IT spending across industries is rising, and so is the diversity of tools and resources. Regardless of the industry, companies recognize that investing in IT can bring long-term benefits like more highly-automated processes, better management practices, and easier scaling. According to an Arcserve report from 2020, the world will store 200 Zettabytes of data by 2025. All this data has to be stored in public or private data centers, computers, and smart devices.
Clients often ask us about the difference between on-premise and cloud infrastructures, and whether they should consider upgrading to the cloud. We spoke to Softjourn’s solutions architect, Taras Romaniv, who shared valuable insights and answered our clients' most burning questions about current infrastructure solutions.
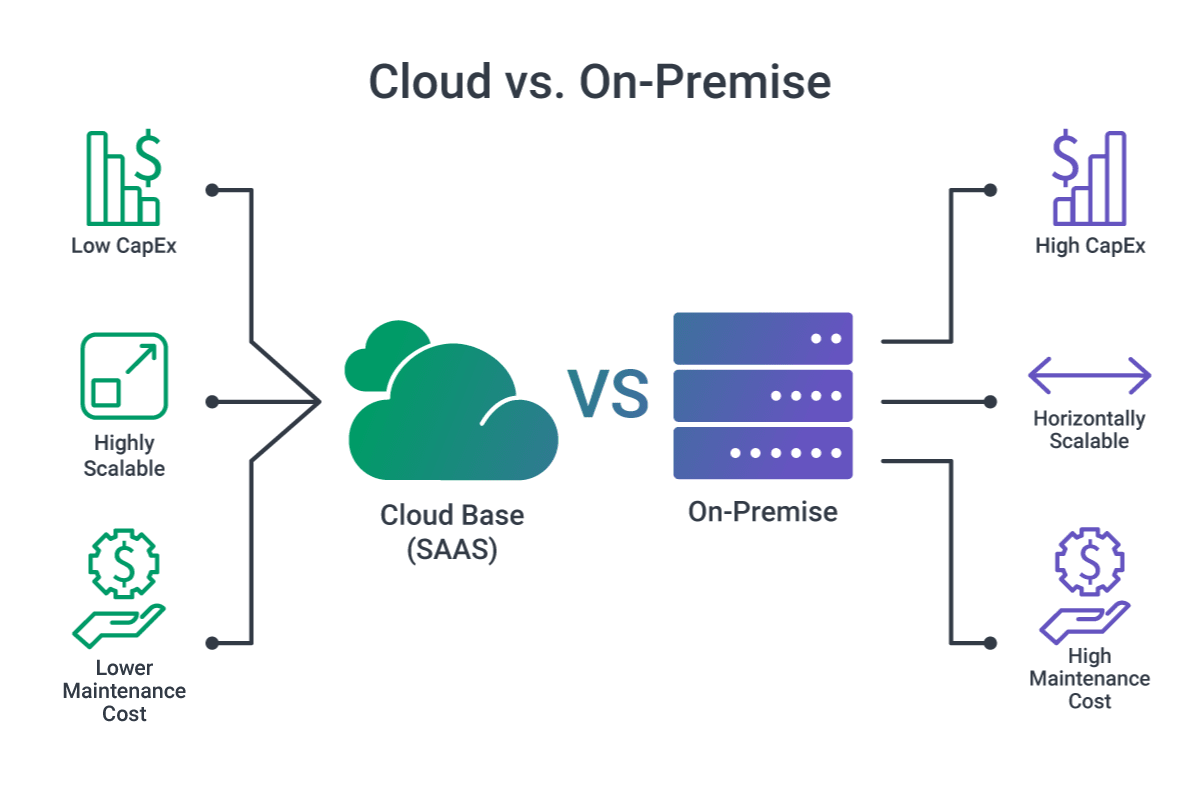
Current Infrastructure Solutions for Business
Before we recommend to our clients whether or not they should move to the cloud, we feel it’s essential to answer common questions about existing infrastructure, such as, what is cloud computing, what are the advantages and disadvantages of cloud computing, and what are the differences between on-premise, cloud (private and public), and hybrid environments.
