In today's fast-paced software development landscape, quality assurance has become the cornerstone of successful product delivery.
Companies with well-established QA processes experience 50% fewer post-release defects and achieve 30% faster time-to-market, while automated testing solutions can reduce testing time by up to 80% and deliver ROI of 300-500% within the first year.1
The question isn't whether your organization needs quality assurance – it's how effectively you can implement and optimize your QA testing process.

What is the QA Process in Software Development?
The QA process encompasses a comprehensive methodology designed to prevent defects, ensure consistent quality standards, and continuously improve product reliability throughout the entire software development lifecycle.
Modern QA methodology and tools integrate seamlessly with development workflows, creating a collaborative environment where QA professionals work alongside developers from project inception through final deployment.
Importance of Quality Assurance in Software Development
Quality assurance serves as the foundation of successful software development, directly impacting user satisfaction, business reputation, and long-term product viability.
Without systematic QA processes, organizations face increased support costs, customer churn, and potential security vulnerabilities that can damage brand trust.
Research consistently demonstrates that defects become exponentially more expensive to fix as they progress through the development lifecycle, with production fixes typically costing up to 30 times more than catching issues during initial development phases.2 These costs stem from the additional overhead of production debugging, emergency patches, customer support, potential downtime, and reputation management required when issues reach end users.
Additionally, robust quality assurance practices enable faster development cycles by catching issues early, reducing debugging time, and creating more stable codebases that support rapid feature deployment.
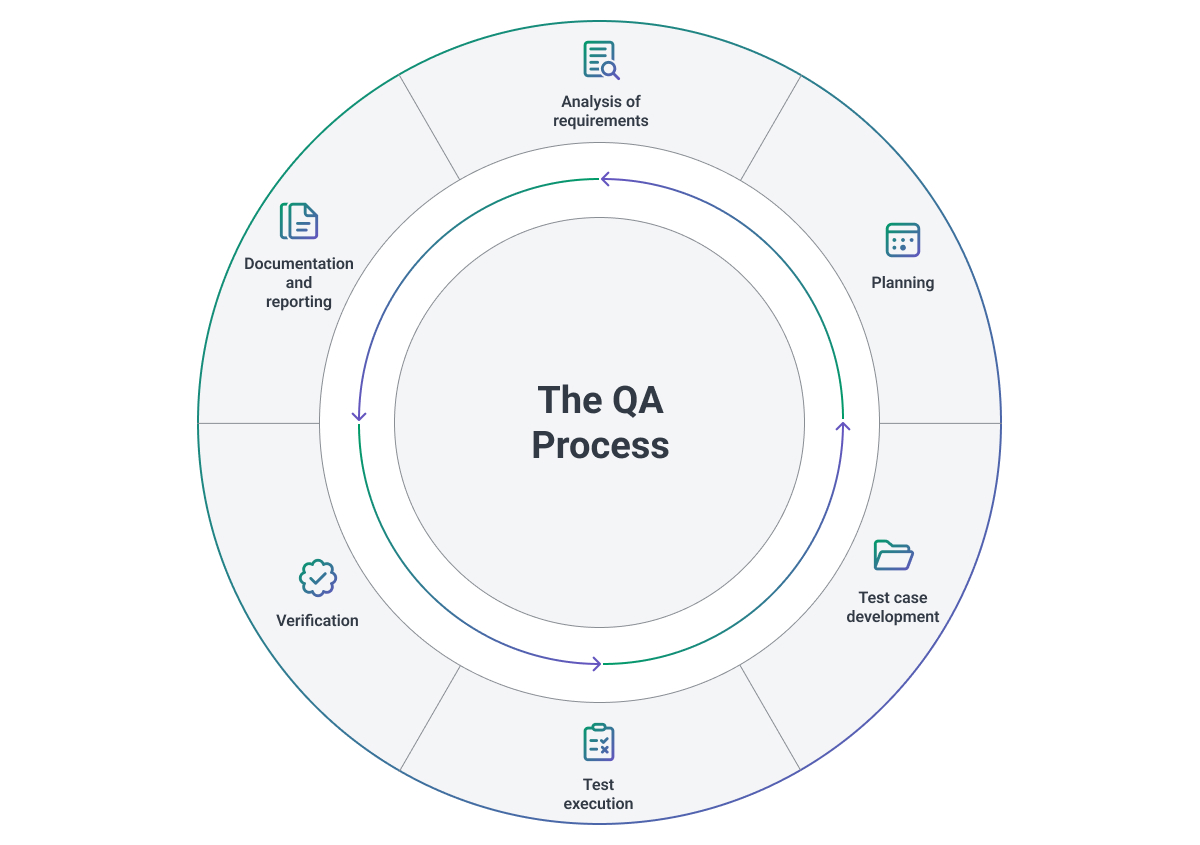
The Impact of QA on Project Management
Quality assurance significantly influences project management outcomes across multiple dimensions, from timeline adherence to resource optimization and stakeholder satisfaction. Effective QA integration transforms project management from reactive problem-solving to proactive risk mitigation.
Timeline and Schedule Impact:
- Early defect detection reduces late-stage rework and delays
- Parallel testing activities accelerate overall delivery timelines
- Predictable QA workflows enable more accurate project forecasting
- Continuous testing prevents last-minute quality bottlenecks
Resource Allocation Optimization: QA teams help project managers optimize resource utilization by identifying high-risk areas that require additional attention while streamlining testing efforts for stable functionality. This strategic approach prevents over-allocation to low-risk areas while ensuring critical components receive adequate validation coverage.
