Generative AI has continued its exponential growth into 2026. In mid-2025, generative AI companies globally had already secured $69.6 billion in funding, with these numbers expected to rise by 2026.
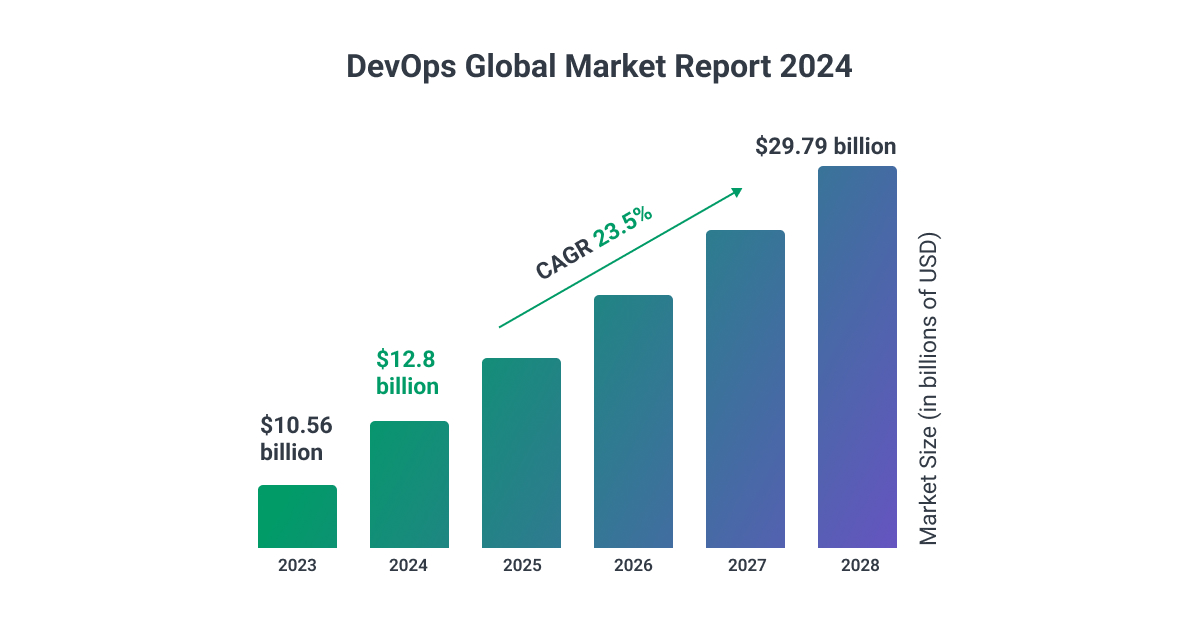
Meanwhile, the DevOps market has seen parallel expansion, reaching $14.95B in 2025, with a CAGR of 25.70% projected to reach $37.33B by 2029.
In this article, we will explore the exciting realm of Generative AI in DevOps, discussing its potential benefits, limitations, emerging trends, and best practices.
Join us as we explore the cutting-edge world of AI-enabled DevOps and discover how this powerful combination is reshaping the future of software engineering.
Introduction to Generative AI in DevOps
With the rise of ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, and other GenAI tools, many businesses are now considering the best approaches to utilize AI to improve efficiency and save money.
What is DevOps?
Let's start with the basics, before jumping into the use of GenAI in DevOps. DevOps is a software development approach that focuses on fostering collaboration and integration between development (Dev) and operations (Ops) teams.
By breaking down silos and promoting effective communication, DevOps aims to streamline the software development lifecycle. It encourages the use of automation, continuous integration, continuous delivery, and continuous deployment to achieve faster and more reliable software releases.
DevOps also emphasizes the importance of agile principles, infrastructure as code, and close collaboration between various stakeholders, including developers, operations professionals, and quality assurance teams.
This approach enables organizations to deliver software products more efficiently, respond rapidly to changing business requirements, and further enhance security and overall customer satisfaction.
Generative AI vs. Artificial Intelligence
AI, or Artificial Intelligence, is a broad term that encompasses a wide range of technologies and methods that enable machines to mimic human intelligence and perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. It involves developing algorithms and models that can process information, reason, learn from data, and make decisions or predictions.
Generative AI, on the other hand, is a specific subset or application of AI. It refers to the use of AI techniques to generate new and original content, such as images, texts, music, videos, and even coding. Generative AI models are designed to learn patterns and structures from training data and then use that knowledge to create new, realistic content that resembles the training data.
Generative AI utilizes deep learning algorithms, such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) or Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), to generate content that didn't exist in the training data.
Generative AI Models
Noteworthy advancements in large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized various domains, including mainstream image generation with Dall-E, MidJourney, Stable Diffusion, and Lensa, as well as conversational AI with ChatGPT, and code generation with Copilot.
The integration of larger transformer architectures, reinforcement learning through human feedback (RLHF), enhanced embeddings, and latent diffusion techniques has endowed these models with almost magical capabilities across a surprisingly diverse range of applications.
Large Language Model Advancements
Generative AI models have evolved dramatically. The latest iterations of GPT 5 and Gemini Ultra leverage multimodal capabilities, allowing for seamless integration of text, image, and even video generation within DevOps workflows. Tools like Copilot X now provide real-time coding suggestions based on live production environments, reducing errors and improving deployment speed.
