In exploring the cloud-based Payments as a Service (PaaS) model, fintechs provide a gateway for businesses to leverage new instant payment rails with minimal risk. This approach allows organizations to enter the market swiftly and efficiently, capitalizing on innovative payment solutions without substantial investment or infrastructure overhaul.
We will explore the PaaS model as well as the benefits of using cloud-based payments, highlighting how these solutions are reshaping the financial industry.
The Emergence of Cloud-Based Payments
In the evolving financial landscape, cloud-based payment systems, such as Banking as a Service (BaaS) and Payments as a Service (PaaS), have become pivotal. Transitioning from private cloud servers to public or hybrid operations has enabled banks to be more agile, meet changing demands, and utilize the robust cybersecurity measures of tech giants like Amazon and Microsoft.
To better understand the synergy between PaaS and cloud-based payments, it's essential to recognize how these models enhance each other. Cloud-based payments leverage the scalability, flexibility, and security of cloud infrastructure, making PaaS an ideal fit. By integrating cloud capabilities, PaaS providers can offer more robust and efficient payment solutions, enabling banks and financial institutions to meet the evolving demands of the digital economy.
The PaaS model empowers banks and financial institutions to offer advanced payment products and services without the significant internal development costs. By leveraging cloud-based third-party platforms, these institutions can adopt a flexible, agile approach, optimizing their offerings efficiently.
Payments as a Service Market
