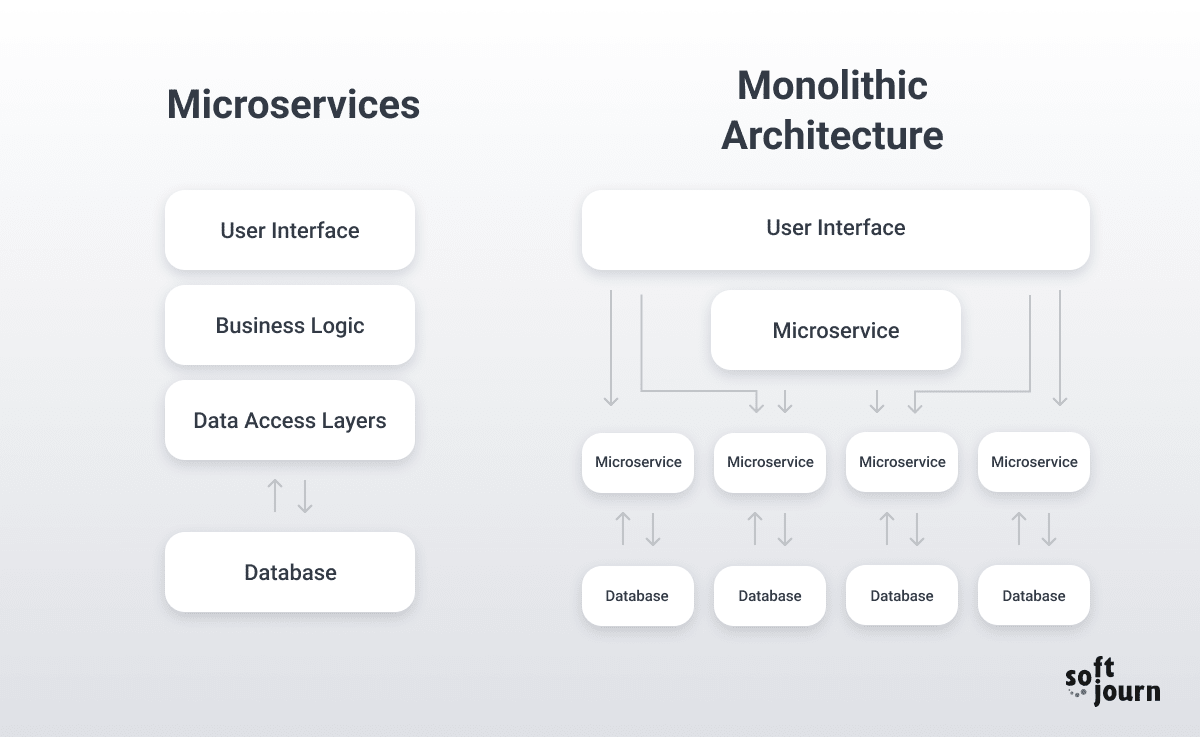
- Improves Performance & Scalability: Modernizing architecture—such as transitioning from monolithic to microservices—ensures applications can handle increased demand and integrate with newer technologies.
- Enhances Security & Compliance: Legacy systems may have security vulnerabilities that put the business at risk. Reengineering includes patching security flaws, ensuring compliance, and adopting security best practices.
- Optimizes Costs Without Full Replacement: Complete rebuilds are expensive and time-consuming. Reengineering focuses on incremental improvements, allowing businesses to modernize at lower cost while preserving core functionality.
- Enables Digital Transformation: Many businesses face challenges integrating legacy systems with cloud services, AI, APIs, or mobile applications. Software reengineering bridges this gap, making transformation smoother.
When Software Reengineering Becomes Critical
Recognizing the right time to modernize your legacy systems requires careful attention to both technical indicators and business impact signals. Many organizations wait until systems completely fail, but proactive identification of warning signs can prevent costly downtime and enable smoother transitions.
Our long-term partnership with UPC (Ukrainian Processing Center) demonstrates the value of proactive modernization. Over 15 years, we've helped UPC evolve from maintaining on-premise systems to implementing cloud-native solutions, handling over 100 million transactions monthly while maintaining zero downtime during critical transitions.
Technical Warning Signs
The technical health of your systems provides the clearest indicators that reengineering may be necessary. These signs often appear gradually but accelerate over time as technical debt compounds.