Cloud solutions are great infrastructure options for many businesses and offer scalable and secure data storage. Until the 2000s, most companies were heavily reliant on on-premise solutions, but all of this changed when Google introduced cloud computing in 2006.
The most prominent benefits of cloud environments are their flexibility as well as digital workflow and maintenance savings since it is entirely operated by third-party vendors who take on responsibility for the technical aspects.
With cloud environments, you can easily add more storage and build automated features. Plus, the environment will always be compatible with the different tech stacks and technologies you wish to use. Currently, the most popular platforms for building cloud environments are AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Public clouds are the most commonly used cloud solution. Public clouds differentiate themselves from private clouds because their users’ systems physically share the same hardware infrastructure, although, and on a software level, the users’ systems or code are isolated, protecting each user’s data.
On-premise solutions provide an environment that is only accessible to one enterprise or client. Private environments are usually located in a company’s data center or administered by a third party. The most significant advantages of using on-premise infrastructure are the high level of security, adherence to regulations, and clearly projected costs.
On-premise solutions require that the company or third party be responsible for maintaining its servers and hardware. It is necessary to have a dedicated server management team who will ensure everything works properly at all times.
Hybrid solutions combine on-premise storage, private cloud, or public cloud service environments. The hybrid environment utilizes the cloud and on-premise solutions with many automated tasks. Since this type of workflow demands interrelation from the local data center to a cloud infrastructure, it is considered a hybrid approach.
Hybrid is usually a temporary solution and is most frequently used when a company reuses its existing on-premise workload, or when a business is in the process of migrating.
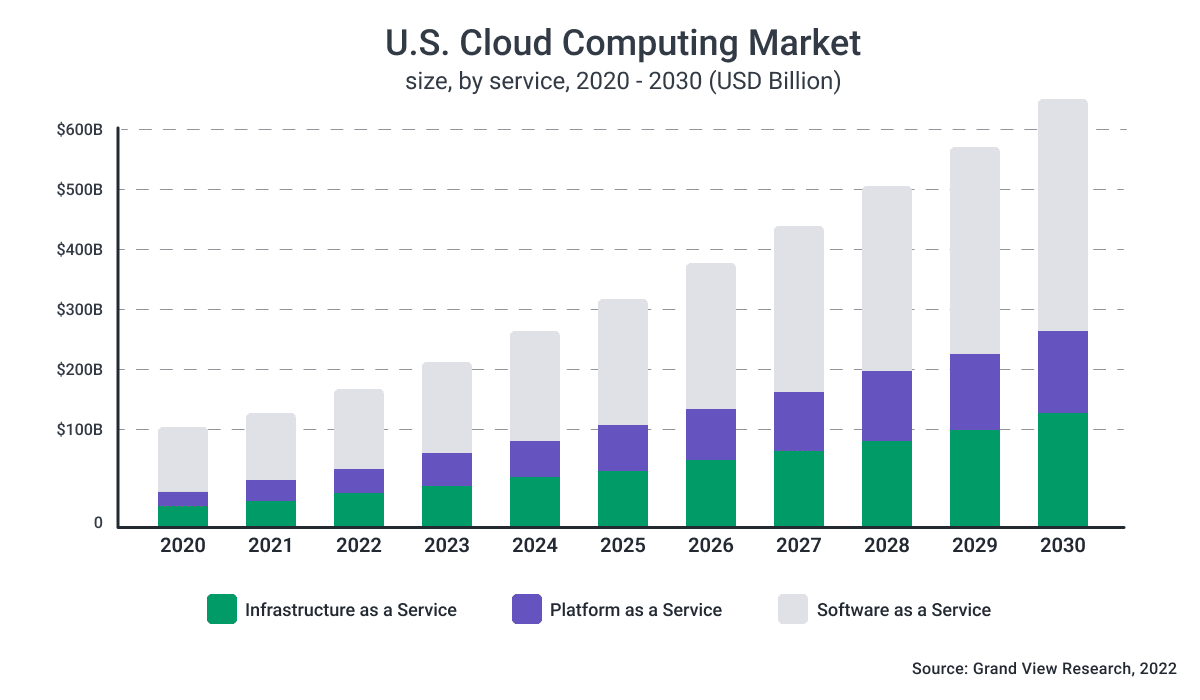
Source: Cloud Computing Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report
A Deeper Look into the Difference Between On-Premise and Cloud Environments
There’s a large range of factors to consider when deciding whether it's time to migrate to a cloud environment. Deciding whether you’ve outgrown an on-premise solution comes down to multiple factors and requires a deep understanding of your business model and its functions.