According to Markets and Markets, the global Payments-as-a-Service (PaaS) market is projected to grow from $56.2 billion in 2020 to $164.3 billion by 2026. This rapid growth is driven by the acceleration toward digital payments, open banking, digital wallets, and the decline of cash usage, significantly impacting the global payments ecosystem.
Financial institutions face complex challenges in this new payment processing world. They must navigate regulatory compliance, risk management, transaction fraud, and maintain control, all while providing excellent customer service.
What is Payments as a Service (PaaS)?
As defined by the McKinsey Global Payments Report, Payments-as-a-Service (PaaS) allows banks to quickly expand and modernize their payment portfolios without high upfront investment. PaaS providers operate cutting-edge cloud-based platforms, offering specialized services like card issuing, payment clearing, cross-border payments, disbursements, and e-commerce gateways.
PaaS enables banks to outsource parts of their payment technology, offering customers flexibility and choice, reducing risk, and simplifying the restructuring of an organization's payments stack.
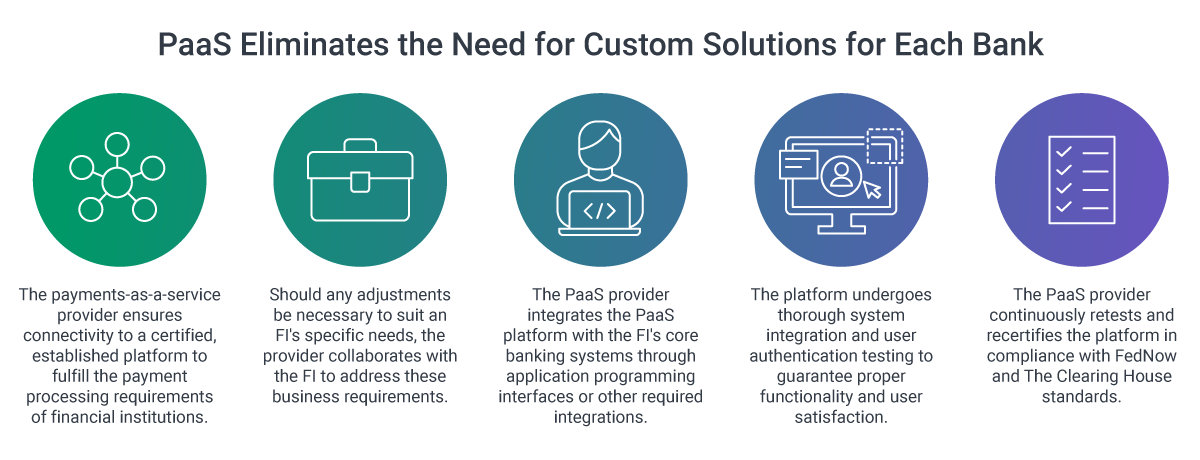
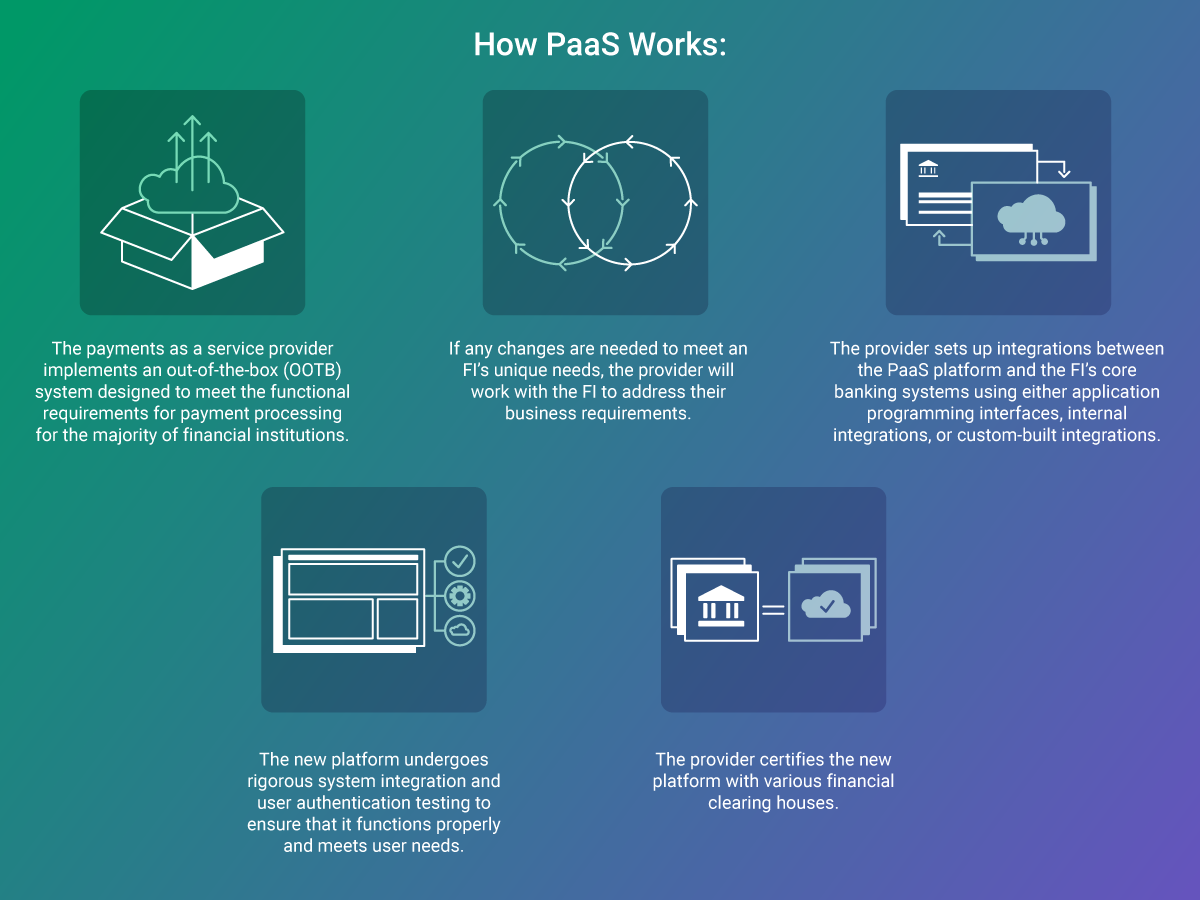
How Payments as a Service Works
PaaS functions like other “as a service” models, where providers host applications and data on their servers, making them accessible to financial institutions over the internet. Services vary by PaaS vendor but typically include software integration, payment processing, reconciliation, settlement, disaster recovery, data security, compliance, reporting, and issue resolution.
PaaS allows financial institutions to offer advanced payment products without heavy internal development costs, moving to a flexible, agile model.