Stakeholder Communication Enhancement: Quality metrics and testing progress provide objective data for stakeholder reporting, replacing subjective quality assessments with measurable indicators. Regular QA status updates enable informed decision-making about release readiness, feature prioritization, and risk acceptance levels.
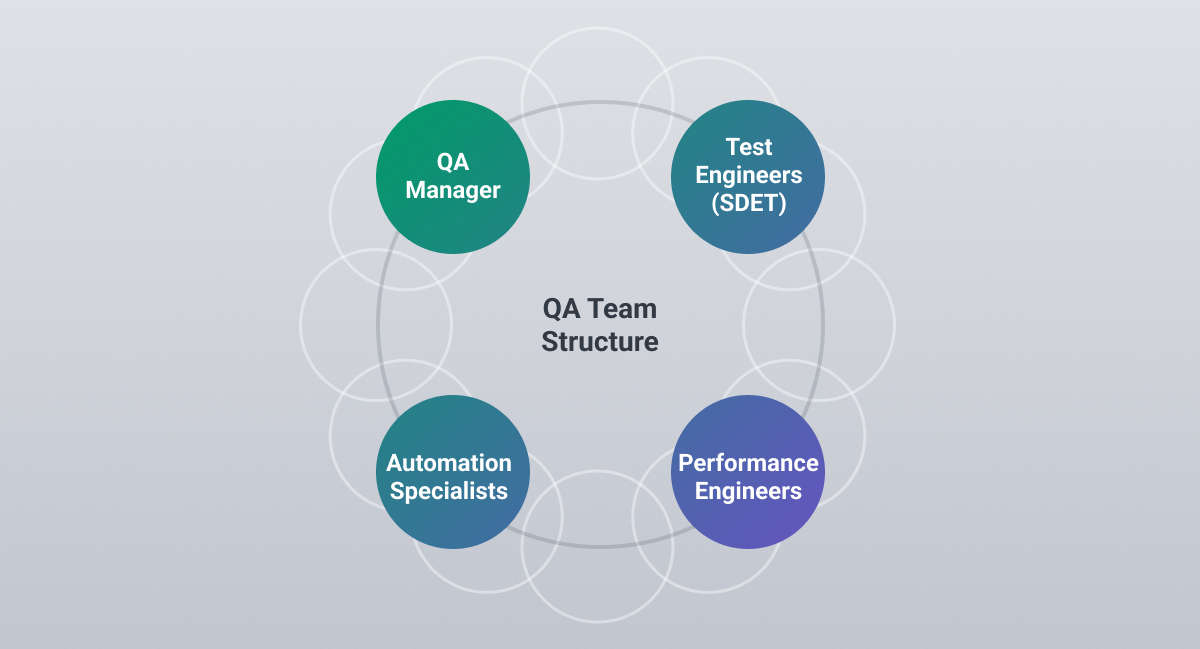
What are the Responsibilities and Roles of the Quality Assurance Team?
QA teams shoulder diverse responsibilities that extend beyond traditional testing activities to encompass quality advocacy, process improvement, and strategic planning.
Quality Planning and Strategy
- Develop comprehensive test strategies and plans
- Define quality standards and acceptance criteria
- Assess project risks and establish mitigation strategies
- Select appropriate testing tools and methodologies
Test Design and Execution
- Create detailed test cases and test scenarios
- Execute manual testing for complex user workflows
- Develop and maintain automated test suites
- Perform exploratory testing to discover edge cases
Defect Management
- Identify, document, and track software defects
- Collaborate with developers on defect resolution
- Verify bug fixes and conduct regression testing
- Analyze defect patterns for process improvement
Quality Advocacy and Communication
- Report quality status to project stakeholders
- Facilitate QA sign off processes for releases
- Provide quality-related guidance to development teams
- Champion quality best practices across the organization
Process Improvement
- Monitor and analyze QA process effectiveness
- Implement continuous improvement initiatives
- Evaluate and recommend new testing tools and techniques
- Conduct retrospectives and lessons learned sessions
The QA team's meaning has evolved to encompass responsibility for establishing quality standards, implementing best practices, and fostering a culture of quality throughout the organization.
This expanded role requires diverse skills and collaborative approaches that integrate seamlessly with modern development practices.