You should take into account your company’s workflow, business goals, security, compliance, level of control, and budget, among other variables.
Most likely, the reasons why a business might continue to use an on-premise solution are that:
- They already own a legacy system
- They have their own data center or servers that they prefer to use
- There are special regulations that must be followed pertaining to data security
- They have specific requirements (a special grade latency or system requirements)
- They are influenced by business factors, such as having a pre-established partnership, a cheaper price, existing teams, or they want to own and maintain their own hardware)
Unless your company has a strong reason to not use the cloud for storage (such as one of the reasons mentioned above) there are not many advantages to using on-premise environments that the cloud cannot offer. In fact, the cloud is so popular for business for a wide variety of reasons.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
- Globally available and maintainable
- Doesn't require a large upfront investment
- Flexible and scalable
- Allows for disaster recovery processes
- Automated for updates and support
- Has solid data security
- Vendor is obligated to manage and run the underlying system
- Cloud providers such as AWS are compliant with many regulations (e.g. HIPAA)
Softjourn’s Solution Architect posits that cloud environments offer “more flexible control over infrastructure costs, faster time to market, better overall flexibility, and improved reliability - all with less business risk and reduced investment and maintenance costs.”
Additionally, FinOps consulting services can even further reduce cloud costs, saving money through optimization and strategic measures.
The following are a few other categories to consider when deciding whether or not to pursue cloud infrastructure.
Maintenance
With on-premise models, since all data is stored in the local servers, your company will be responsible for its support and maintenance. In contrast, cloud-based environments are hosted via the environment of the service vendor.
Flexibility
When you use the cloud, you can easily change the capacity of the environment depending on your business needs and if you plan to scale up or down. If you use an on-premise environment you will not receive the same level of flexibility.
Security & Compliance
Security is and should always be one of the main concerns of every business. Depending on the business case, private cloud or on-premise might offer heightened security. However, public clouds are still considered to be very secure. For example, AWS enables companies to rely on tight security to comply with multiple regulations, such as HIPAA, PCI-DSS, FedRAMP, GDPR, FIPS 140-2, and more.
Control
You will have the highest level of control with on-premise or private cloud infrastructure, which makes either a good option in case of any issues with external hardware.
Expense
Cloud computing is significantly more affordable as it has little upfront costs, and it also is cheaper for low-to-mid workloads due to its flexibility. However, for huge, global, or very specific types of workloads, on-premise might be more affordable, disregarding the higher upfront costs.
Moving existing on-premise virtual machines to the cloud "as is" can result in higher costs. Softjourn can assist in creating more cost-effective solutions and migrating them to the cloud with efficient allocation of cloud resources.
Public Cloud Versus Private Cloud
So you’ve decided to utilize a cloud solution - great! Next, you will need to consider whether it is best to use a public or private cloud solution. Most of the currently available cloud solutions are SaaS (software-as-a-service) or PaaS (platform-as-a-service). The public cloud PaaS market is evaluated to be worth $110 billion in 2022, with the likelihood to keep growing in the next few years.
One of the most common types of cloud computing deployment is public clouds. Storage and servers are operated and owned by a cloud service provider – like AWS or Azure – that delivers them to users on the internet. All software and hardware maintenance and other supporting infrastructure are managed by the cloud provider.
The benefits that public clouds provide to users are high reliability, lower costs, less time spent on maintenance, automated deployments, recoverability, reliability, and pretty much limitless scalability. Public clouds are different from private clouds because users share physical hardware infrastructure with other users while having their own separate and private software.