PaaS can serve various functions, including:
- Card issuing
- E-commerce gateways
- Payment processing
- Payment clearing
- Payment engine hosting
- Cross-border payments
- Transaction management
- Disbursements
- Information security management
- Risk management
- Reconciliation and settlement
- Third-party collections
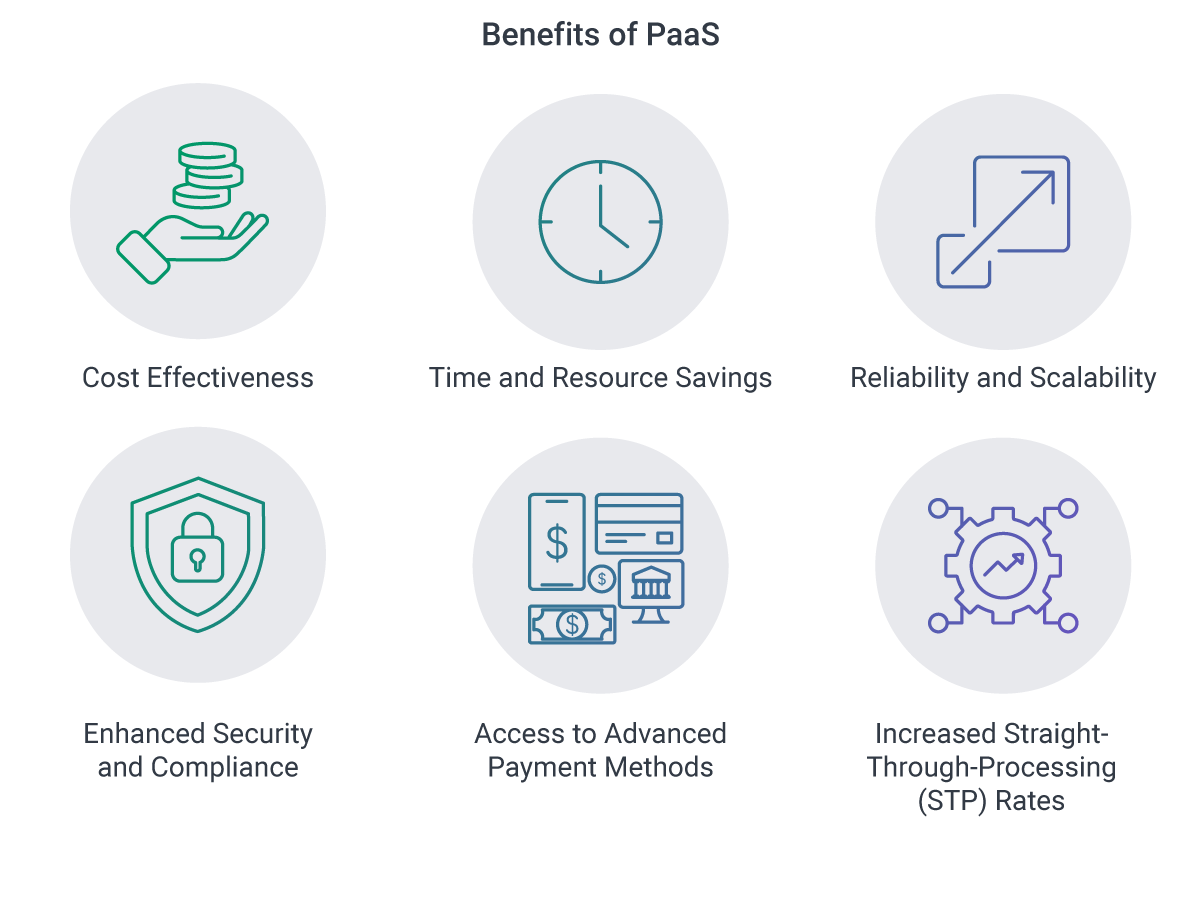
The Benefits of Payments-as-a-Service for Financial Institutions
PaaS offers multiple benefits for banks and fintech companies, including:
- Cost Optimization: Reduces costs by eliminating the need for specialized in-house teams and expensive hardware and software.
- Flexible Pricing: Adapts pricing structures based on product, transaction volume, and business size, offering transparent, fixed costs and pay-per-use models.
- Faster Time-to-Market: Ready-to-go service provider products enable quicker deployment of new functionalities.
- Improved Reliability and Scalability: Cloud-based platforms scale automatically, providing greater system availability.
- Enhanced Security and Fraud Prevention: Third-party platforms reinforce security measures, monitor suspicious activities, and manage compliance.