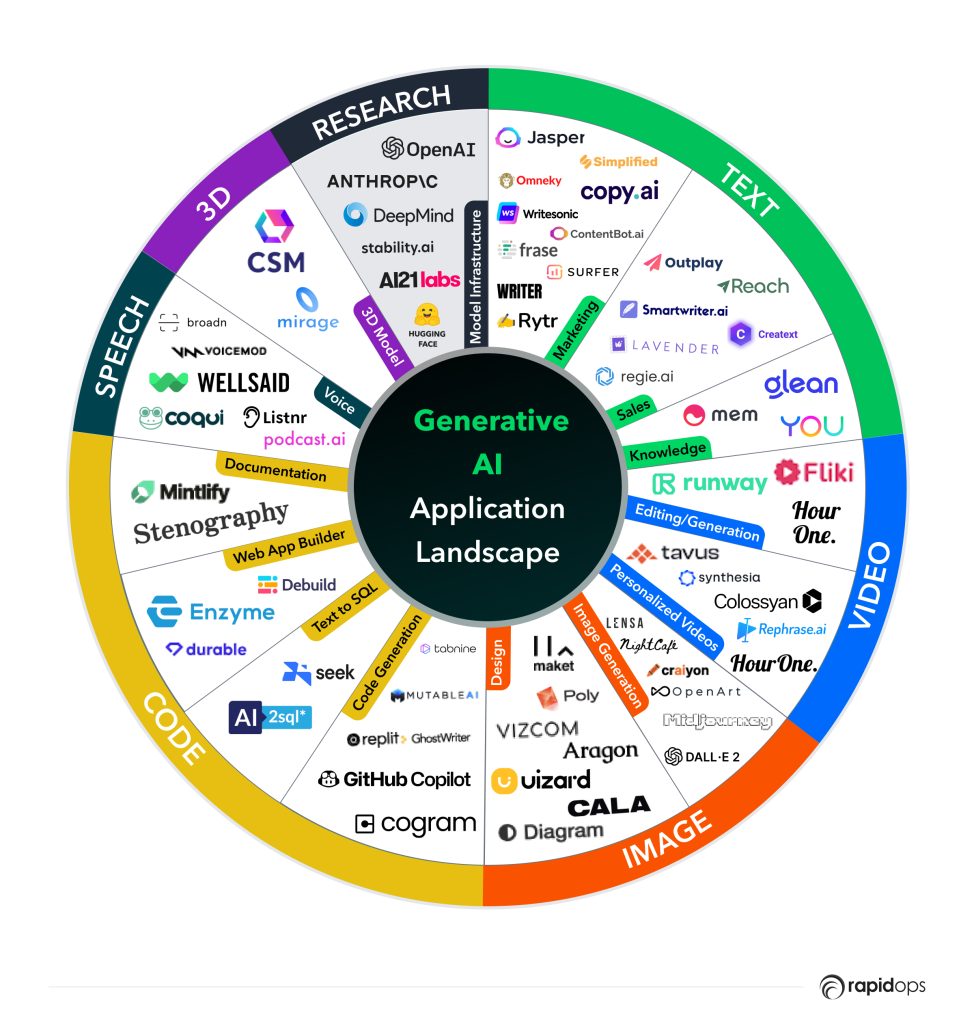
Generative AI Tools: The Power and Pressure Game Is On - Source
The Rise of AIOps: When Artificial Intelligence Meets Operations
The most significant trend reshaping DevOps in 2026 is the integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning into operational workflows—a practice known as AIOps (Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations). This represents a fundamental paradigm shift from reactive to predictive operations.
AIOps is no longer a futuristic concept but a present-day reality. The integration of AI and ML into DevOps workflows is enabling predictive monitoring, anomaly detection, and automation at an unprecedented scale.
According to recent industry data, 67% of DevOps teams have increased their investment in AI for DevOps in the last year alone, signaling a widespread recognition of its transformative potential.
From Reactive to Predictive
Traditional monitoring tools would alert teams when something broke; a reactive approach often meant scrambling to fix issues after they'd already impacted users.
AI-powered systems flip this model entirely. They can predict failures before they occur, automatically remediate issues without human intervention, and optimize performance in real-time based on historical patterns and current conditions.
This predictive capability is transforming how teams approach system reliability and incident management. Instead of firefighting, DevOps engineers can focus on strategic improvements and innovation.
AIOps platforms analyze vast amounts of operational data (logs, metrics, traces, and events) to identify patterns that would be impossible for humans to detect manually.
The Automation Imperative
DevOps teams today are stretched thin and burning out under the weight of increasing system complexity and velocity demands. AI and automation offer a lifeline, helping teams win back time, tame complexity, and scale with confidence.
By 2026, DevOps engineers will spend significantly less time writing scripts from scratch and more time training AI systems to handle the heavy lifting of routine operational tasks.
Tools like GitHub Copilot and Datadog AI are already optimizing CI/CD pipelines and detecting anomalies automatically, reducing the cognitive load on human operators while improving reliability and speed.
A Critical Inflection Point
AIOps represents more than just another tool in the DevOps toolkit, as it's a fundamental reimagining of how software operations work. As systems become more distributed and complex, human-scale monitoring and management become untenable. AI fills this gap, providing the scalability and speed needed to manage modern cloud-native architectures effectively.
For organizations aiming to grow faster, safer, and smarter, embracing AIOps is essential for remaining competitive in an increasingly AI-driven landscape.
How is GenAI in DevOps Different from Machine Learning Operations (MLops)?
MLops, short for Machine Learning Operations, is a discipline that focuses on the operational aspects of deploying, managing, and monitoring machine learning models in production environments. It encompasses a range of practices, tools, and workflows aimed at streamlining the development and deployment of ML models, ensuring their scalability, reliability, and performance in real-world applications.
Unlike generative AI in DevOps, which specifically refers to the application of generative models within the DevOps domain, MLops goes beyond the use of generative models. While MLops can involve the utilization of generative AI techniques for tasks like data augmentation or synthetic data generation, its scope is much broader.
MLops involves the entire lifecycle of Machine Learning models, including data preparation, model training, validation, deployment, and ongoing monitoring and maintenance. It focuses on enabling efficient collaboration between data scientists, ML engineers, and operations teams to ensure seamless integration of ML models into production systems.
How Does Generative AI Work in DevOps?
Generative AI in DevOps combines the power of artificial intelligence technologies with the principles of DevOps, enabling teams to automate various stages of the software development and deployment process. From code generation to testing, monitoring, and even troubleshooting, Generative AI brings a new level of speed, accuracy, and scalability to DevOps practices.
However, achieving success in this approach necessitates meticulous planning and a comprehensive grasp of both DevOps and AI concepts.
Benefits of AI in DevOps
By leveraging Generative AI, organizations can unlock numerous benefits in their software development lifecycle.
Improved application performance, proactive detection and resolution of operational issues, real-time threat detection, smoother collaboration among teams, and continuous monitoring of code quality are just a few examples of the advantages that Generative AI brings to DevOps.