*Performance issues during modernization can significantly impact user experience and business operations if not properly managed.
Performance Degradation*
- Response times exceeding SLA requirements by 50% or more
- Memory leaks causing regular system restarts
- Database queries taking over 10 seconds for routine operations
- Inability to handle concurrent user loads during peak times
Beyond performance issues, the operational burden of maintaining legacy systems often becomes the primary driver for modernization decisions.
Maintenance Crisis
- Bug fixes taking 3x longer than new feature development
- 70% or more of development time spent on maintenance activities
- Critical skills shortage (COBOL, legacy frameworks, discontinued technologies)
- Documentation gaps affecting over 60% of the codebase
Integration Barriers
- API limitations preventing modern system integrations
- Data silos blocking business intelligence and analytics initiatives
- Cloud migration blocked by architectural constraints
- Mobile and web frontend development hindered by backend limitations
While technical indicators reveal system health, business impact metrics often provide the compelling justification needed for modernization investments.

Business Impact Indicators
The business consequences of aging systems extend far beyond IT departments, affecting revenue, customer satisfaction, and strategic initiatives.
Financial Strain
- Maintenance costs exceeding 15% of total IT budget
- Lost revenue due to system downtime (over $100K annually)
- Compliance violations risking regulatory penalties
- Competitive disadvantage due to feature limitations
Financial pressures from legacy systems often coincide with strategic limitations that prevent organizations from pursuing growth opportunities.
Strategic Limitations
- Digital transformation initiatives stalled or abandoned
- Customer experience degradation (over 20% satisfaction drop)
- New market entry blocked by system constraints
- Merger and acquisition integration challenges
To move from symptom identification to strategic decision-making, organizations need a structured approach to evaluate whether reengineering is the right choice.
Decision Framework
Use this assessment matrix to evaluate reengineering necessity:
| Factor | Weight | Score (1-5) | Weighted Score |
| Performance Issues | 25% | ___ | ___ |
| Maintenance Costs | 20% | ___ | ___ |
| Security Vulnerabilities | 20% | ___ | ___ |
| Integration Challenges | 15% | ___ | ___ |
| Compliance Risks | 10% | ___ | ___ |
| Strategic Alignment | 10% | ___ | ___ |
| Total | 100% | ___ |
Scoring Guide:
- 4.0-5.0: Immediate reengineering required
- 3.0-3.9: Plan reengineering within 12 months
- 2.0-2.9: Monitor closely, prepare for future reengineering
- 1.0-1.9: Continue current maintenance approach
Strategic Reengineering Approaches
Selecting the right modernization approach requires understanding both your current system constraints and future business objectives. Based on our experience helping companies modernize their software systems, there are five primary approaches to software reengineering, each with distinct advantages, limitations, and ideal use cases.
- Rehosting ("Lift and Shift")
Best For: Applications with sound architecture but infrastructure limitations
Process: Migrate existing applications to modern infrastructure (cloud, containers) with minimal code changes. This includes database migration with schema preservation and network/security configuration updates.
Benefits:
- Fastest implementation timeline (2-6 months)
- Lowest risk of functionality loss
- Immediate infrastructure cost savings
- Foundation for future modernization efforts
Limitations:
- Doesn't address architectural debt
- Limited performance improvements
- May not resolve fundamental scalability issues
Investment Range: $50K - $200K | Timeline: 2-6 months | Risk Level: Low
When rehosting doesn't address underlying code quality issues, refactoring offers a more comprehensive approach to improving system maintainability.
- Code Refactoring
Best For: Applications with solid business logic but accumulated technical debt
Process: Systematic code cleanup and optimization, design pattern implementation, database query optimization, and UI/UX improvements without major architectural changes.
Benefits:
- Improved maintainability and code readability
- Better performance through optimization
- Reduced bug frequency and faster debugging
- Enhanced developer productivity
Limitations:
- Limited architectural improvements
- May not address fundamental scalability constraints
- Risk of ongoing technical debt if not comprehensive
Investment Range: $100K - $500K | Timeline: 6-12 months | Risk Level: Low-Medium
For systems that have outgrown their original architectural foundations, more fundamental changes may be required to achieve scalability and integration goals.