- Streamlined Compliance Management: Providers ensure adherence to standards like ISO 27001 and PCI-DSS.
- Access to Advanced Payment Methods: PaaS integrates new transfer methods, such as blockchain, enhancing customer payment options.
- Increased Straight-Through-Processing (STP) Rates: Seamlessly embeds critical systems for uninterrupted data flow.
What Are Cloud-Based Payments?
Cloud-based payments refer to payment processing systems that utilize cloud technology to handle transactions. These systems offer enhanced scalability, flexibility, and security by leveraging the infrastructure provided by cloud service providers.
Cloud-based payment solutions enable financial institutions to manage transactions more efficiently, integrate with other digital services, and provide a seamless payment experience to their customers. This approach reduces the need for significant on-premises infrastructure, allowing for cost savings and quicker adaptation to market changes.

Why Cloud-Based Payments Matter
Cloud-based payment systems offer banks a lifeline in generating non-interest income and diversifying revenue streams. By charging transaction fees and offering value-added services like fraud detection and data analytics, banks can achieve substantial gains. Public cloud models, such as AWS and Azure, provide cost-effective, scalable, and reliable alternatives to traditional private cloud infrastructure.
The Benefits for Banks of Using a Cloud-Based Payment System
- Greater Flexibility and Scalability: Cloud-based systems easily adapt to peaks in payment volumes, meeting customer demand effectively.
- Easy Integration: These systems seamlessly integrate with external accounting and management software, providing real-time sales and data reports.
- Robust Security: Cloud-based systems comply with PCI DSS standards, ensuring secure processing, acceptance, and storage of credit card information.
- Lower Cost: Cloud-based processing saves time and reduces infrastructure costs with a pay-per-use pricing model.
- Efficiency and Speed to Market: Cloud systems enable rapid deployment of payment technologies and aid data integration, speeding up product launches.
- Sustainability: Moving to the cloud reduces the carbon footprint of traditional private data centers, supporting greener banking practices.
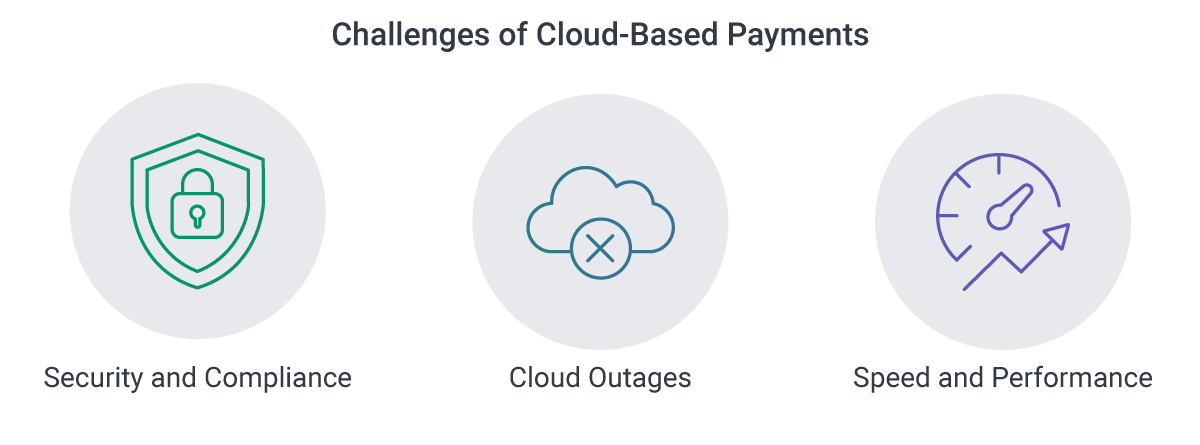
Challenges of Cloud-Based Payments
Despite the benefits, cloud-based payments pose challenges:
- Security and Compliance: Storing sensitive payment information with third-party providers increases the risk of breaches.
- Cloud Outages: Dependence on cloud providers can lead to service disruptions; hybrid cloud architectures can mitigate this risk.
- Speed and Performance: Real-time payment processing in the cloud requires improved infrastructure and 5G networks for widespread adoption.
Security Measures for Cloud-Based Payments
To protect sensitive payment information, cloud-based systems implement:
- Data Encryption: Advanced cryptographic algorithms secure data during transmission and storage.
