In the rapidly evolving digital age, where new technologies are constantly emerging, it's a challenge for most technologies to maintain relevance for more than ten years.
For decades, we've used Java for software development across industries, helping companies build scalable, secure, and high-performance applications.
However, as technology evolves, many businesses wonder whether Java remains a relevant choice.
In this article, we explore Java’s enduring role in modern development, its continued demand, and why it remains a trusted technology for enterprises worldwide.
Is Java Still Used in 2026?
Despite being over 30 years old and facing competition from newer languages like Kotlin and Go, Java continues to dominate enterprise software, Android development, and backend systems.
With over 90% of Fortune 500 companies employing Java and consistently ranking among the top ten most popular programming languages worldwide, Java is still going strong.
Softjourn's Long-term Java engineer, Orest Guziy, said that Java has been getting more attention than ever since Java changed its release processes to every 6 months.
So the short answer is yes — Java remains extremely relevant in 2026. Will it continue to stay popular over the next few years? Keep reading to find out!

Java's Popularity Over the Years
Java is one of the most widely used programming languages in the world, and its popularity has only grown since its launch in 1995.
In this section, we will explore some statistics on Java's popularity from various surveys and indices, highlighting its continued relevance and importance in the software development industry.
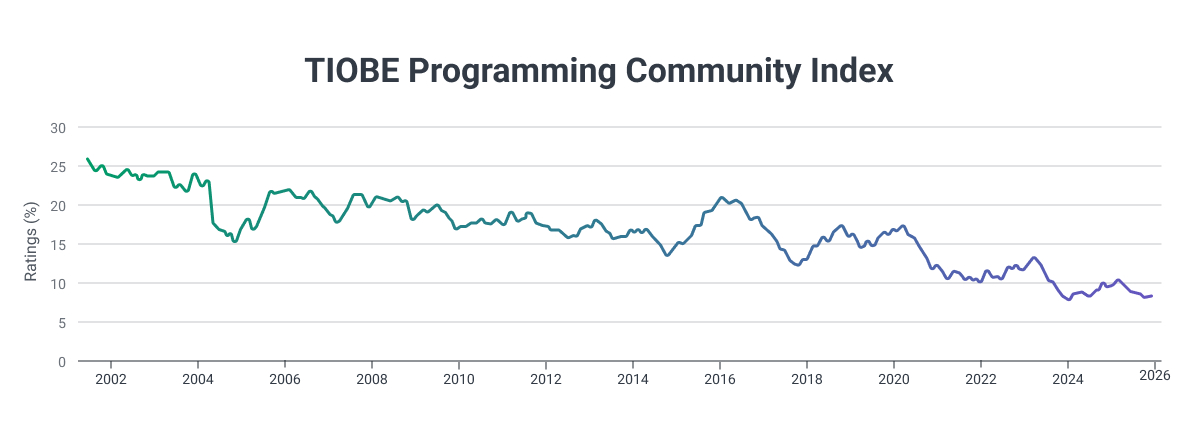
TIOBE Index
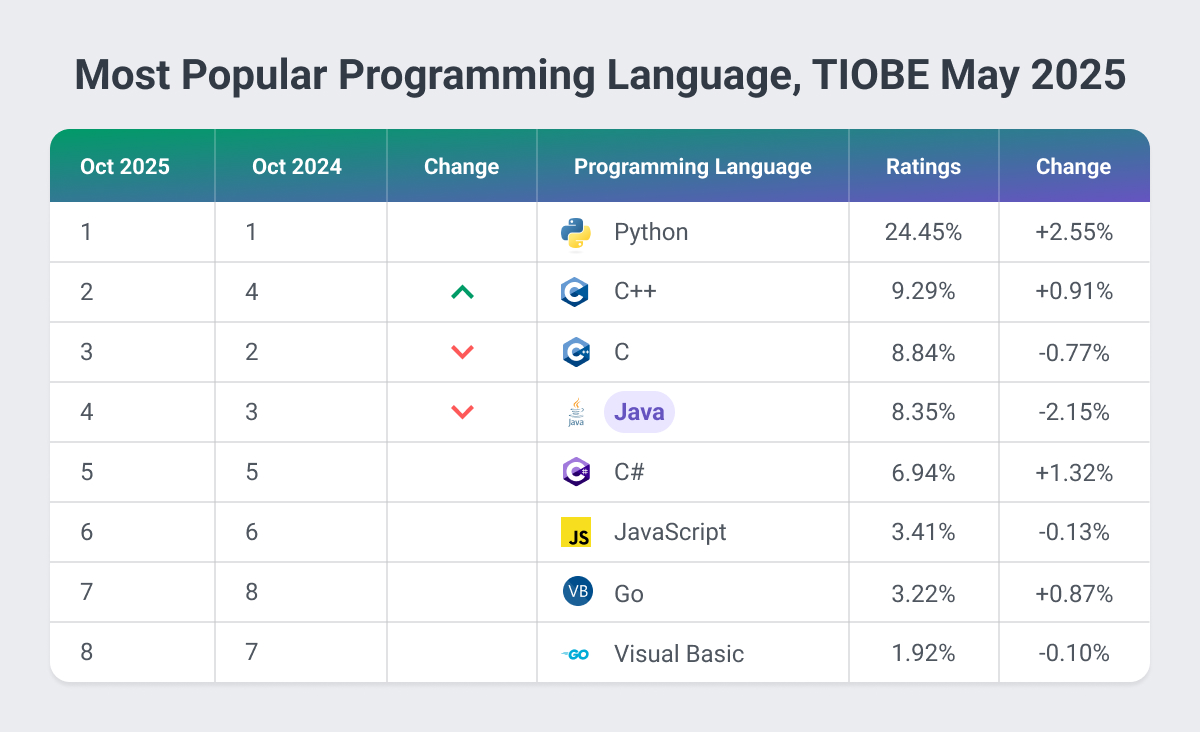
According to the TIOBE Index, Java has been one of the most popular programming languages globally since 2001.
Stack Overflow Developer Survey
In the most recent Stack Overflow Developer Survey, Java was the seventh most commonly used language, with 30% of respondents saying they extensively use Java in their work.