- Rearchitecting
Best For: Applications requiring fundamental architectural changes for scalability and integration
Process: Transition from monolithic to microservices architecture, API-first design implementation, modern design pattern adoption (CQRS, Event Sourcing), and cloud-native architecture implementation.
Benefits:
- Significant scalability improvements
- Enhanced integration capabilities with modern systems
- Future-proof architecture supporting business growth
- Improved development team productivity and agility
Limitations:
- Higher complexity and implementation risk
- Longer timeline requirements
- Requires significant team upskilling
- Complex data migration challenges
Investment Range: $300K - $1.5M | Timeline: 12-24 months | Risk Level: Medium-High
In extreme cases where technical debt has accumulated to the point where refactoring and rearchitecting aren't viable, rebuilding specific components becomes necessary.
- Strategic Rebuilding
Best For: Core components with irreparable technical debt that cannot be effectively refactored
Process: Complete rewrite of specific system components, modern technology stack adoption, API compatibility maintenance, and phased rollout with parallel system operation.
Our work with IMS Management Services exemplifies this approach. When their decades-old ticketing system became unwieldy with patches and updates, we recommended a complete rewrite from ASP.NET to C#.NET. The transformation eliminated manual developer intervention for each event setup, enabling self-service capabilities for event producers while significantly reducing internal maintenance overhead.
Benefits:
- Eliminates accumulated technical debt completely
- Enables modern development practices implementation
- Optimal performance and scalability potential
- Clean, maintainable codebase for future development
Limitations:
- Highest risk of functionality loss during transition
- Longest timeline requirement
- Most expensive approach
- Requires comprehensive testing and validation
Investment Range: $500K - $3M | Timeline: 18-36 months | Risk Level: High
When legacy systems fundamentally misalign with current business processes or industry standards, replacement with modern solutions may be the most effective path forward.
- Strategic Replacement
Best For: Systems with fundamental business process misalignment or extreme obsolescence
Process: Commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) solution evaluation, custom development for unique requirements, comprehensive data migration planning, and extensive change management.
Benefits:
- Modern functionality available immediately
- Ongoing vendor support and maintenance
- Industry best practices built-in
- Potential long-term cost savings
Limitations:
- Customization limitations
- Vendor lock-in concerns
- Extensive change management requirements
- Complex data migration challenges
Investment Range: $200K - $2M (plus licensing) | Timeline: 12-30 months | Risk Level: Medium-High
Choosing between these five approaches requires careful evaluation of your specific business needs against each option's strengths and limitations.
Approach Selection Matrix
| Business Need | Rehosting | Refactoring | Rearchitecting | Rebuilding | Replacement |
| Quick cost reduction | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Performance improvement | ⚠️ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Scalability enhancement | ❌ | ⚠️ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Integration capabilities | ❌ | ⚠️ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Modern UX requirements | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Compliance adherence | ⚠️ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Team skill constraints | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
| Budget constraints | ✅ | ✅ | ⚠️ | ❌ | ⚠️ |
| Timeline pressure | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ⚠️ |
Legend: ✅ = Ideal fit, ⚠️ = Partial fit, ❌ = Poor fit
Implementation Roadmap
Once you've selected your modernization approach, success depends on systematic execution through clearly defined phases. Our proven implementation framework ensures projects stay on track while minimizing risks to business operations.
Our experience with Myers-Briggs demonstrates the importance of structured implementation. Over our 9-year partnership, we've successfully modernized their mobile application from Xamarin to Ionic within a tight 3-month timeline, maintaining full functionality while enabling cross-platform deployment.