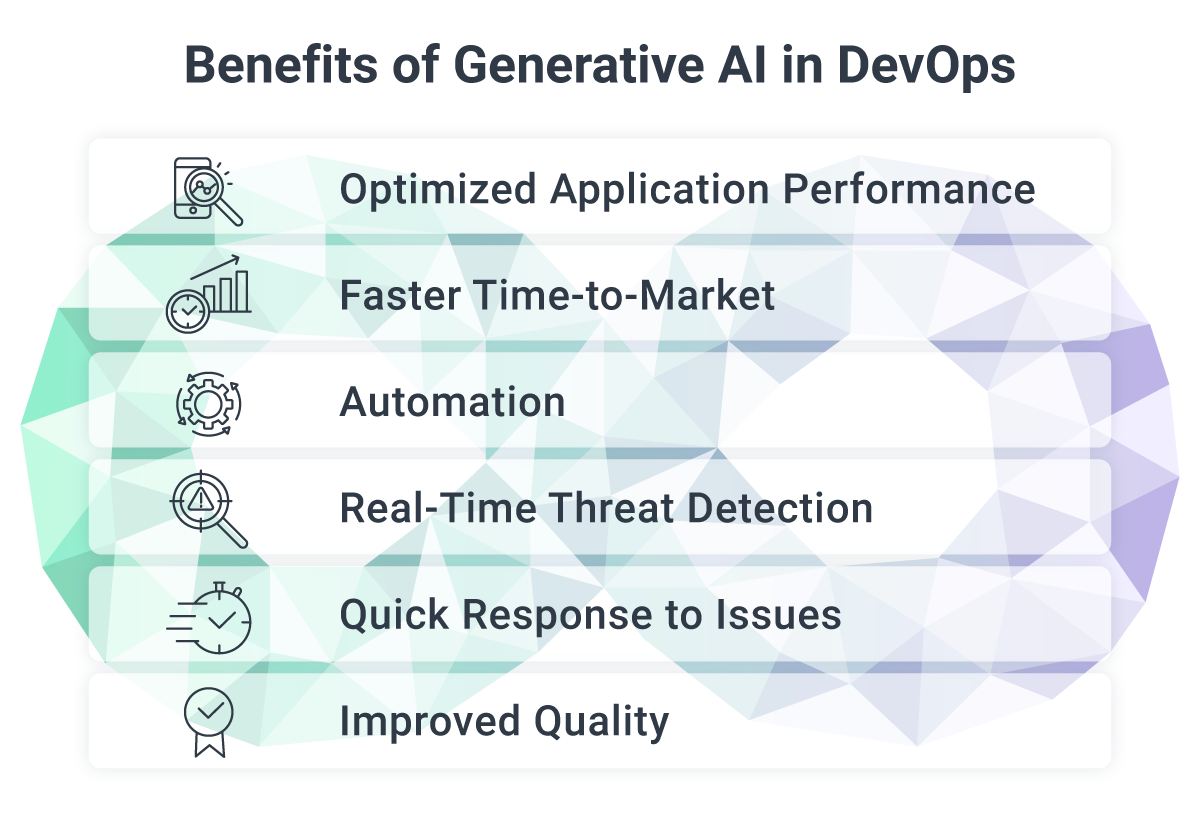
Optimized Application Performance
By automating repetitive tasks and analyzing vast amounts of data, AI empowers the DevOps team with faster and more precise decision-making capabilities.
Within the DevOps domain, AI can be leveraged to create predictive analytics models that forecast system performance, leading to optimized application performance.
Faster Time-to-Market
With automation and improved accuracy, DevOps teams can deliver software faster while maintaining high quality. This not only enables organizations to stay ahead in competitive markets but also allows them to respond quickly to customer demands and adapt to rapidly changing business needs.
Automation
AI-driven automation and CI/CD streamline the entirety of the DevOps process, encompassing testing, deployment, and beyond. It eliminates the need for manual intervention in repetitive tasks like testing, debugging, and code generation. This reduction in workload allows DevOps teams to concentrate on high-value activities such as designing and developing innovative features.
Real-Time Threat Detection
In the realm of DevOps security, AI plays a pivotal role in identifying and promptly addressing threats and vulnerabilities. By identifying abnormal behavioral patterns in applications, servers, and networks, AI can detect potential security risks in real-time. Integrating security checks into the DevOps pipeline ensures that applications are thoroughly secured prior to deployment.
Quick Response to Issues
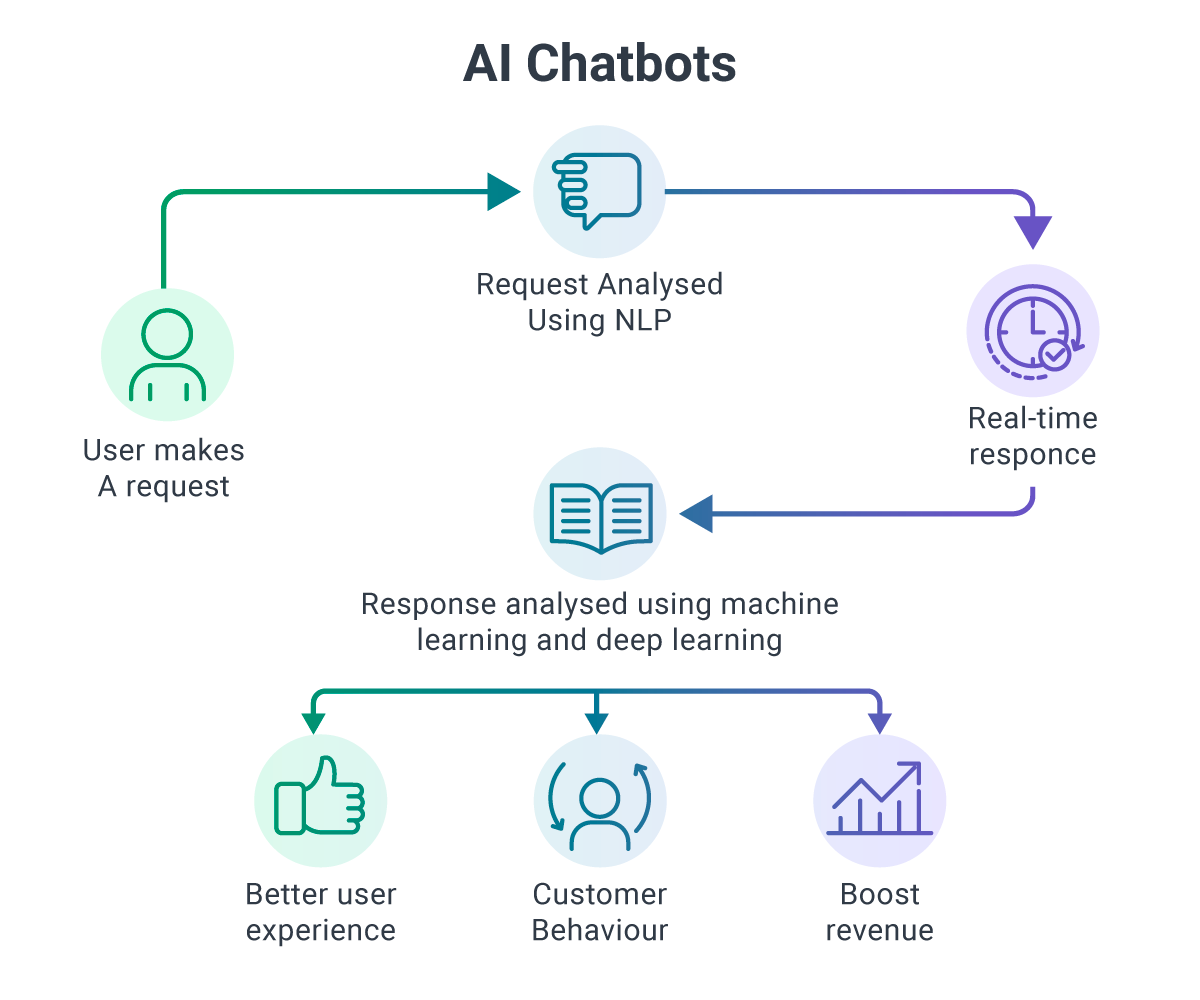
Through the implementation of Natural Language Processing (NLP) and machine learning, AI fosters seamless communication and collaboration among DevOps teams. By incorporating AI-powered chatbots, team members gain access to 24/7 support, assistance with common queries, and knowledge sharing capabilities, resulting in smoother and faster responses to issues.
Improved Quality
AI within the DevOps landscape reduces manual errors and minimizes the necessity for human intervention. It accelerates development speed while enhancing code quality, ultimately saving time and reducing costs. Continuous monitoring facilitated by AI ensures that software development remains efficient and maintains a high level of quality.
Predictive vs. Reactive Operations
Perhaps the most transformative benefit of AI in DevOps is the fundamental shift from reactive to predictive operations. This change represents a quantum leap in how teams approach system reliability and incident management.
In traditional reactive models, monitoring tools would alert engineers when something broke—a server went down, response times spiked, or an error rate exceeded thresholds. By the time the alert fired, users were already experiencing problems, and teams scrambled to diagnose and fix issues under pressure.
AI-powered predictive systems flip this model entirely. By continuously analyzing patterns in system behavior, resource utilization, and application performance, these systems can forecast potential failures hours or even days in advance. Machine learning algorithms identify subtle anomalies and trends that human operators would miss, enabling teams to address issues before they impact production.