GitHub State of the Octoverse Report
In GitHub's latest State of the Octoverse report, Java was named the fourth most popular language on their platform, regarding the number of users contributing to projects, after Typescript, Python, and JavaScript.
Indeed
According to Indeed in 2025, Java is the third most in-demand programming language, after Python and JavaScript, with a median salary of $116,000 in the United States. Java developer salary has increased by 11% over the last five years.
Why is Java one of the Most Popular Languages Over the Years
Java has been one of the most popular programming languages for several years, and its popularity has remained steady over time. Since its introduction in 1995, it has consistently been among the top programming languages used in industry and academia.
Even though there are newer languages out there, Java has remained popular due to its versatility and robustness. It can be used for everything from developing Android apps to building enterprise-level applications.
Sure, there are some drawbacks to using Java; as it can be slower than other languages, and it isn’t the easiest language to learn, but overall, it is still a very strong option for developers.
Arkadiusz Drysch, CTO and Java expert at Stratoflow said:
"Java is a great support for advanced applications. This programming language enables building high-performance software that is scalable, efficient, and secure. Such systems developed in Java are capable of processing a million queries per second. For this and many other reasons, Java remains a world-class leader when it comes to building back-end applications."
Finally, the continuous evolution of the Java language, with new features and updates being added regularly, has helped to keep it relevant and popular over the years.
Java Popularity in 2026
Even after nearly three decades since its inception, Java is still heavily used by a significant number of programmers, and a plethora of products are being built using it.