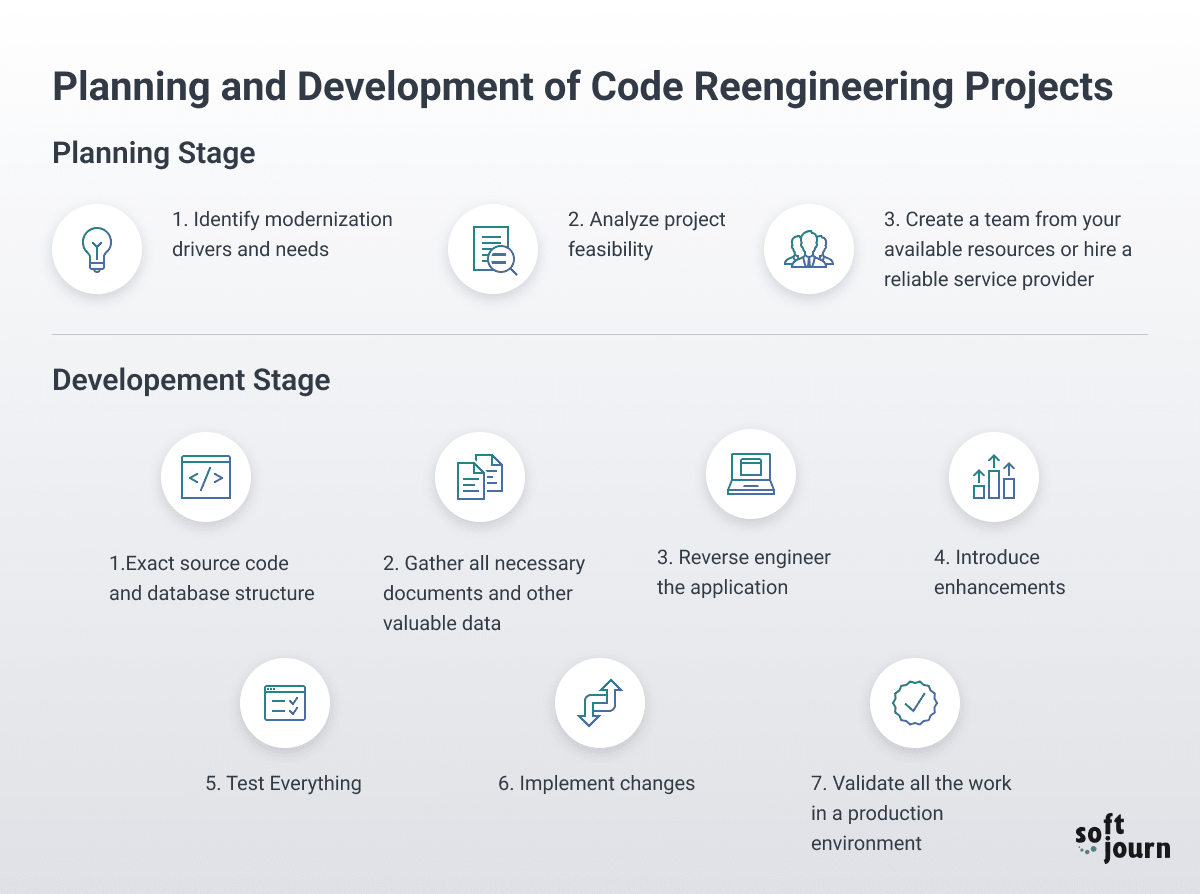
Phase 1: Foundation Setting (Months 1-2)
The foundation phase establishes the infrastructure, team, and knowledge base necessary for successful modernization.
Team Assembly
- Solution Architect for technical leadership and decision-making
- Business Analyst for requirements gathering and stakeholder management
- DevOps Engineer for infrastructure and deployment automation
- QA Lead for testing strategy and quality assurance
- Project Manager for coordination and risk management
With your team in place, establishing the right technical environment and processes is critical for development efficiency.
Environment Preparation
- Development environment provisioning and configuration
- CI/CD pipeline establishment with automated testing
- Monitoring and logging infrastructure setup
- Documentation repository creation and organization
- Security framework implementation
Perhaps most critically, comprehensive understanding of the existing system prevents costly surprises and ensures nothing important is overlooked during modernization.
Knowledge Transfer
- Comprehensive legacy system documentation review
- Stakeholder interview sessions and requirements gathering
- User workflow analysis and pain point identification
- Technical architecture deep-dive and dependency mapping
- Business rule extraction and validation
Building on the foundation phase, the analysis and design phase transforms requirements into actionable technical plans.
Phase 2: Strategic Analysis & Design (Months 2-4)
This phase converts business requirements and technical constraints into detailed architectural designs and implementation plans.
System Architecture Design
- Target architecture definition aligned with business objectives
- Integration pattern specification for external systems
- Data migration strategy planning with risk assessment
- Security framework design incorporating modern standards
- Performance requirements specification and benchmarking
With architecture defined, detailed project planning ensures smooth execution and stakeholder alignment throughout the development process.