The public cloud works best for companies needing:
- Data storage
- Data Archival
- Application Hosting
- Latency intolerant or mission-critical web tiers
- On-demand hosting for microsites and applications
- Auto-scaling environment for large applications
Private cloud can be considered a wide term for a couple of different environments. The first type of private cloud we’ll describe is an on-premise environment that is managed by software to make it "cloud-like" (e.g. Cisco Private Cloud or IBM Cloud Private).
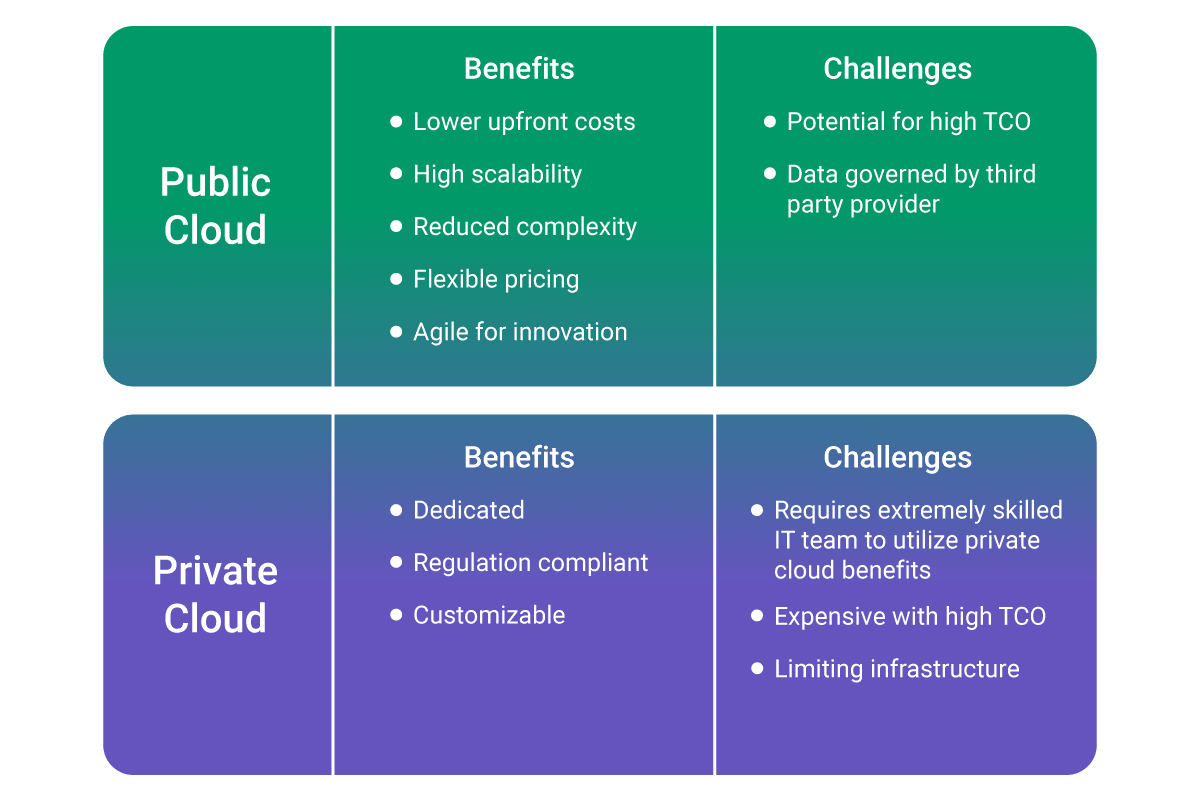
With this type of private cloud, all services and infrastructure are fully private and owned by the organization. This means that the physical hardware is hosted by a third-party service provider and the software and the infrastructure is maintained by a private network. The advantages of this type of private cloud are that they allow businesses to have more control over hardware security and maintenance.
The second type of private cloud is a dedicated cloud infrastructure that is offered and configured by cloud providers specifically for an organization. While the private cloud offers a great level of control and security, it requires that the organization purchase and maintain the entire infrastructure and acquire and retain the tech talent to do so, making the private cloud significantly more expensive. However, this might be worthwhile if you:
- Need strict security, latency, regulatory, and data privacy levels not yet met by the public cloud.