Real-time optimization takes this even further. AI systems don't just predict problems; they automatically remediate them. When an AI model detects that a microservice is experiencing memory pressure that will lead to an out-of-memory crash in 30 minutes, it can automatically scale resources, restart instances, or adjust traffic routing to prevent the issue entirely, often without any human intervention.
This shift has measurably improved operational outcomes. Organizations implementing AI-enhanced DevOps workflows report a 30% reduction in deployment failures and a 20% improvement in deployment speed. Perhaps more importantly, many incidents are prevented entirely, never making it into these statistic calculations at all because they're resolved before users notice anything wrong.
The predictive approach also changes team culture. Instead of constantly firefighting and responding to emergencies, DevOps engineers can focus on strategic improvements, architecture optimization, and innovation. This not only improves system reliability but also reduces burnout and improves job satisfaction for technical teams.
Limitations of AI for DevOps
The adoption of AI-enabled DevOps has gained popularity across organizations. However, it is essential to navigate the limitations and challenges associated with Generative artificial intelligence in DevOps.
Considerations such as the cost of implementation, data privacy regulations, and the need for skilled personnel should be carefully addressed to ensure successful integration and optimal outcomes.
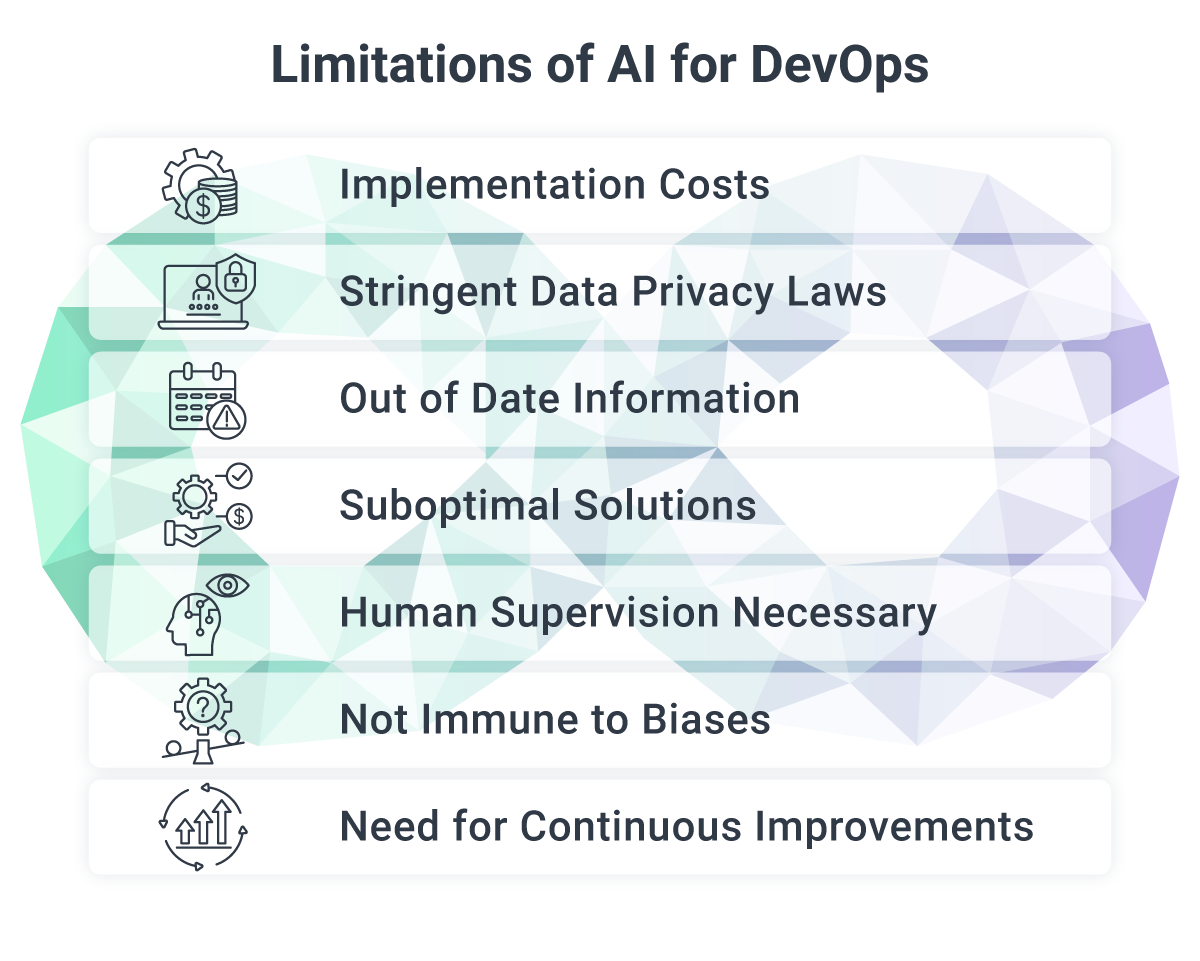
Implementation Costs
The complete implementation of AI-enabled DevOps demands substantial investments in costly hardware, software, and skilled personnel. The expenses associated with AI systems pose a significant challenge for organizations seeking to adopt AI-enabled DevOps, making it unaffordable for many.
Stringent Data Privacy Laws
The implementation of robust data privacy regulations poses another obstacle. AI-enabled DevOps relies heavily on data, yet in numerous jurisdictions, laws governing personal data protection prohibit companies from collecting, processing, and utilizing personal data for analysis. Consequently, AI-enabled DevOps encounters significant challenges in accessing and analyzing data due to strict privacy regulations.
Out of Date Information
When you consider one of the most popular generative AI tools, ChatGPT, it is easy to understand why the outputted information is not flawless. ChatGPT's knowledge cutoff date varies by model, but for the current version, it is June 2024, which is now nearly two years behind.
Additionally, ChatGPT lacks the ability to access real-time external resources, such as the web, rendering it a fixed repository of data from over a year ago.
Suboptimal Solutions
A limitation of Generative AI in DevOps is the inherent risk of generating incorrect or suboptimal solutions. AI models are trained on historical data and patterns, which may not always capture the full complexity and context of real-world scenarios.
Human Supervision Necessary