Key Roles Involved in the QA Process:
QA Manager
- Coordinates quality initiatives across projects
- Establishes QA best practices and standards
- Manages resource allocation and team development
- Execute manual testing and exploratory testing
- Design test cases and validate functionality
- Perform user acceptance testing coordination
Automation Specialists
- Develop and maintain automated test suites
- Implement continuous integration testing
- Optimize automation testing tools and frameworks
Performance Engineers
- Conduct load testing and stress testing
- Monitor application performance metrics
- Identify scalability bottlenecks
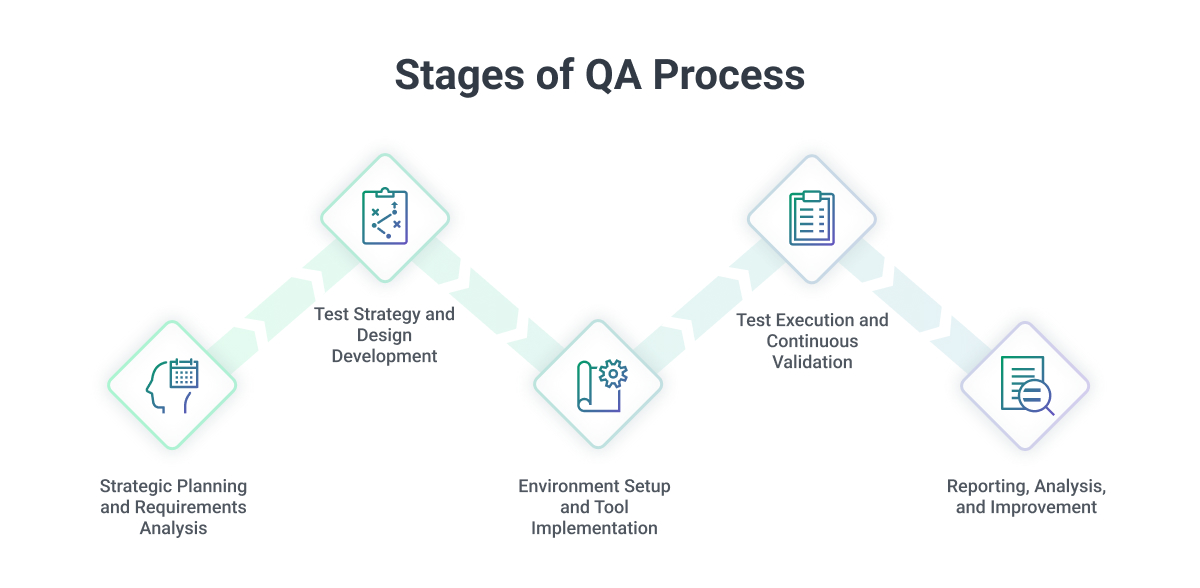
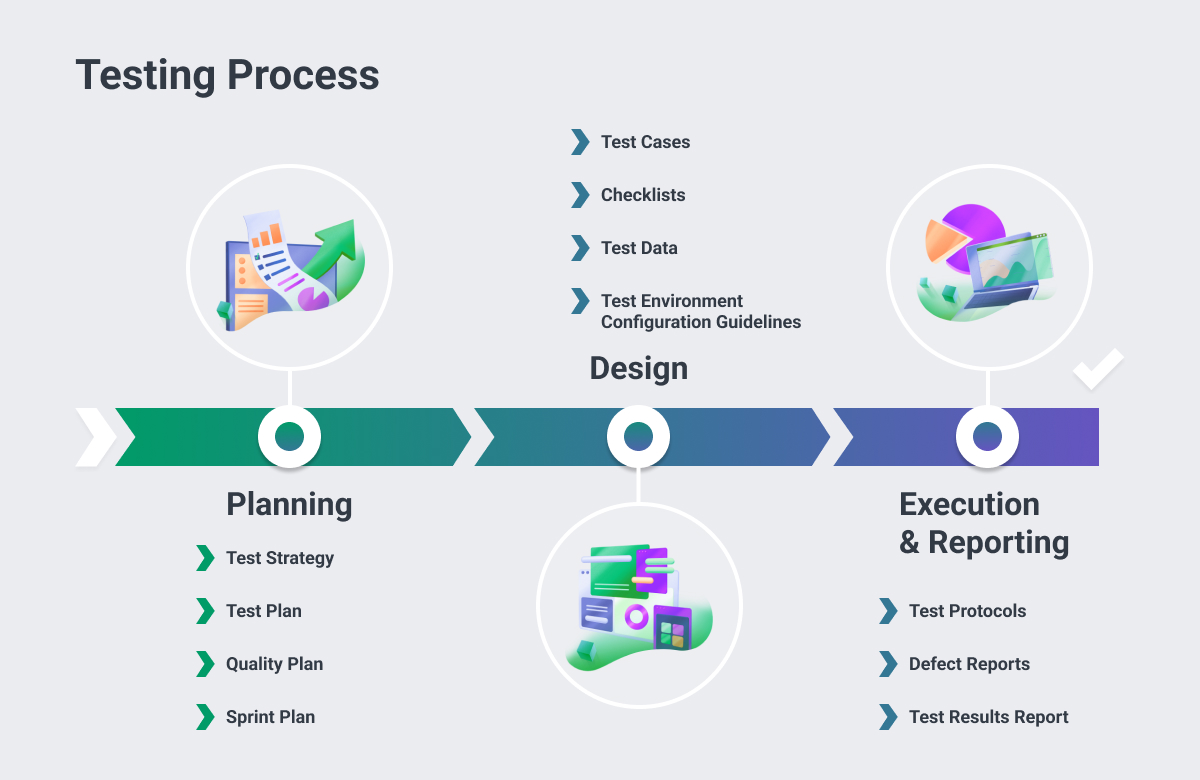
Quality Assurance Process Steps: Your Complete Framework
Understanding the Stages of the QA Process
The quality assurance process follows a structured progression of interconnected stages that build upon each other to ensure comprehensive product validation.
Step 1: Strategic Planning and Requirements Analysis
QA begins with understanding project goals, defining quality standards, and identifying high-risk areas to focus resources effectively.
Activities:
- Review business requirements and user stories
- Define acceptance criteria and success metrics
- Choose appropriate tools and QA methodology
- Identify quality risks early
Step 2: Test Strategy and Design Development
Develop scalable, reusable testing strategies aligned with project goals and timelines.