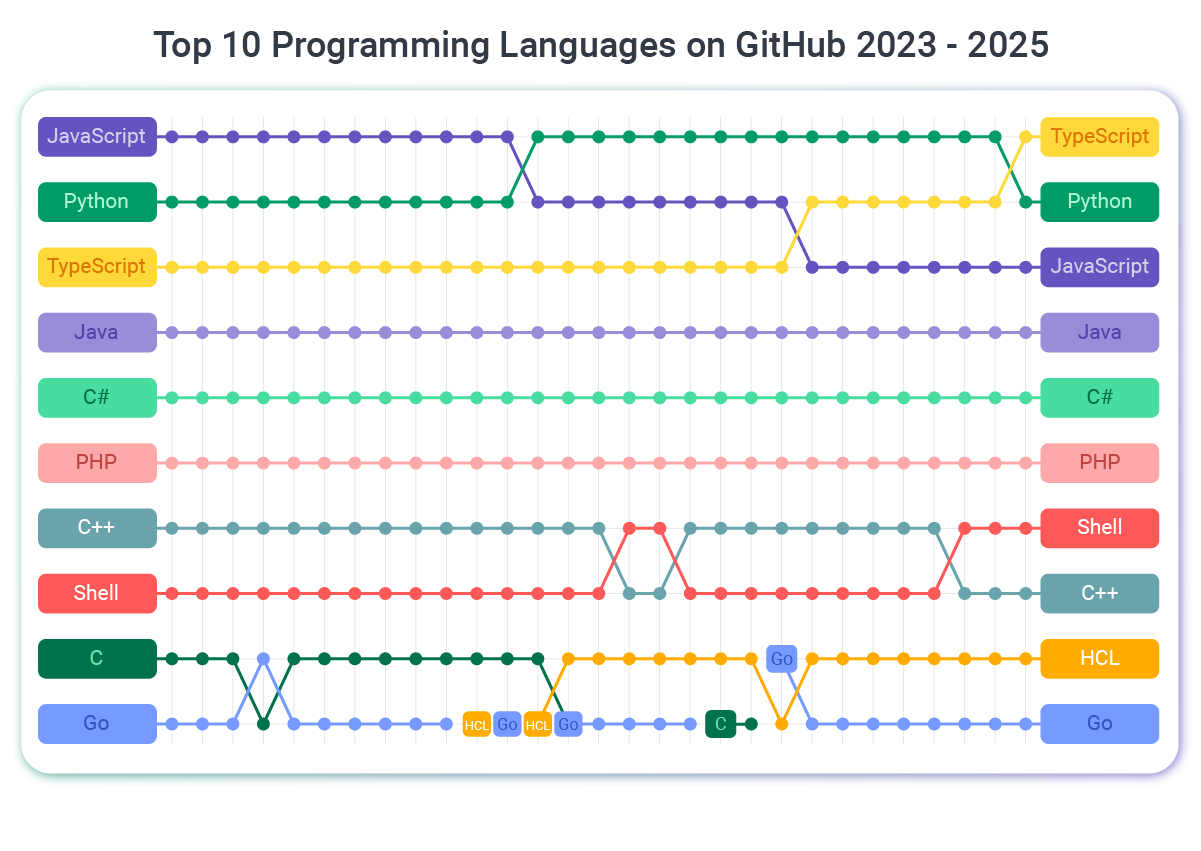
According to the 2025 TIOBE Programming Community index, which is an indicator of how widely used a programming language is, Java ranked fourth, just behind Python, C, and C++, with a positive change, showing Java is on the rise.
Similarly, the RedMonk Programming Language Rankings for 2025 ranked Java as the third most popular language, after JavaScript and Python, based on data from GitHub and Stack Overflow.
Java remains one of the most in-demand programming languages. According to recent data, 39.5% of recruiters are actively seeking Java developers, making it the third most sought-after language in the industry. Currently, DevJobsScanner shows 47,000 listings for Java engineers, and Indeed has over 39,000 open positions.
Java also ranks second in search volume among programming language tutorials, representing 15.15% of all programming language learning searches.

An estimated 9 million Java developers are currently employed globally, with projections showing 18.7 million new Java developer positions emerging by 2026. In the United States alone, the Java developer workforce is expected to grow by 13% by 2028.
With this level of competition for Java talent, securing experienced developers quickly can be challenging. That's where partnering with an established development firm makes the difference. At Softjourn, we maintain a team of skilled Java professionals ready to jump on your project—whether you need integration specialists, legacy system modernization, or greenfield development. Instead of spending months recruiting, you can start building within weeks.
What is Java Used For?
We've seen that Java is still going strong. So, where is it being used in 2026? Let's break down its main applications across key industries.
Cloud-based Applications
Java is well-suited for cloud-native development, which refers to cloud-based applications that rely on internet computing. Cloud computing has five key attributes, including on-demand capability, broad network access, resource pooling, rapid elasticity, and measured service.
Java can be used to develop cloud applications in three delivery models, including IaaS, PaaS, or SaaS, and there are several cloud building tools available for Java, such as AWS SDK for Java, Oracle Cloud service, and Google App Engine.