While Generative AI brings significant advancements to the DevOps landscape, it is crucial to acknowledge the need for a skilled human overseer in the process. Despite the automation capabilities of Generative AI, human expertise remains invaluable for effective decision-making, quality control, and handling complex scenarios.
A DevOps expert is essential to validate the outputs generated by Generative AI, ensuring that they align with the desired goals, industry best practices, and compliance requirements.
AI Skills Gap and Team Burnout
While AI promises to alleviate DevOps team workload, the transition itself presents significant challenges around skills and organizational change. DevOps teams are currently stretched thin, managing increasingly complex distributed systems while under pressure to deliver faster releases. This combination fuels burnout and turnover, creating a paradox: teams need AI to reduce their workload, but they lack the bandwidth to learn and implement it effectively.
Organizations face a critical choice: invest in upskilling their existing teams or risk falling behind as competitors adopt AI-driven workflows. However, training programs take time, and teams are already overburdened. This creates a challenging transition period where workload may actually increase before the benefits of AI automation are realized.
The Black Box Problem
A particular concern is the temptation to treat AI systems as "black boxes" - tools that magically work without needing to understand their inner workings. This approach is dangerous in DevOps, where understanding system behavior is crucial for troubleshooting and optimization. If engineers don't understand how AI models make decisions, they can't effectively validate outputs, debug issues, or optimize performance.
Not Immune to Biases
In the context of DevOps, generative AI models can pose significant limitations related to biases in the training data. DevOps processes increasingly rely on AI-generated outputs for decision-making, automation, and problem-solving. However, if the training data used to develop these generative models contains biases, those biases can propagate and impact critical decision-making processes within DevOps workflows.
Biases in AI systems are notoriously difficult to quantify. When embedded prejudices exist in training data, they can manifest in how systems are built, deployed, and managed. AI tools fundamentally reflect the behavior and patterns they were trained on, making them inherently susceptible to the same biases present in their source data.
This challenge is particularly acute for large language models used in DevOps. These models are trained on vast amounts of data scraped from the internet, which means they inevitably absorb the biases (both subtle and overt) that exist across online content. These biases can influence everything from code suggestions to infrastructure recommendations to incident prioritization.
Need for Continuous Improvements
As new technologies, frameworks, and security threats emerge, they must be continuously adapted and fine-tuned to stay relevant and effective. This means that your team must have the domain knowledge and experience to assess the performance of Generative AI models and make necessary adjustments to optimize their results.