Implementation Planning
- Detailed work breakdown structure creation
- Sprint planning and backlog prioritization
- Risk mitigation strategy development and monitoring
- Comprehensive testing strategy documentation
- Go-live planning with rollback procedures
The development phase represents the core transformation work where architectural plans become functional systems.
Phase 3: Iterative Development (Months 4-12)
This extended phase focuses on systematic implementation using agile methodologies that enable continuous feedback and course correction.
Development Methodology
- Two-week sprint cycles with regular stakeholder reviews
- Continuous integration with automated testing (85%+ coverage target)
- Progressive feature migration with validation checkpoints
- Performance monitoring and optimization throughout development
- Security testing integrated into the development process
Quality assurance throughout development prevents costly fixes later and ensures the modernized system meets all requirements from day one.
Quality Assurance Framework
- Unit testing with comprehensive code coverage
- Integration testing for all system touchpoints
- Performance testing under realistic load conditions
- Security penetration testing and vulnerability assessment
- User acceptance testing with business stakeholders
The final phase transitions from development to production while optimizing system performance based on real-world usage patterns.
Phase 4: Deployment & Optimization (Months 12-18)
This critical phase manages the transition from legacy to modern systems while minimizing business disruption.
Phased Rollout Strategy
- Pilot deployment with limited user group for validation
- Gradual traffic migration (10% → 50% → 100%) with monitoring
- Performance monitoring and system tuning based on real usage
- User feedback collection and rapid iteration cycles
- Legacy system decommissioning with data archival
Post-launch activities ensure the modernized system delivers maximum business value and operates efficiently over the long term.
Post-Launch Optimization
- Performance tuning based on production metrics and user behavior
- User experience refinements based on feedback and analytics
- Additional feature development to maximize business value
- Knowledge transfer to maintenance team for ongoing support
- Project retrospective and lessons learned documentation
Risk Management & Mitigation
Even the best-planned modernization projects face potential risks that can impact timeline, budget, or outcomes. Proactive risk management involves identifying potential issues early and implementing strategies to prevent or minimize their impact.,
Critical Risk Categories
Understanding and preparing for different types of risks ensures your project stays on track despite inevitable challenges.
Technical Risks
Technical challenges often pose the most immediate threats to project success, particularly around data integrity and system performance.
Data Loss or Corruption
- Risk Level: High | Probability: 15% | Impact: Critical business disruption
- Mitigation Strategies:
- Comprehensive backup strategy with point-in-time recovery capabilities
- Parallel system operation during critical transition periods
- Data validation checksums and automated reconciliation processes
Our UPC server migration project exemplifies effective data protection. We implemented comprehensive backup strategies and conducted extensive stress testing with simulators that subjected servers to conditions more challenging than live operations, ensuring zero downtime during the transition.
Performance Degradation
- Risk Level: Medium | Probability: 30% | Impact: User experience degradation
- Mitigation Strategies:
- Continuous performance testing throughout development
- Load testing with 3x expected peak capacity
- Gradual traffic migration with immediate rollback capabilities
Modern systems rarely operate in isolation, making integration reliability crucial for overall system functionality.
Integration Failures
- Risk Level: Medium | Probability: 25% | Impact: System functionality loss
- Mitigation Strategies:
- Early integration testing with all external systems
- API versioning and backward compatibility maintenance
- Circuit breaker patterns for system resilience
Beyond technical challenges, business and organizational risks can derail even technically successful projects.
Business Risks
Business-related risks often prove more challenging to manage than technical issues because they involve human behavior and organizational dynamics.
Project Scope Creep
- Risk Level: High | Probability: 40% | Impact: Budget and timeline overruns
- Mitigation Strategies:
- Formal change control process with approval workflows
- Regular scope review sessions with stakeholders
- Clear requirement sign-off procedures
User adoption challenges can undermine even the most technically successful modernization efforts.
User Resistance
- Risk Level: Medium | Probability: 35% | Impact: Adoption challenges
- Mitigation Strategies:
- Early and continuous user involvement in design process
- Comprehensive training programs and support materials
- Change management specialists dedicated to user adoption
Measuring Success
Establishing clear success metrics from the project outset ensures stakeholder alignment and provides objective measures of modernization value. Effective measurement combines technical improvements with business outcomes to demonstrate ROI.