Deliverables:
- Test strategy documents
- Test case libraries and templates
- Automation framework planning
- Tool integration scope
Step 3: Environment Setup and Tool Implementation
Set up a reliable infrastructure that mirrors production conditions and supports efficient testing.
Requirements:
- Cloud-based or containerized environments
- Automated deployment and rollback pipelines
- Performance monitoring tools
Step 4: Test Execution and Continuous Validation
Execute manual and automated test suites with continuous feedback loops to catch issues early.
Focus Areas:
- Regression and exploratory testing
- Integration and performance testing
- Security and API testing
Step 5: Reporting, Analysis, and Improvement
Collect data, evaluate effectiveness, and refine QA practices.
Key Outputs:
- Quality dashboards and test reports
- Bug pattern analysis
- Lessons learned
- Plans for improving future cycles
By mastering each step, QA teams can reduce bottlenecks and build quality directly into the development lifecycle.

Agile QA Process: Transforming Quality for Modern Development
What is the Role of Quality Assurance in Agile Methodologies?
The QA process in agile environments requires fundamental changes to traditional quality assurance approaches. Instead of discrete testing phases that occur after development completion, agile QA processes emphasize continuous testing activities that run parallel to development work.
The adoption of agile methodologies has become widespread across the industry, with 68% of companies having implemented some form of Agile approach in their development processes.2 This widespread adoption reflects the proven effectiveness of agile QA processes in delivering faster, more responsive software development cycles while maintaining quality standards.
Agile QA methodologies focus on collaboration, flexibility, and rapid feedback loops. QA professionals work closely with developers throughout each sprint, providing immediate feedback on quality issues and participating in daily standups, planning sessions, and retrospectives.
Agile QA Characteristics:
- Continuous collaboration between QA and development teams
- Rapid feedback loops throughout sprint cycles
- Flexible test planning that adapts to changing requirements
- Integrated quality validation in daily development activities
- Customer-focused quality metrics rather than internal process measures
Implementing Continuous Testing Strategies
Continuous testing represents one of the most significant advantages of modern agile QA processes. Rather than waiting for development completion, continuous testing integrates quality validation throughout the development cycle.
Benefits of Continuous Testing:
- Immediate feedback on code quality impact
- Reduced defect resolution costs and complexity
- Faster identification of integration issues
- Improved developer productivity and confidence
- Enhanced overall product stability
The implementation requires sophisticated automation strategies and robust CI/CD pipeline integration. Automated test suites run continuously as code changes are committed, providing immediate feedback while code is fresh in developers' minds.
Essential Tools for Effective QA Process
Top Automation Tools for Quality Assurance

Essential Tools for an Effective QA Process
QA today relies on a powerful ecosystem of tools that enhance speed, accuracy, and collaboration across teams. Below is a streamlined breakdown of the most impactful categories:
Test Management Tools
Help teams plan, organize, and track testing activities, manage test cases, and monitor coverage and progress.
Examples: TestRail, Zephyr, PractiTest
Automation Testing Tools
Accelerate repetitive testing and improve reliability, especially for regression and integration tests.
Examples: Selenium, Cypress, Playwright, Appium
Bug & Issue Tracking Tools
Enable teams to log, track, and resolve defects throughout the testing lifecycle.
Examples: Jira, Bugzilla
Performance Testing Tools
Validate scalability and stability under load and stress conditions.
Examples: JMeter, Gatling, LoadRunner
CI/CD & Integration Tools
Support automated testing pipelines and ensure stability with every code change.
Examples: Jenkins, CircleCI, GitHub Actions
API Testing Tools
Ensure API endpoints perform reliably and securely in every environment.
Examples: Postman, SoapUI, RestAssured
Cloud & Infrastructure Testing Tools
Provide scalable, cross-device environments and parallel execution to reduce test cycle times.
Examples: BrowserStack, Sauce Labs, AWS Device Farm
Choosing the right toolset depends on your QA team’s goals, technical expertise, and integration requirements. A well-integrated QA toolchain can streamline workflows, reduce errors, and accelerate releases.