Many companies are hiring Java developers to assist with transitioning to the cloud for improved business continuity, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Major cloud-based platforms like Netflix, Dropbox, and Twitter rely on Java for their infrastructure.
Mobile Applications
The technology stack used for developing mobile apps depends on the target platform. While Objective-C and Swift are used for developing iOS apps, Android apps are primarily built using Java.
Java is the preferred language for Android app development because Android is used on 73% of devices globally, whereas iOS is only used on 25%.
Java's platform independence is a key advantage for those looking to build both Android and iOS applications. This makes it a popular choice for businesses developing cross-platform applications.
As a language that can run on any operating system, it eliminates the need for developers to write and maintain separate codebases for different platforms. This can save businesses time and resources, allowing them to focus on delivering their product to a wider audience.
Companies like Spotify, Uber, and Netflix use Java extensively in their mobile applications.

Enterprise Applications
Java EE (Enterprise Edition) provides the scalability, security, and multi-tiered architecture that large-scale enterprise systems require. It's particularly well-suited for banking systems, supply chain management, and transaction processing where reliability is non-negotiable.
Java's robust APIs and framework support simplify complex enterprise operations, from customer relationship management to inventory control. The language's maturity and extensive ecosystem mean that enterprises can build, maintain, and scale their systems with confidence.
Major companies like Barclays, Goldman Sachs, and Citigroup rely on Java for their core enterprise systems, as do business software leaders like Salesforce, IBM, and TCS.
Web-based Applications
Java offers the benefits of simplified coding and enhanced security, making it an excellent choice for developing applications in areas such as healthcare, education, insurance, and e-commerce. The language's robust security features are particularly valuable when handling sensitive user data and transactions.
Java is compatible with a range of powerful tools, including Servlets, JSPs, Hibernate, Spring, Struts, Apache HTTP web-server, Apache Tomcat, and Thymeleaf, which can be utilized to develop sophisticated web-based applications.
E-commerce platforms commonly leverage Java, often using open-source solutions like Broadleaf. Major web applications, including LinkedIn, Amazon, and Alibaba are built using Java.
Big Data Technologies
Java has become a cornerstone of the big data ecosystem, serving as the foundation for technologies like Apache Hadoop and Apache Spark, and integrating deeply with modern cloud-native data platforms such as Databricks, Kafka, and Flink. Its strong performance, reliability, and mature ecosystem make it essential for streaming pipelines, distributed processing, and large-scale analytics.
Java's integration with big data tools is seamless, making it the go-to language for data engineers building scalable data pipelines and analytics platforms. The language's ability to handle complex computations while maintaining reliability has made it essential in the big data landscape.
AI and Machine Learning Applications
Java's reliability, portability, and vast ecosystem make it increasingly popular for AI and machine learning projects. With libraries and frameworks like Deep Java Library (DJL), ND4J, and integration with TensorFlow, Java enables developers to build intelligent systems for natural language processing, computer vision, and predictive analytics.
The language's strong typing and robust error handling make it particularly valuable for production AI systems where reliability is critical. Java's scalability also means that AI applications can grow from prototype to enterprise-scale deployment without requiring a complete rewrite.
With 92% of company executives planning to increase AI and ML expenditures, demand for Java developers skilled in these technologies continues to grow. Companies like IBM Watson, Oracle AI, and various Google AI initiatives leverage Java in their machine learning infrastructure.
Financial and Trading Applications
Java powers some of the world's most demanding financial systems, from high-speed trading platforms to risk management tools. Its high performance, robust security features, and reliable server-side operations make it ideal for managing transactions, risk analysis, and data processing in banks and financial institutions.
The language's ability to handle real-time data processing and complex calculations while maintaining data integrity is essential in this high-stakes environment.
Financial institutions, including JP Morgan, Nomura, HSBC, Deutsche Bank, and Barclays use Java for their core financial server applications.
Desktop Applications
Java provides several advantages for desktop applications. It is platform-independent, which means that it can run on any operating system, such as Windows, macOS, and Linux, making it an ideal choice for businesses that need to develop cross-platform applications.
Additionally, Java's robustness and security features make it a preferred language for developing desktop applications, especially for enterprise-level software.
With Java, developers have access to a large number of libraries and frameworks, which provide them with tools for creating rich and interactive user interfaces.
Furthermore, Java's automatic memory management feature allows for efficient memory usage, which can be critical for large desktop applications.