Key Performance Indicators
Success measurement should encompass technical system improvements, business value delivery, and operational efficiency gains.
Technical Metrics
- System Performance: Response time improvement (target: 50% reduction)
- Reliability: Uptime increase (target: 99.5% availability)
- Maintainability: Time to implement changes (target: 40% reduction)
- Scalability: User capacity increase (target: 300% improvement)
- Security: Vulnerability reduction (target: zero critical vulnerabilities)
While technical metrics validate system improvements, business metrics demonstrate the real-world value of modernization investments.
Business Metrics
- Cost Reduction: Maintenance cost savings (target: 40-60% annually)
- Revenue Impact: New revenue opportunities enabled through improved capabilities
- User Satisfaction: Net Promoter Score improvement
- Compliance: Audit findings reduction (target: zero compliance gaps)
- Time to Market: Feature delivery acceleration (target: 50% faster)
Operational improvements often provide the most sustainable long-term benefits by enabling faster, more reliable development and deployment processes.
Operational Metrics
- Development Productivity: Story points per sprint increase
- Bug Resolution: Mean time to resolution improvement
- Deployment Frequency: Release cycle acceleration
- Change Failure Rate: Production incident reduction
- Recovery Time: Mean time to recovery improvement
Quantifying return on investment requires systematic tracking of both costs and benefits throughout the modernization lifecycle.
ROI Calculation Framework
Investment Components
- Development team costs (internal and external resources)
- Infrastructure and tooling expenses
- Training and change management investments
- Productivity loss during transition periods
- Risk mitigation and contingency planning
Benefit Components
- Annual maintenance cost reduction
- Infrastructure cost savings
- Developer productivity improvements
- Revenue from new business capabilities
- Risk avoidance value (security, compliance, downtime)
Sample ROI Scenario
- Total Investment: $800,000
- Annual Benefits: $400,000
- Payback Period: 2 years
- 3-Year NPV: $1,200,000
- ROI: 150%
Real-World Success Stories
These case studies demonstrate how different organizations have successfully navigated modernization challenges across various industries and technical scenarios.
Mobile E-commerce Platform Innovation: LightningBuy
Challenge: Mobile purchases remained painful and time-consuming for consumers, with 10+ steps involved in purchasing a single item. This complexity led to high abandonment rates, frustrating both consumers and merchants who lost potential sales.
Approach: Softjourn partnered with LightningBuy to develop a revolutionary mobile browser-based e-commerce platform that eliminates unnecessary purchase steps through intelligent pop-up integration and streamlined checkout processes.
Results:
- Reduced mobile purchase process to just a few clicks
- Eliminated need for customer account creation across different sites
- Seamless integration with merchant advertising and content pages
- Enhanced user experience through intelligent payment processing
Key Success Factors: Collaborative partnership approach, proactive problem-solving, and deep understanding of mobile commerce challenges.
"It was great to find someone to work with us as a collaborative partner. When you're creating something totally new, it is absolutely necessary to have a partner offer suggestions, be proactive, and think 3 steps ahead." - CEO/Founder at LightningBuy
Financial Services Core System Modernization: UPC
Challenge: Ukrainian Processing Center (UPC), processing over 100 million transactions monthly across 15+ European countries, needed to modernize critical Unix-based transaction processing systems while maintaining zero downtime and regulatory compliance.
Approach: Strategic 15-year partnership combining system maintenance, cloud migration, and continuous enhancement of core TPII processing systems with comprehensive stress testing and gradual modernization.
Results:
- Zero downtime during critical system transitions
- Successfully migrated from on-premise to cloud infrastructure
- Maintained 100% regulatory compliance throughout transformation
- Enhanced processing capabilities for mobile banking and e-commerce
- Sustained 15-year partnership demonstrating long-term value
Key Success Factors: Comprehensive testing with simulators exceeding production conditions, parallel system operation, and extensive regulatory validation.
"Since 2009, the Softjourn team has been maintaining the processing system, which is the core of our business; they've done a great job!" - Andriy Berezyuk, Business Development Director at UPC
Complex Business Integration: Bullet SME Platform
Challenge: Irish fintech company Bullet needed to integrate multiple acquired software solutions (Polydone project management and Quoters business tool) while simultaneously developing a banking product, without conducting traditional due diligence on the acquired systems.