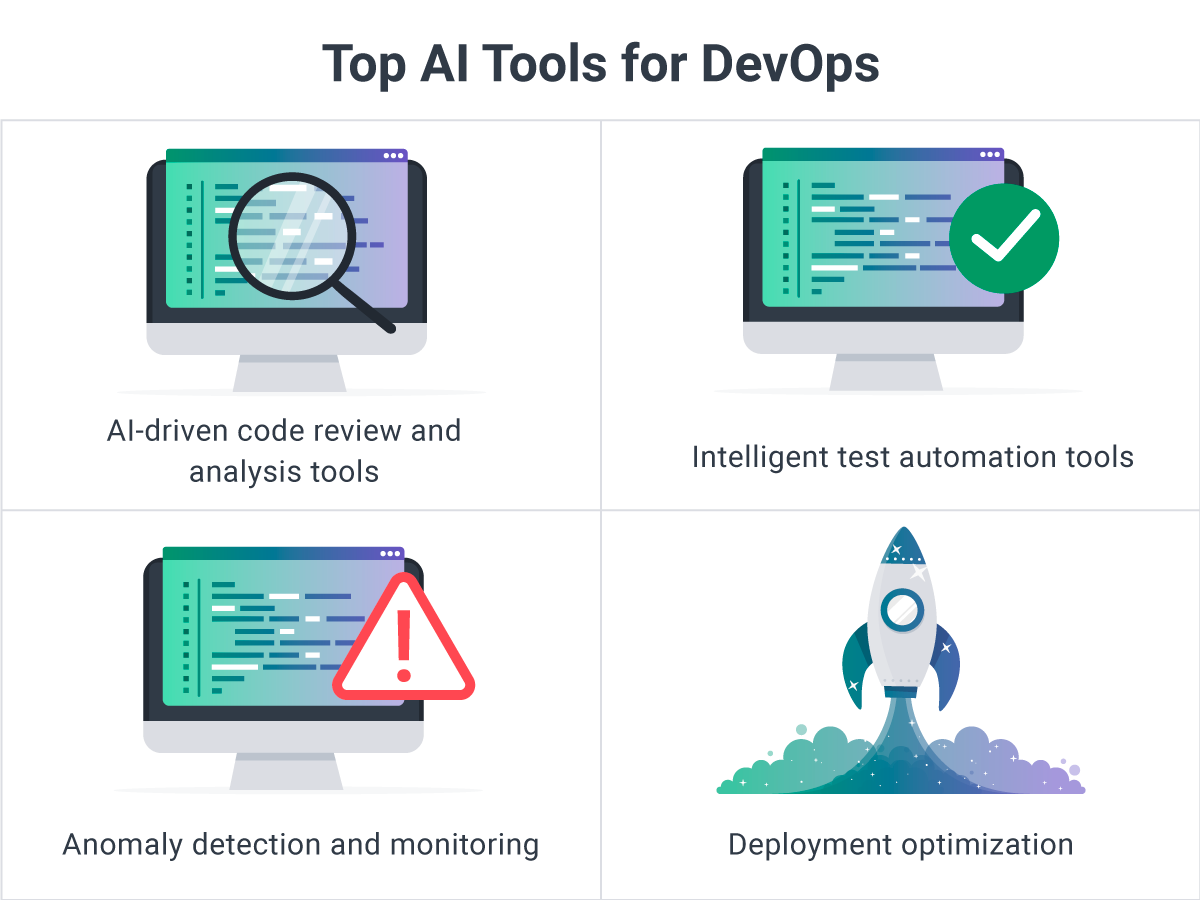
Top AI Tools for DevOps
With the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) into the DevOps process, a new generation of tools has emerged to streamline the development pipeline, reduce manual intervention, and proactively identify potential issues.
Here are the top AI-powered DevOps tools transforming the industry in 2025:
1. GitHub Copilot
GitHub Copilot, powered by OpenAI's Codex, acts as a developer's virtual co-pilot, offering AI-driven code suggestions and automating repetitive coding tasks. Its context-aware suggestions reduce coding errors, significantly boosting developer productivity. Integrated seamlessly with GitHub Actions and CI/CD pipelines, Copilot accelerates code reviews and ensures high-quality deployments. For teams working with Kubernetes and containerized environments, Copilot's ability to suggest infrastructure-as-code configurations makes it an invaluable asset.
2. Dynatrace
Dynatrace's Davis AI engine redefines observability in DevOps by processing vast datasets in real time to offer automated root cause analysis and anomaly detection. As an AI-powered observability platform, it tracks performance metrics across hybrid cloud environments, ensuring proactive issue resolution before users are impacted. Its compatibility with modern CI/CD workflows provides end-to-end visibility into Kubernetes workloads and microservices architectures, making it essential for teams scaling operations in complex environments.
3. Datadog
Datadog is a comprehensive monitoring platform that unifies infrastructure, application, and security monitoring into a single pane of glass. Its AI-driven Watchdog feature automatically detects anomalies without requiring manual threshold configuration, enabling rapid incident response. With over 1000 integrations, Datadog seamlessly connects with containerized environments and cloud platforms, providing real-time insights that help teams maintain reliability and performance. For DevOps teams managing multi-cloud deployments, Datadog's AI capabilities ensure nothing slips through the cracks.
4. Harness
Harness leverages AI to simplify continuous delivery, greatly reducing deployment times. Its machine learning algorithms continuously monitor pipeline health, automatically triggering rollbacks when anomalies are detected. This intelligent automation enables seamless multi-cloud deployments and reduces the risk of failed releases. Harness empowers teams to scale efficiently while maintaining deployment quality, making it ideal for organizations experiencing rapid growth or managing complex release processes.
5. Snyk
Snyk embeds security directly into DevOps pipelines, using AI to prioritize vulnerabilities based on exploitability and business impact. Rather than overwhelming teams with every potential security issue, Snyk intelligently suggests fixes and even automates remediation for common vulnerabilities. Integrated with CI/CD workflows, it ensures secure code deployment in Kubernetes clusters and container registries.
6. PagerDuty
PagerDuty's AI-driven Event Intelligence module streamlines incident management by intelligently grouping related alerts and routing them to the appropriate responders based on context and historical patterns. This reduces alert fatigue and ensures faster resolution times. By integrating with monitoring systems and CI/CD pipelines, PagerDuty provides real-time insights into system health and deployment status.
7. Kubiya
Kubiya is an AI virtual assistant designed specifically for DevOps workflows. It automates routine tasks like infrastructure provisioning, pipeline management, and troubleshooting through natural language interactions. This reduces context switching and allows engineers to accomplish tasks without leaving their communication platforms. Kubiya's integration with modern DevOps toolchains delivers real-time alerts and actionable insights, making it a game-changer for teams looking to streamline operations and improve efficiency.