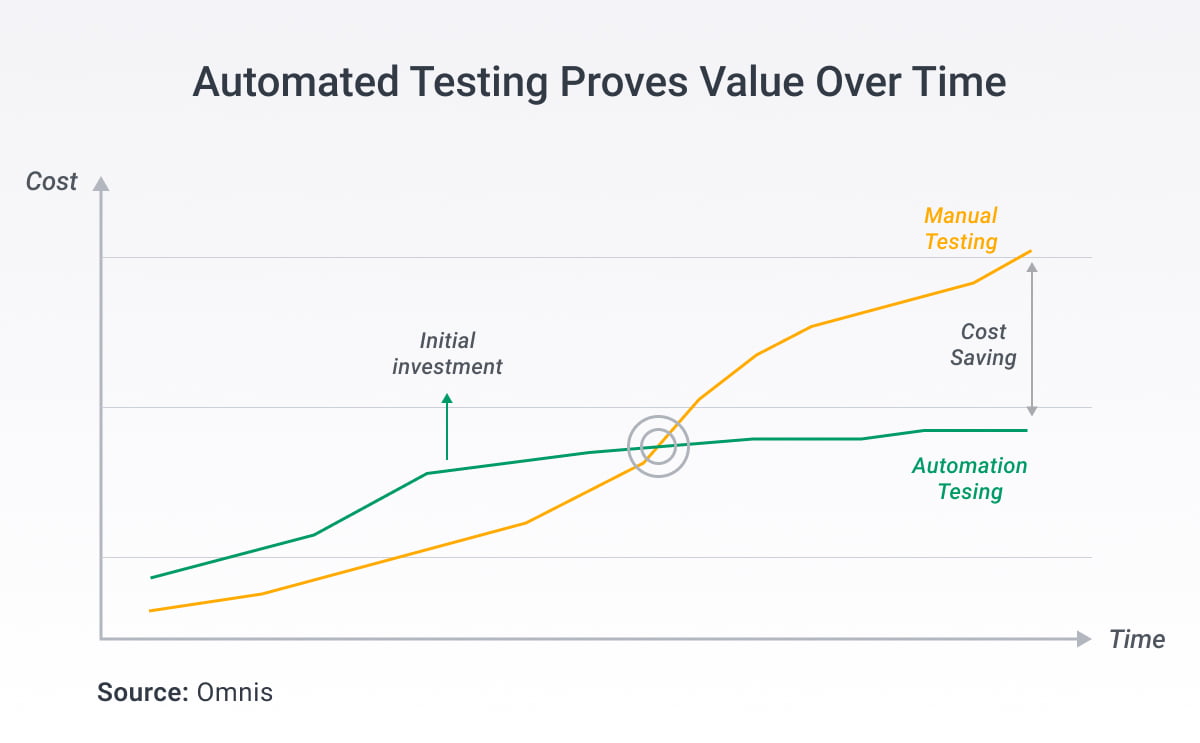
Automation vs. Manual Testing: Finding the Right Balance
Understanding Complementary Testing Approaches
If you’re wondering whether automated or manual testing is better, you might be asking the wrong question. Both approaches serve essential but different purposes within comprehensive QA processes.
Automation Excels At:
- Regression testing for stable functionality
- Repetitive test case execution
- Performance and load testing scenarios
- API testing and integration validation
- Continuous integration feedback
Manual Testing is Essential For:
- Exploratory testing and edge case discovery
- Usability validation and user experience testing
- Complex scenario verification requiring human judgment
- Ad-hoc testing based on real user behavior
- Initial feature validation before automation investment
Modern QA best practices leverage both approaches strategically, with automation handling predictable scenarios while freeing human testers for high-value activities requiring creativity and critical thinking.
Strategic Automation Implementation
Effective automation strategies focus on high-return scenarios while minimizing maintenance overhead.
Automation Priority Areas:
- Smoke Testing - Basic functionality validation
- Regression Testing - Preventing feature degradation
- API Testing - Backend service validation
- Performance Testing - Scalability and reliability validation
- Security Testing - Vulnerability scanning and validation
The development of maintainable automated test suites requires attention to framework architecture and test design principles. Well-designed frameworks emphasize reusability, modularity, and clear separation of test logic from test data.
Software QA Best Practices for Excellence
Establishing Comprehensive Quality Standards
Effective quality assurance begins with clear, well-communicated quality standards that guide all development and testing activities. These standards should address functional requirements, performance expectations, security criteria, and usability guidelines.
Quality Standards Should Address:
- Functional Requirements - Feature completeness and accuracy
- Performance Expectations - Response times and scalability targets
- Security Criteria - Vulnerability prevention and data protection
- Usability Guidelines - User experience and accessibility standards
- Reliability Metrics - Uptime requirements and error rates
Quality standards must be both aspirational and achievable. The key lies in finding the right balance that challenges teams to excel while remaining practical and attainable.
Regular review and updating of quality standards ensures they remain relevant as technology, customer expectations, and business requirements evolve. This ongoing refinement process should involve input from development teams, QA professionals, and business stakeholders to ensure that standards continue to support both quality objectives and business goals.
Optimizing Test Coverage and Efficiency
Achieving comprehensive coverage while maintaining efficiency requires strategic risk-based approaches.
Teams must identify the most critical areas of their applications and ensure these receive thorough testing attention while avoiding over-testing of low-risk functionality. This risk-based approach to testing enables teams to maximize quality outcomes while optimizing resource utilization.
The integration of manual testing and automated testing approaches plays a crucial role in coverage optimization. Automated tests excel at providing rapid feedback on core functionality and regression scenarios, while manual testing is essential for usability validation, exploratory testing, and complex scenario verification.
The most effective QA processes leverage both approaches strategically to achieve comprehensive coverage efficiently.
Coverage Optimization Strategies:
- Critical Path Testing - Focus on core user workflows
- Boundary Value Analysis - Test edge cases and limits
- Equivalence Partitioning - Group similar test scenarios
- Risk-Based Prioritization - Allocate resources based on impact
- Exploratory Testing - Discover unexpected issues through investigation
Test data management has emerged as a critical efficiency factor. Teams investing in robust test data strategies execute tests faster, achieve better coverage, and maintain reliable results.