Blockchain Applications
Java provides a secure and robust foundation for building blockchain-based systems. With frameworks like Hyperledger, it supports distributed ledger technologies for secure transactions and data integrity. Java's strong typing, extensive security features, and scalability make it well-suited for enterprise blockchain implementations.
The language's flexibility allows for integration with existing enterprise platforms, making it easier for organizations to adopt blockchain technology without completely overhauling their systems. Java's maturity also means there's a large pool of experienced developers who can work on blockchain projects.
Companies, including IBM (Hyperledger), Walmart, and Mastercard, use Java in their blockchain implementations.
Educational Applications
Java powers e-learning platforms and interactive teaching tools, making education accessible and engaging for millions of students worldwide. Its scalability and reliability allow for seamless integration of multiple modules for content management, student interaction, and assessment.
The language's platform independence is particularly valuable in education, where students and teachers may be using different operating systems. Java's strong security features also protect sensitive student data and academic records.
Educational platforms, including Coursera, Blackboard, and Khan Academy, use Java in their infrastructure.
Chatbots and Virtual Assistants
Java has become a popular choice for building chatbots and virtual assistants due to its strong support for natural language processing (NLP) and integration with machine learning libraries. These intelligent systems can provide enhanced user interaction and automation capabilities across multiple channels.

Java's scalability allows chatbots to handle thousands of concurrent conversations, while its robust error handling ensures reliable performance even under heavy load. The language's extensive ecosystem means developers have access to numerous NLP and AI frameworks.
Companies including HDFC Bank (Eva chatbot), Amazon (Alexa backend services), and Google (Dialogflow) leverage Java in their conversational AI systems.
Java's Evolution in 2026: Trends and Updates
Java remains a cornerstone of modern software development, powering everything from mobile and web applications to enterprise systems and AI-driven solutions. As we move into 2026, Java continues to evolve, adapting to emerging technologies and addressing the demands of developers worldwide.
Softjourn's Java Engineer, Orest Guziy, said, "Java's integration with trending technologies, such as cloud-native development, microservices architecture, and AI/Machine Learning, got a significant boost and continues to evolve."

Here’s a look at the top trends and updates shaping Java’s development landscape in 2026:
1. The Rise of Cloud-Native Java
Java’s cloud-native evolution continues to accelerate as teams modernize legacy systems and adopt containerized architectures. Java now integrates more deeply with cloud platforms, offering improved support for Kubernetes, distributed systems, and dynamic scaling. Enhancements in frameworks and runtime optimizations make Java a strong fit for elastic workloads and high-traffic environments.
Key developments include GraalVM Native Image for faster startup times, Java-optimized serverless support across AWS Lambda and Azure Functions, and growing adoption of Quarkus and Micronaut for low-memory cloud deployments.
2. Microservices Architecture Driven by Modern Java Frameworks
Microservices remain one of the strongest drivers of Java adoption in 2026. Frameworks like Spring Boot, Quarkus, and Micronaut continue to dominate, enabling modular services that scale independently and deploy quickly. The introduction of virtual threads in JDK 21 and beyond allows microservices to handle massive concurrency with far less complexity, reducing the need for reactive patterns.
Java’s native compatibility with modern observability tools such as OpenTelemetry also improves tracing, metrics, and debugging across distributed systems, making Java microservices easier to monitor in production.
3. Intelligent Applications and Java’s Rapid AI Adoption
Java’s role in AI has accelerated dramatically as organizations move from experimental prototypes to production-grade intelligent systems. According to a recent large-scale survey from Microsoft, 97 percent of developers say they would choose Java to build intelligent applications, while 90 percent mistakenly believe they need deep Python or machine learning expertise to get started.
Modern Java-first AI frameworks like MCP Java SDK, Spring AI, and LangChain4j are changing that. These tools allow developers to integrate large language models, vector databases, and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) using familiar Java patterns; similar to working with REST APIs or traditional databases.
Developers highlighted several essential capabilities for AI-powered Java applications, including RAG for context-aware responses, embeddings and vector stores for semantic search, function calling for dynamic workflows, and intelligent agents for automation. As Java remains the backbone of enterprise software, these advancements position Java developers to lead the next generation of intelligent, business-critical applications — without needing to become AI specialists.