8. Azure DevOps
Azure DevOps combines AI-driven analytics with robust CI/CD capabilities to predict build failures before they occur and optimize pipeline performance. Its intelligent insights help teams identify bottlenecks and improve deployment frequency. With support for hybrid cloud environments, Azure DevOps enables teams to scale seamlessly across Azure, AWS, and on-premises systems. Its deep integration with the Microsoft ecosystem makes it particularly powerful for enterprises already invested in Azure infrastructure.
9. Spacelift
Spacelift enhances infrastructure as code (IaC) with AI-driven automation and policy enforcement. Its machine learning capabilities detect configuration drift and ensure compliance with organizational standards, reducing the risk of misconfigurations that could lead to security vulnerabilities or outages. By automating multi-cloud deployments and providing intelligent insights into infrastructure changes, Spacelift empowers teams to manage complex IaC workflows efficiently and securely.
AI-Driven Code Review and Analysis Tools
Beyond specific platforms, a category of AI-powered code review and analysis tools has emerged to analyze code quality, identify security vulnerabilities, and provide improvement suggestions. These tools employ machine learning algorithms trained on millions of code repositories to understand patterns of bugs, anti-patterns, and security flaws. They integrate directly into pull request workflows, providing developers with immediate feedback and reducing the burden on human code reviewers.
Anomaly Detection and Monitoring Platforms
Modern anomaly detection tools leverage AI to analyze extensive datasets generated throughout the DevOps lifecycle. By identifying patterns, detecting deviations, and predicting future system issues, they enable proactive monitoring and troubleshooting. These platforms learn normal system behavior and can distinguish between benign variations and genuine problems, dramatically reducing false positive alerts while catching real issues earlier.
Deployment Optimization Tools
AI algorithms now empower operations teams to determine optimal environment configurations and deployment schedules for their applications. These tools analyze historical deployment data, system performance metrics, and business patterns to recommend the best times and strategies for releases. This minimizes risks, maximizes performance, and results in more successful deployments with fewer rollbacks.
Intelligent DevOps tools
Powered by AI, these tools utilize ML algorithms to comprehend the behaviors of applications and automatically generate relevant tests, expediting the software testing and process.
AI is transforming DevOps by enhancing automation, security, and efficiency in tools like Docker, Ansible, and Terraform. Docker leverages AI for container optimization, automated performance tuning, and AI-driven security scanning.
Ansible integrates AI for predictive failure detection, self-healing infrastructure, and natural language automation with tools like Ansible Lightspeed.
Terraform benefits from AI-powered infrastructure optimization, automated policy enforcement, and intelligent provisioning to streamline cloud deployments.
Together, these AI advancements enable DevOps teams to build, deploy, and manage infrastructure with greater speed, reliability, and cost efficiency.
Latest Generative AI News and Trends

PromptOps
The recent introduction of PromptOps demonstrates the effectiveness of this DevOps approach. With PromptOps, users can simply input a natural language question related to a Kubernetes query or action and receive a tailored Kubectl command in response.
This command includes references and even specific command lines that may not be available elsewhere on the web. PromptOps leverages conversational context to eliminate the need for repeatedly specifying the exact entity name with each query, enhancing convenience and efficiency in Kubernetes operations.
Scaling Generative Troubleshooting
Cloud application troubleshooting suffers from extended downtime and challenges in identifying performance issues. A Splunk study found that the median downtime exceeds 5 hours, with most problems linked to environment changes.
This indicates an unresolved problem in the field. Generative AI offers a solution by automating initial troubleshooting, extracting insights from complex data, and streamlining remediation coordination.
With the ability to determine real problems and their root causes, generative approaches hold promise for improving incident management and reducing downtime in cloud application troubleshooting.
AI in Observability and Monitoring
Generative AI now plays a pivotal role in observability platforms like Datadog and New Relic, automatically correlating logs, traces, and metrics to predict and resolve outages before they occur. This has led to a 40% improvement in MTTR (Mean Time to Recovery) across major cloud environments.

Advanced Chaos Engineering
Chaos engineering emerged at Netflix with the Chaos Monkey tool, which intentionally attacked different parts of their application to test real-time responses and remediation efforts.
Open-source tools like Litmus, ChaosBlade, and Chaos Mesh have expanded this approach. However, these methods have limitations in terms of generic attack classes and slow, manual remediation processes, hampering the overall improvement loop.
Generative approaches, leveraging modern transformers and automation capabilities, hold promise in increasing the quantity and quality of meaningful situations and automating remediation. This will accelerate the learning loop, enhance robustness, and show initial advancements in 2026.
AI-Preventative DevOps Hiring Tools
To mitigate the risk of unqualified DevOps engineers leveraging generative AI to pass hiring tests and certifications, evaluation tools have emerged as a solution. These tools, such as live-broken tests, have been specifically designed to assess the essential day-to-day skills of a DevOps engineer. Importantly, these evaluations are robust and resistant to manipulation by AI models.
AI hiring tools are becoming more sophisticated. In addition to live-broken tests, AI Simulation Environments (AISEs) are now used to evaluate DevOps candidates in real-time simulated environments, testing their ability to troubleshoot complex infrastructure issues on the fly.
The Future of AI-Enabled DevOps
The outlook for AI-Enabled DevOps appears bright as the need for efficient and scalable software development processes continues to grow. However, integrating AI into DevOps demands meticulous deliberation to achieve seamless integration and maximize its advantages.
Some potential implementations of AI in DevOps encompass automated testing and other monitoring tools, intelligent decision-making, and predictive analysis. Prioritizing security and data privacy is crucial when embracing AI in DevOps to mitigate vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with regulations.
To fully harness the complete potential of AI-enabled DevOps, organizations are encouraged to collaborate with a software development partner equipped with expert DevOps professionals. By partnering with such a team, businesses can benefit from their in-depth knowledge and experience in integrating AI into DevOps practices.
These experts can provide valuable insights, guidance, and support throughout the process, ensuring seamless integration and maximizing the benefits of AI in software development and operations teams.
Looking ahead, AI-native development platforms are expected to dominate by 2026, enabling autonomous pipeline orchestration. This next phase, termed "Self-Healing DevOps", will see AI not only predict issues but also autonomously apply patches and reconfigure environments in response to anomalies.