![10_Tips_for_a_Successful_QA_Strategy.jpg]()
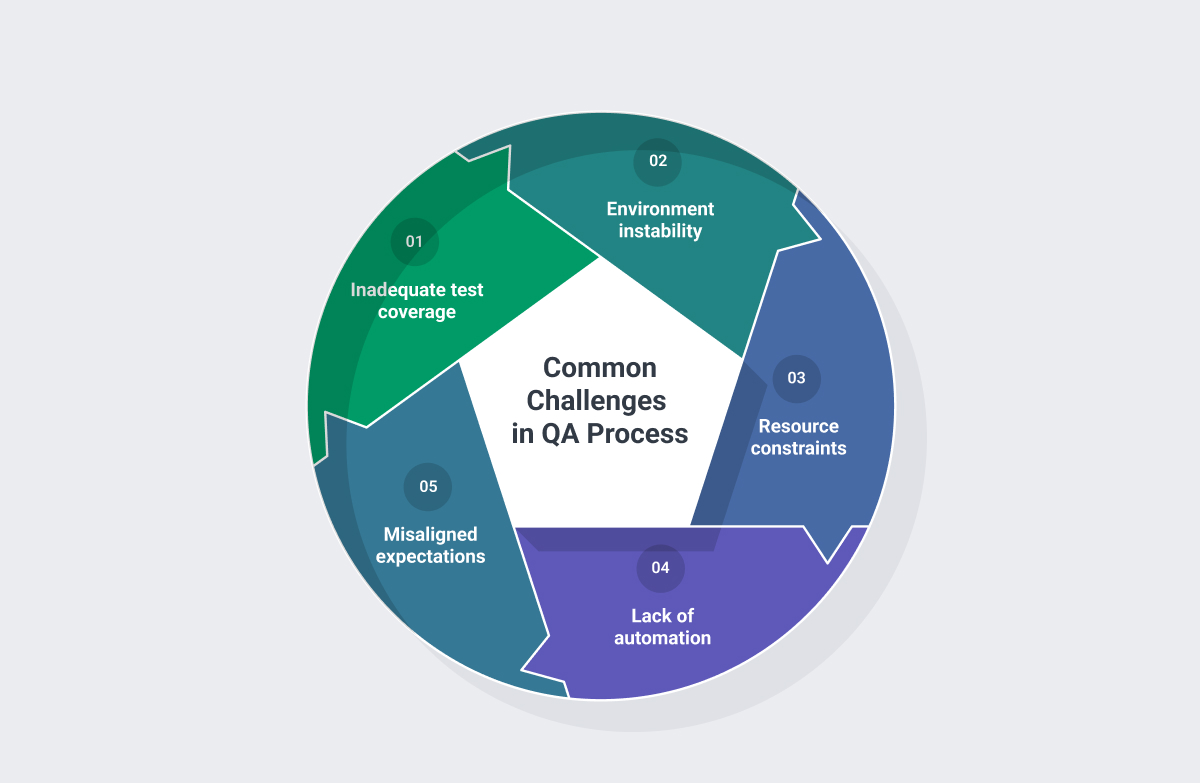
Common Challenges in QA Process and Solutions
Addressing Risks in Quality Assurance
Even strong QA processes face risks that can derail timelines or compromise quality. Addressing these proactively can make the difference between smooth releases and costly post-launch fixes.
- Inadequate Test Coverage
Challenge: Not all high-risk areas are tested, especially under time pressure.
Solution: Use risk-based prioritization and critical-path analysis to focus resources where they’ll make the biggest impact. Automate stable areas to free testers for exploratory scenarios.
- Poor Communication Between Devs and QA
Challenge: Misaligned expectations and unclear feedback loops lead to late-stage issues.
Solution: Embed QA in daily standups, backlog grooming, and retros. Use shared dashboards to align progress and highlight blockers in real-time.
Incorporating User Feedback into Agile QA
Agile QA doesn’t rely only on automated tests and CI/CD pipelines. Real users often surface edge cases that internal testing environments miss, so mature Agile teams incorporate customer support channels into their quality workflows.
Support platforms such as Zendesk allow support teams to route user-reported defects and usability issues directly into engineering backlogs. When connected to sprint planning and triage processes, these tickets act as an additional quality signal alongside automated testing and QA validation.
Including support feedback in the QA cycle helps teams identify recurring production issues, prioritize fixes, and validate improvements based on real user experience rather than only pre-release testing.
- Unstable or Misconfigured Test Environments
Challenge: Bugs caused by the test setup—not the code—waste valuable time.
Solution: Use Infrastructure as Code (IaC) and containerization to ensure test environments mirror production. Automate setup and teardown for reliability and consistency.
- Testing Backlogs
Challenge: Features are delivered faster than they can be fully tested.
Solution: Implement incremental testing and triage backlogs by business impact. Use automation for regression to keep pace with new code.
Quality Assurance Documentation and Process Management
Managing Documentation and Reporting Effectively
Effective QA documentation serves multiple critical functions within the software development process. Beyond simply recording test cases and procedures, comprehensive QA documentation creates institutional knowledge, supports process consistency, and enables effective knowledge transfer between team members.
The key lies in creating documentation that provides value without becoming a burden that slows development progress.
Modern Documentation Approaches:
- Automated Test Reports - Generated from test execution results
- Dashboard Visualizations - Real-time quality metrics and trends
- Integrated Wiki Systems - Living documentation that updates automatically
- Video Documentation - Screen recordings for complex test procedures
- API Documentation - Auto-generated from code annotations
The structure of QA documentation should support both immediate operational needs and long-term knowledge management objectives.
Implementing Effective QA Sign-Off Processes
The QA sign off process represents a critical control point that ensures quality standards are met before product releases. However, traditional sign-off processes often create bottlenecks that slow delivery without adding significant value. Modern QA sign off procedures focus on risk-based assessments that provide meaningful quality validation while supporting rapid delivery cycles.

Best Practices for Testing Backlog Management
Testing backlogs accumulate when activities fall behind development velocity or requirements emerge faster than testing capacity allows.