4. Innovations from Project Valhalla
Java’s Project Valhalla is transforming performance with value types and enhancements that reduce memory overhead and improve data handling. These improvements are especially impactful for numerical computing, scientific workloads, and high-performance applications that require predictable memory efficiency.
5. Lightweight Concurrency with Project Loom
Project Loom introduces virtual threads, dramatically simplifying concurrent programming. Virtual threads allow developers to build high-throughput applications without complex reactive code, improving scalability and reducing cognitive load. This trend is especially impactful for cloud-native and microservices architectures where concurrency is critical.
6. Modular Libraries and Compact Object Headers
Java continues to streamline development with modular imports, more efficient packaging, and runtime optimizations like compact object headers. These improvements reduce memory usage, lower compute costs, and improve deployment efficiency in containerized or resource-limited environments.
7. Deprecations and Security Enhancements
Java is phasing out legacy features, improving internal security, and modernizing the platform. Deprecation warnings for older APIs such as sun.misc.Unsafe guide developers toward safer alternatives. These changes support stronger security postures and reduce technical debt for enterprise systems.
8. Simplifying Development for Beginners
To keep Java approachable for new developers, features like Simple Source Files and Compact Source Files streamline the learning curve. These enhancements reduce boilerplate and help new developers get started with functional Java programs quickly, supporting the continued growth of the Java community.
JDK 25: The Next Long-Term Support Release
Released in September 2025, JDK 25 marks Java's newest Long-Term Support (LTS) version and introduces features that enhance developer productivity and application performance:
- Compact Source Files (JEP 512): Enables instance main methods and class-less files, making Java more accessible for beginners and rapid prototyping.
- Flexible Constructor Bodies (JEP 513): Allows validation and setup code before super() calls, improving code clarity and fail-fast behavior.
- Scoped Values (JEP 506): Provides a lightweight, immutable alternative to ThreadLocal, designed specifically for virtual threads and structured concurrency.
- Compact Object Headers (JEP 519): Reduces memory footprint on 64-bit architectures, particularly benefiting large heaps and microservice deployments.
Java Case Studies
1. Future-Proofing UPC’s Open Banking Platform: A Strategic AWS Migration
Softjourn leveraged Java to modernize UPC’s financial operations, migrating its on-premise infrastructure to AWS to meet new regulations and enhance scalability. By utilizing Java’s robust capabilities in conjunction with serverless AWS architecture, Softjourn ensured seamless PCI DSS compliance and improved performance. This phased migration not only reduced costs but also positioned UPC for future growth while maintaining the reliability of critical services like card transactions and APIs. Read Full Case Study.
Key Results:
- Enhanced scalability and security for financial operations.
- Streamlined compliance with strict financial regulations.
- Reduced operational costs through serverless technologies.
2. Elasticsearch Optimization for an Expense Management Leader
For an expense management leader, Softjourn utilized Java to overhaul and upgrade a complex Elasticsearch system from version 2.3.4 to 7.9. Java’s efficiency was pivotal in developing a custom comparison tool that validated the accuracy of search queries before launching the new version. This tool also enabled smoother future upgrades, ensuring minimal downtime and improved scalability. Read Full Case Study.
Key Results:
- 0.02% error margin in over 500,000 search queries.
- Faster and more accurate search functionalities.
- Streamlined future Elasticsearch upgrades.
3. SecuTix: Supporting Business Growth with Salesforce Integration
Softjourn developed a Salesforce plugin using Java to seamlessly integrate SecuTix’s ticketing system with third-party databases. The integration enabled real-time updates for venues, events, and ticket availability while securely synchronizing customer data across systems. Java’s adaptability ensured reliable performance and scalability as SecuTix expanded its global operations. Read Full Case Study.
Key Results:
- Enhanced data synchronization and real-time updates.
- Increased ticket sales by enabling broader event processing.
- Improved customer relationship management with Salesforce integration.
Java Will Remain a Top Programming Language in 2026
Java remains a popular programming language with a vast ecosystem, strong community, and proven track record.
While Java has pros and cons, we predict it will continue to be a dominant programming language. Its ability to support various platforms, including cloud and mobile, makes it an excellent choice for businesses looking to develop and scale applications.
If you're looking to extend your team with Java talent, Softjourn has expert Java developers who can help you build or expand your solution. Contact us today to get an estimate for your project!