- Are highly regulated and need data hosted privately and securely.
- Need high-performance access to a file system, such as media companies.
- Host applications that have predictable usage patterns and demand low storage costs.
- Require greater adaptability, configurability, and flexibility.
- Host business-critical data and applications.
Tap Into the Endless Possibilities of the Cloud
We recommend cloud environments in about 99% of cases when clients seek a secure, flexible, and overall great option for business scalability. Understanding your business requirements is the first step towards making a well-informed decision in choosing whether to keep your data stored on-premise or in a cloud environment.
If you feel like you are at a crossroads on which path to take, we’d be happy to help guide you in the direction that is best for your business. At Softjourn, we analyze how each type of environment will impact and benefit your business. Please reach out for a free consultation where we can advise you on the best solution for your business requirements and goals.
Have you already made a decision on a solution? Deploying cloud technology can be challenging and often comes with confusion, frustration, and unnecessary costs.
Softjourn is experienced in cloud solutions and we can provide you with expert consulting and technicians specialized in the main cloud computing platforms such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform. Contact us today and find out more.
FAQs
- Why move to the cloud?
There can be potentially significant long-term and short-term savings in terms of cost and human resources when an organization migrates to the cloud.
Organizations also tend to become more robust and flexible to adapt to rapidly changing market environments since they’re able to shift from one solution to another or try out multiple solutions before deciding on one without incurring large expenses. There are also considerable gains on the cybersecurity front when switching to the cloud.
- Are cloud solutions safe?
While the cloud does have its risks, cloud providers dedicate extensive measures to keep customer data safe. They have dedicated risk management resources to mitigate all kinds of threats and come with multiple levels of redundancies. It’s difficult for an organization to achieve this level of security on-premise. In theory, on-premise may seem safer because you have more control over the infrastructure, but in practice, it is very rare that you will find much difference in terms of data safety between on-premise and cloud infrastructure. For those who want to upgrade to the cloud but are hesitant because of shared hardware, we recommend private cloud solutions.
- When is the right time to move from on-premise to the cloud?
Unless you have a unique business requirement, it is always a good time to move to the cloud! Public cloud computing services offer nearly unlimited scalability. Plus, costs are growing lower and cloud platforms are providing access to next-generation technologies, such as AI/ML, serverless computing, blockchain, and real-time analytics. The cloud offers more robust security, stronger data governance, easier management of data locality issues, and lower latency.
- What factors would influence a business to keep an on-premise solution?
Cloud is much cheaper at the beginning. It is also cheap to some level of load (because it is more flexible). However, for huge global workloads, on-premise may be a cheaper solution. Sometimes, companies need to use their existing hardware resources and extend them with the capabilities of the cloud platform.
- What is a hybrid cloud solution and when would I use it?
A hybrid cloud is a solution that includes multiple environments, such as on-premise, private cloud, and public cloud environments. Hybrid storage is often a temporary solution that companies utilize when they either reuse their existing on-premise workload or are in the process of migrating.
- What is the difference between public cloud and private cloud?
Public clouds are the most commonly used cloud solution. Public clouds differentiate themselves from private clouds because their users’ systems physically share the same hardware infrastructure, although, on a software level, the users’ systems or code are isolated, protecting each user’s data.
- What advice would you give to clients who have trouble choosing between infrastructure types?
There’s no universal answer as it depends on your business’ needs. However, in most cases, we find cloud infrastructure to be the best solution. Talking with an expert consultant is advisable before selecting an option, and we are happy to guide you toward the best decision for your company.
- How hard is it to move from on-premise to the cloud?
The difficulty of moving from on-premise to the cloud depends on the project size, its load, the architecture, and many other aspects. While it can be fairly simple to move some small POC/MVPs to the cloud, for bigger projects it will likely be a complex multistage process. We recommend relying on an experienced technical team who knows the ins and outs of moving to the cloud.