Backlog Management Strategies:
- Priority-Based Triage - Focus on highest-risk, highest-value areas
- Capacity Planning - Align testing resources with development velocity
- Incremental Testing - Break large features into testable components
- Automated Regression - Reduce manual testing overhead for stable features
- Risk Assessment - Defer lower-priority activities when necessary
By assessing the business impact and technical risk associated with different features or components, teams can allocate testing resources more effectively while ensuring that critical functionality receives appropriate attention.
Metrics to Measure QA Process Success
Key Performance Indicators for Quality Excellence
Measuring QA process effectiveness requires a balanced scorecard approach that considers quality outcomes, process efficiency, and business impact.
These metrics help teams understand whether their QA efforts translate into positive customer experiences and business outcomes. Tracking these metrics over time enables teams to identify trends and measure the impact of process improvements.
Quality Outcome Metrics:
- Defect Density - Defects per lines of code or functionality
- Defect Escape Rate - Production defects not caught during testing
- Customer Satisfaction Scores - End-user quality perception
- Mean Time to Resolution - Speed of defect fixing
- Test Coverage Percentage - Code and functionality coverage levels
Process Efficiency Metrics:
- Test Execution Velocity - Tests completed per time period
- Automation Coverage Ratio - Percentage of automated versus manual tests
- Environment Uptime - Testing infrastructure reliability
- Resource Utilization - QA team productivity and capacity usage
- Cycle Time - Time from development completion to QA sign off
Business Impact Metrics:
- Time to Market - Release velocity and deployment frequency
- Support Ticket Volume - Quality-related customer issues
- Revenue Impact - Quality issues affecting business outcomes
- Customer Retention - Quality correlation with customer loyalty
Strategies for Enhancing QA Team Performance
High-performing QA teams share common characteristics that enable them to deliver exceptional quality outcomes while supporting rapid development cycles.
Performance Enhancement Factors:
- Cross-functional Collaboration - Seamless integration with development teams
- Continuous Learning - Ongoing skill development and technology adoption
- Process Improvement Focus - Regular retrospectives and optimization
- Customer Value Orientation - Quality decisions based on user impact
- Tool Mastery - Effective utilization of QA methodology and tools
Building these characteristics requires intentional investment in team development and supportive organizational cultures that value quality excellence.
Real-World QA Success Stories
Real-world implementation of comprehensive QA processes demonstrates significant business impact across various industries and project types. These examples illustrate how strategic quality assurance initiatives translate into measurable business outcomes.
Building an Automated QA Process for Tribal Credit’s Fintech Platform
Tribal Credit engaged Softjourn to design and implement comprehensive manual and automated QA processes for both their legacy 1.0 system and new 2.0 platform. We established high-level automation strategies, optimized regression testing, and implemented CI/CD pipelines. The result: a fully structured QA process that accelerated releases, improved platform stability, and provided better monitoring and test coverage moving forward.
Performance Testing for a Global Expense Management Platform
Softjourn’s QA team partnered with a leading expense management and AP automation provider to identify and resolve system performance bottlenecks. We focused on API and web service load testing to ensure the platform could scale with new features and growing user demand. As a result, the client improved response times, system stability, and end-user satisfaction across both web and mobile apps.
Expanding QA Capabilities with SDETs for an Expense Management Client
To support code quality at scale, Softjourn helped an expense management platform integrate SDETs. This blend of development and testing expertise accelerated release cycles and improved code coverage. The result was a more agile QA process aligned with DevOps.
Ensuring App Store Readiness for a Ticketing Client’s iOS Access Control App
A US-based ticketing platform engaged Softjourn to help update and test their iOS access control app for compatibility with the latest iOS version. We conducted targeted regression testing, identified critical bugs, and provided expert development support to ensure the app met App Store requirements.
QA Validation for Spektrix’s Apple & Google Wallet Ticket Integration
Spektrix partnered with Softjourn to build seamless Apple and Google Wallet integration into their ticketing platform. Our QA team ensured compliance with platform-specific guidelines, tested cross-device compatibility, and validated the user experience across iOS and Android. The result was a fast, intuitive feature that enhanced their digital ticketing platform.
Future-Proofing Your QA Process
Emerging Technologies and QA Evolution
The field of quality assurance continues to evolve rapidly as new technologies and approaches emerge. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are beginning to transform QA processes through intelligent test generation, automated defect prediction, and smart test optimization.
These technologies promise to significantly enhance QA effectiveness while reducing manual effort requirements.
Cloud computing and containerization technologies are also reshaping QA processes by enabling more flexible, scalable testing approaches. Teams can now provision test environments on demand, run tests at massive scale, and integrate testing activities more seamlessly into development workflows. These technological advances support more comprehensive testing while reducing infrastructure costs and complexity.