- Tokenization: Tokens replace sensitive data, reducing breach risks.
- PCI DSS Compliance: Providers adhere to strict security standards.
- Fraud Detection: Real-time algorithms identify and mitigate potential threats.
We recommend utilizing Financial Security Services to ensure that cloud-based payment systems are secure and compliant.

Current Cloud-Based Payment Solutions and PaaS Providers
As the adoption of cloud-based payments continues to grow, numerous providers are offering innovative solutions to meet the demands of modern financial institutions. These PaaS providers deliver comprehensive platforms that streamline payment processing, enhance security, and improve operational efficiency.
In this section, we will explore some of the leading cloud-based payment solutions and the PaaS providers driving this transformation in the financial services industry:
Paystand
Paystand automates the cash cycle using blockchain technology, offering real-time payments and reducing transaction costs. By leveraging a cloud-based PaaS model, Paystand provides features such as zero-fee processing, automated billing, and comprehensive reporting. This cloud infrastructure ensures scalability and robust security, allowing businesses to manage payments efficiently and transparently.

Stripe
Stripe's APIs enable comprehensive online payments management, with functionalities like recurring billing, instant payouts, and multi-currency support. Stripe offers seamless integration with various e-commerce platforms and applications, allowing businesses to quickly adapt to changing payment needs. The cloud-based infrastructure ensures high availability and reliability, crucial for handling large transaction volumes.

PayPal
PayPal simplifies payment processes through a robust PaaS platform that supports various payment methods, including credit cards, bank transfers, and digital wallets. With cloud-based features such as invoicing, payment tracking, and buyer protection, PayPal provides a trusted and secure environment for merchants and consumers alike.

Adyen
Adyen offers a unified payments platform that supports global payments, fraud prevention, and detailed analytics. As a cloud-based PaaS provider, Adyen meets the needs of large enterprises with complex payment requirements. Its platform supports multiple payment methods and currencies, leveraging cloud technology to provide scalable, secure, and reliable payment solutions.

The PaaS Business Model
Payment service providers use modern technology to offer their operational functions to financial institutions and non-banks through a cloud-hosted Core Banking Platform.
These platforms integrate with both legacy and new generation systems via an API-driven approach, connecting with payment networks, operating systems, databases, and development toolkits. Their services are divided into technology implementation and day-to-day operations.
Technology Implementation Services
- Issuing Switch: Manages customer onboarding to transaction processing, supporting real-time processing and settlement. For example, PaaS can provide payment cards for transport operators, usable as tickets at various touchpoints.
- Acquiring Switch/App: Helps financial institutions acquire merchants or aggregators, providing seamless API/SDK integration. Institutions can issue QR codes to merchants via a hosted acquiring switch.
- Regulatory Enhancements: Develops solutions to comply with new regulatory requirements and directives.
Payment Operations and Product Support
- Reconciliation and Settlement: Offers three-way reconciliation (switch, Core Banking, and card network).
- Dispute Management: Handles disputes using business rules, ensuring smooth recovery and risk management.
- Transaction Monitoring: Provides support to resolve issues in the production environment.
- Merchant Acquisition Support: Manages merchant onboarding, transaction settlement, fraud management, and reconciliation.
- Customer Complaint Management: Resolves customer complaints and provides updates via SMS/email alerts.
- Analysis and Statistics: Generates daily, monthly, or annual reports, including trend analysis.
- User Management and Security: Manages user access based on roles and authorizations.
PaaS Pricing Structure
- One-off Implementation Costs: Includes costs for platform customization, user acceptance testing, and core banking integration. These costs are generally lower than in legacy models.
- Pay-per-Use Costs: Involves transaction-based invoicing with a minimum commercial commitment.
- Monthly/Annual Maintenance Costs: Covers application maintenance and hardware allocation based on organizational needs.

Next Steps: Cloud-Based Payments as a Service
Cloud-based Payments as a Service (PaaS) solutions are revolutionizing the financial industry by offering scalability, flexibility, and robust security. By leveraging cloud-based payment systems, financial institutions can provide enhanced services, better customer experiences, and drive significant growth.
At Softjourn, we understand the complexities of implementing advanced payment systems. Our extensive experience in fintech consulting services and payment system integration makes us a trusted partner for banks and fintechs.