Approach: Comprehensive 3-month integration assessment combining business goal analysis, codebase evaluation, and strategic roadmap development with multiple implementation options and cost-benefit analysis.
Results:
- Successful integration of multiple unvetted software acquisitions
- Clear roadmap for neobank development focused on SME needs
- Enhanced platform stability through thorough compatibility testing
- Improved collaboration between integrated system components
- Strategic foundation for UK and Ireland market expansion
Key Success Factors: Thorough compatibility testing, enhanced system stability through comprehensive debugging, and improved cross-component communication.
"Small businesses might use five-plus financial products for bookkeeping, accounting, and banking. That's the scenario we're solving for at Bullet—to make managing the financial aspect of business simple, seamless, and cost-effective." - Peter Connor, CEO and Co-Founder
Checklist for Successful Modernization
This comprehensive checklist ensures no critical steps are overlooked during your modernization journey, from initial assessment through post-implementation optimization.
Pre-Project Assessment
- [ ] Comprehensive system documentation completed
- [ ] Stakeholder requirements gathered and prioritized
- [ ] Technical architecture assessment conducted
- [ ] Risk analysis and mitigation strategies developed
- [ ] Budget and timeline estimates validated
- [ ] Team skills assessment and training plan created
During implementation, maintaining high standards across all development activities ensures quality outcomes and reduces post-launch issues.
Implementation Excellence
- [ ] Development environment configured with CI/CD
- [ ] Automated testing framework implemented (85%+ coverage)
- [ ] Performance monitoring and alerting established
- [ ] Security testing integrated into development process
- [ ] Regular stakeholder communication and feedback loops
- [ ] Change management and user training programs active
Final validation ensures the modernized system meets all requirements and delivers expected business value before full production deployment.
Success Validation
- [ ] Performance benchmarks met or exceeded
- [ ] User acceptance testing completed successfully
- [ ] Security audit passed with zero critical findings
- [ ] Business metrics showing measurable improvement
- [ ] Knowledge transfer to maintenance team completed
- [ ] Project retrospective and lessons learned documented
Partner with Softjourn for Your Modernization Journey
At Softjourn, we've helped numerous companies successfully modernize their software systems to stay competitive, scalable, and efficient. With years of experience in software development and consulting, we understand the unique challenges of maintaining legacy systems while adapting to new technologies.
Our Proven Approach
We've refined our modernization methodology through dozens of successful projects across diverse industries and technical environments.
Comprehensive Assessment: Our Business Analysts and Solution Architects begin every engagement with a thorough audit of your current system specifications, architecture, and business requirements to recommend the right solutions for your specific context.
Strategic Planning: We work closely with your team to map out concrete improvements, identify the right places for modifications, and develop a phased approach that minimizes business disruption.
Our experienced development teams bring both technical expertise and business acumen to every modernization project.
Expert Execution: Our experienced development teams handle everything from code optimization and security enhancements to complete architectural transformations, ensuring your modernized system supports your business growth objectives.
Why Choose Softjourn
Our track record and approach differentiate us from other modernization partners.
- Proven Track Record: Successfully delivered legacy modernization projects across diverse industries, including our 15-year partnership with UPC and 9-year collaboration with Myers-Briggs
- Strategic Approach: Focus on business value, not just technical improvements
- Risk Mitigation: Comprehensive planning and phased implementation to minimize project risks, demonstrated through zero-downtime migrations
- Long-term Partnership: Ongoing support and optimization to ensure continued success
Ready to Begin Your Modernization Journey?
Legacy software modernization doesn't have to be a massive, disruptive undertaking. With the right strategy, approach, and partner, you can transform your aging systems into competitive advantages that drive business growth.
If you're considering legacy software modernization and need help selecting the right approach that won't disrupt your internal processes, Softjourn can help. Our analysts and expert teams will provide everything you need to gain a stable, customizable system that supports your growth objectives.
Use the assessment frameworks and strategies outlined in this guide to evaluate your current situation and develop a tailored modernization strategy that delivers measurable business value. The investment in software reengineering typically pays for itself within 18-24 months through reduced maintenance costs, improved productivity, and new business capabilities.
Don't let legacy systems hold back your digital transformation initiatives. Contact us today to discuss how we can help modernize your software infrastructure for long-term success.