Best Business Practices for Using Generative AI
Successfully integrating AI into DevOps practices requires more than just deploying new tools; it demands thoughtful planning, cross-functional collaboration, and a commitment to responsible AI use.
Here are the essential best practices for organizations looking to leverage AI in their DevOps workflows:
Align AI Initiatives with Business Goals
Before implementing any AI tool, clearly define what problems you're trying to solve. Are you aiming to reduce deployment failures? Improve security posture? Decrease incident response time? Optimize cloud costs? Choose AI solutions that directly address your organization's most pressing DevOps challenges and measure success against concrete business metrics.
Prioritize Data Privacy and Security
AI systems require data to function, but not all data should be shared with AI models. Establish clear policies about what information can be input into AI systems, particularly when using external AI services. Avoid entering sensitive company information, proprietary code, customer data, or intellectual property into public AI models, as these inputs may be used to train the models and could potentially be leaked.
For organizations in regulated industries—healthcare, finance, government—ensure AI tools comply with relevant frameworks such as HIPAA, GDPR, SOC 2, and industry-specific requirements. Consider using private, on-premises, or dedicated AI deployments for handling sensitive data rather than public cloud services.
Respect Intellectual Property Rights
AI-generated code and content raise complex intellectual property questions. Organizations must ensure that text, code, or other outputs generated by AI don't violate copyrights, patents, or licenses. This includes:
- Verifying that AI-generated code doesn't inadvertently copy copyrighted code from training data
- Ensuring AI tools respect open-source licenses when suggesting code
- Establishing clear policies about ownership of AI-generated content
- Reviewing and understanding the terms of service for AI tools regarding IP rights
Legal precedents for AI-generated content are still evolving, and companies should consult legal counsel when establishing AI usage policies.
Implement Robust Validation and Human Oversight
AI should augment human decision-making, not replace it entirely. Establish workflows where humans validate AI outputs before they impact production systems or customer-facing services. This is particularly critical for:
- AI-generated code being deployed to production
- Security recommendations and automated remediation actions
- Customer-facing chatbots and support systems
- Infrastructure changes suggested by AI optimization tools
Because AI-generated content often "reads like a human wrote it," it's easy to trust everything an AI system produces, even when it's inaccurate or incomplete. Teams must remain vigilant and skeptical, verifying information and validating outputs against known good practices and organizational standards.
Address Bias and Fairness
AI models reflect the biases present in their training data. In DevOps contexts, this can manifest in various ways—from hiring tools that discriminate against certain candidates to monitoring systems that disproportionately flag certain types of services or teams. Organizations should:
- Regularly audit AI systems for bias in outputs and decision-making
- Ensure diverse teams are involved in AI tool selection and implementation
- Establish feedback loops where users can report problematic AI behaviors
- Use AI governance tools that provide ongoing bias audits and transparency
- Recognize that while bias can be minimized, it may never be completely eliminated
Industry expert, Oluwaniyi Darasimi, mentioned, "human feedback is supposed to help mitigate bias, however, you need a very rigorous methodology - specifically, that the people providing feedback are from diverse enough backgrounds to ensure bases are covered in terms of bias."
Comply with Emerging AI Regulations
The regulatory landscape for AI is rapidly evolving. In 2026, frameworks like the EU AI Act and the AI Accountability Framework in the United States require organizations to conduct algorithmic impact assessments (AIAs) and maintain transparency about AI system use.
Stay informed about regulations in your jurisdiction and industry, and build compliance into your AI implementation from the start rather than retrofitting it later.
Assemble Cross-Functional Teams
AI implementation in DevOps shouldn't be a purely technical decision. Assemble cross-functional teams including:
- DevOps engineers who understand operational needs
- Security professionals who can assess risks
- Legal and compliance experts who understand regulatory requirements
- Data scientists or ML engineers who understand AI capabilities and limitations
This team should collaborate to determine the best use cases for AI, which company policies may be affected, what ethical standards should guide AI use, and how to monitor and govern AI systems over time.
Start Small and Scale Gradually
Rather than attempting to transform your entire DevOps workflow with AI overnight, start with pilot projects in constrained environments. This allows teams to learn, make mistakes safely, and build expertise before rolling out AI tools more broadly. Choose initial use cases that are:
- Well-defined with clear success metrics
- Lower risk if something goes wrong
- Likely to demonstrate value quickly
- Representative of broader use cases you'll tackle later
Invest in Training and Upskilling
AI literacy is becoming a core competency for DevOps professionals. Invest in comprehensive training programs that help teams understand:
- AI and machine learning fundamentals
- Specific AI tools being implemented in your organization
- How to validate AI outputs and recognize limitations
- Prompt engineering and effective interaction with AI systems
- Ethical considerations and bias recognition
Monitor AI Systems Like Any Other Production System
AI tools are not "set and forget" solutions. They require ongoing monitoring, evaluation, and refinement. Establish observability for AI systems just as you would for applications and infrastructure:
- Track accuracy and error rates of AI predictions and recommendations
- Monitor for concept drift where AI performance degrades over time
- Measure business impact and ROI of AI implementations
- Collect user feedback on AI tool usefulness and accuracy
- Regularly review and update AI models as your systems and practices evolve
Recognize Limitations and Maintain Realistic Expectations
AI is a powerful tool, but it's not magic. Set realistic expectations with stakeholders about what AI can and cannot do. Acknowledge that:
- AI systems will make mistakes and require human oversight
- Implementation takes time, resources, and cultural change
- Initial results may be underwhelming before optimization
- Not every DevOps task is suitable for AI automation
- AI augments human capabilities rather than replacing human judgment
Foster a Culture of Responsible Innovation
Finally, create an organizational culture that values both innovation and responsibility. Encourage teams to explore AI capabilities while maintaining healthy skepticism. Celebrate successful AI implementations while openly discussing failures and lessons learned. Make it safe to question AI recommendations and override them when human judgment suggests a different path.
As industry expert, Siddhartha Allen, aptly summarized: "Implementing AI is a great way to be more efficient and effective at your tasks—do explore it, but recognize the limitations."
Final Word
The future of DevOps is AI-driven, and staying ahead requires expertise and a strategic approach. Softjourn’s AI and DevOps specialists are ready to help you harness the power of AI to drive innovation and scalability. Let's explore how AI can transform your DevOps pipeline today.