Whether you need to streamline your payment processes or integrate cutting-edge payment technologies, our team of experts is here to help. Contact us today to learn how we can support your journey toward a more agile and secure payment infrastructure.
FAQs
Q: What is Payments as a Service (PaaS)?
A: Payments as a Service (PaaS) is a cloud-based delivery model where financial institutions outsource their payment processing infrastructure and expertise to third-party providers. This allows them to efficiently build and deploy new payment products and services without the need for significant internal development and investment.
Q: How does Payments as a Service (PaaS) work?
A: PaaS works similarly to Software as a Service (SaaS). Third-party providers host payment applications and data on their servers, databases, and cloud infrastructure. They then offer these services to financial institutions over the internet through a cloud-based delivery model, ensuring scalability, security, and efficiency.
Q: Why has Payments as a Service (PaaS) become popular?
A: PaaS has gained popularity because it allows financial institutions to bring new products and services to market quickly without compromising quality or security. This rapid speed-to-market helps banks and other institutions meet customer expectations, adapt to market changes, leverage emerging trends, and develop new revenue streams while maintaining regulatory compliance.
Q: What challenges does Payments as a Service (PaaS) address?
A: PaaS addresses numerous challenges, including navigating the evolving regulatory landscape, combating sophisticated cybersecurity threats, meeting growing consumer demand for new products and services, keeping up with rapid technological innovation, and replacing or integrating aging legacy systems.
Q: What benefits does Payments as a Service (PaaS) offer?
A: PaaS offers several benefits, such as greater speed and agility, lower operating costs, shorter time-to-market for new products and services, on-demand scalability, reduced complexity, and easy access to qualified IT talent. These advantages help financial institutions enhance their payment solutions and remain competitive.
Q: What are Cloud-Based Payments?
A: Cloud-based payments refer to payment processing systems that utilize cloud technology to handle transactions. These systems offer enhanced scalability, flexibility, and security by leveraging the infrastructure provided by cloud service providers. They allow financial institutions to manage transactions more efficiently and integrate with other digital services seamlessly.
Q: How do Cloud-Based Payments and PaaS enhance each other?
A: Cloud-based payments leverage the scalability, flexibility, and security of cloud infrastructure, making PaaS an ideal fit. By integrating cloud capabilities, PaaS providers can offer more robust and efficient payment solutions, enabling banks and financial institutions to meet the evolving demands of the digital economy.
Q: What is the Role of SaaS in PaaS?
A: SaaS plays a crucial role in implementing PaaS solutions. By leveraging SaaS, businesses can access advanced payment processing capabilities without significant upfront investment in hardware and software. SaaS-based PaaS solutions are typically subscription-based, allowing companies to scale their payment processing capabilities as needed. This model also facilitates continuous updates, easier integration with other business systems, and enhanced operational efficiency.
Q: What is PaaS in Cloud Computing?
A: A typical PaaS product in cloud computing is a combination of three main components:
- Cloud Infrastructure: This includes the OS, virtual machines, networking, storage, and firewalls, providing a secure, networked computing environment for development.
- Software: This encompasses tools required for creation, deployment, and maintenance, supporting development workflows with scaffolding, templating, and debugging components. This layer is scalable, secure, and future-proof.
- GUI: The graphical user interface allows users to view functions and interact with the PaaS platform, enabling development teams to perform their tasks efficiently.
Q: What are the types of PaaS?
A: PaaS comes in several forms to support various development processes:
- Public PaaS: Vendors offer middleware for developers to create, configure, and manage servers and databases, with shared or standalone infrastructure options.
- Private PaaS: Deployed on dedicated infrastructure managed by a company’s IT team, offering better safety, compliance, and customization.
- Hybrid PaaS: Combines public and private PaaS, allowing companies to deploy clouds based on security and access needs.
- Communication PaaS: Provides real-time communication capabilities like messaging, voice, and video through pre-built libraries and APIs.
- Mobile PaaS: Delivers backend capabilities for creating, deploying, and managing mobile applications, supporting SDKs for Android and iOS.
- Open PaaS: Open-source platforms giving users control over application building and hosting, reducing setup time and effort.




