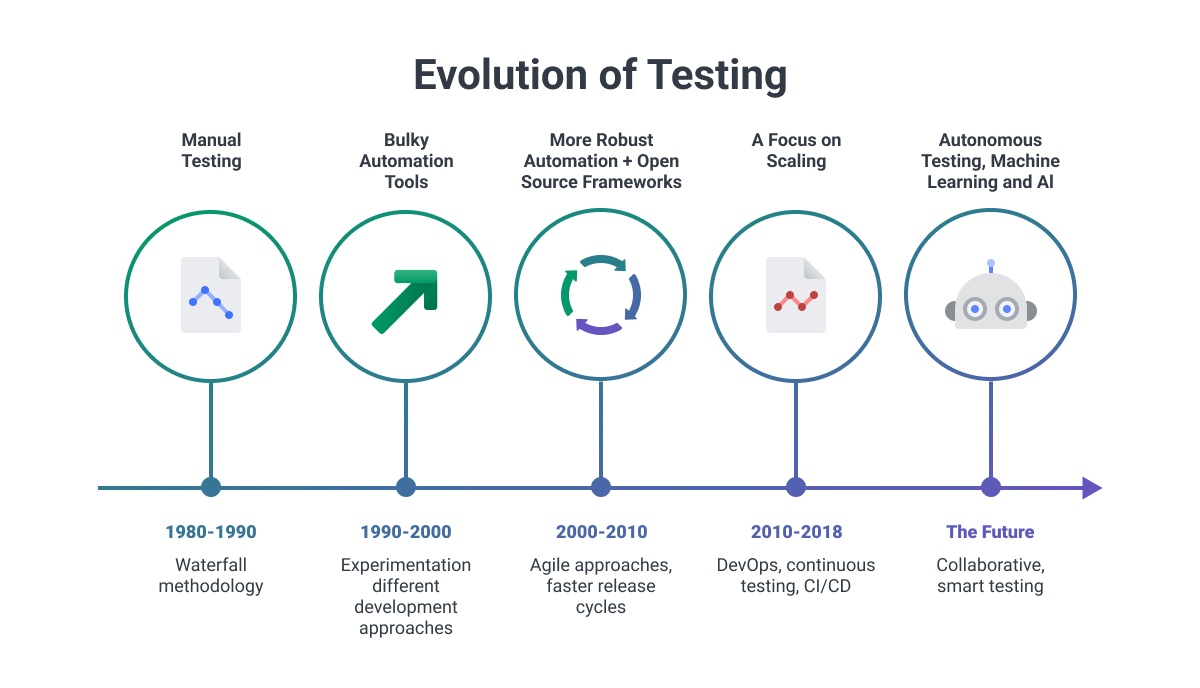
Transformative Technologies:
- Artificial Intelligence - Intelligent test generation and defect prediction
- Machine Learning - Smart test optimization and pattern recognition
- Cloud Computing - Scalable testing infrastructure and environments
- Containerization - Consistent testing environments and rapid provisioning
- DevSecOps Integration - Security testing embedded throughout development
These technological advances support more comprehensive testing while reducing infrastructure costs and complexity.

Building Your QA Excellence Foundation
The transformation of quality assurance from a final checkpoint to a strategic enabler represents one of the most significant shifts in modern software development. Organizations that embrace comprehensive QA processes don't just reduce defects—they accelerate delivery, improve customer satisfaction, and build sustainable competitive advantages in increasingly quality-conscious markets.
Your QA Excellence Roadmap:
Success in quality assurance requires commitment to continuous improvement, strategic thinking, and adaptive capabilities that evolve with changing technology landscapes. The frameworks, practices, and strategies outlined in this guide provide your foundation for building QA processes that meet today's challenges while preparing for tomorrow's opportunities.
Immediate Next Steps:
- Assess your current QA process maturity using the frameworks provided
- Identify the highest-impact improvement opportunities for your team
- Implement measurement systems that track both quality outcomes and business impact
- Invest in team development and tool capabilities that support long-term success
Long-term Vision: The future of quality assurance lies in intelligent automation, predictive quality analytics, and seamless integration with business objectives. Organizations that begin this journey today position themselves for sustained success as customer expectations and technological capabilities continue to evolve.
Quality assurance excellence isn't achieved overnight—it's built through consistent application of proven practices, continuous learning, and unwavering commitment to customer value. The investment you make in QA process improvement today pays dividends through reduced support costs, improved customer loyalty, and faster time-to-market for future innovations.
Ready to transform your QA process? The principles and practices outlined in this guide provide your roadmap to quality excellence. Start with assessment, implement systematically, measure continuously, and adapt confidently as your organization grows and evolves.
Frequently Asked Questions About QA Processes
What does QA stand for?
QA stands for Quality Assurance, representing a systematic approach to preventing defects and ensuring software products meet specified quality standards throughout the development lifecycle.
What is the first step of QA?
The first step of quality assurance involves strategic planning and requirements analysis, where QA teams establish clear understanding of project objectives, quality standards, and success criteria before development begins.
What is the difference between QA and testing?
QA focuses on preventing defects through process improvement and quality standards implementation, while testing involves executing specific validation activities to identify existing defects. QA is process-oriented; testing is product-oriented.
How long does the QA process take?
QA process duration varies based on project complexity, team size, and quality requirements. Agile QA processes integrate continuously with development cycles, while traditional approaches may require 20-30% of total project timeline for comprehensive testing activities.
What skills do QA professionals need?
Modern QA professionals require technical skills (automation tools, programming, databases), analytical abilities (problem-solving, attention to detail), communication skills (stakeholder interaction, documentation), and business acumen (understanding user needs, risk assessment).
What is the QA process in Agile?
The QA process in Agile is a systematic approach to quality assurance that integrates testing into the development lifecycle. It involves continuous testing and feedback loops to ensure that the product meets quality standards throughout the development process.
How does quality assurance testing differ from quality control?
Quality assurance testing focuses on preventing defects through a structured process and methodologies, while quality control is about identifying defects in the finished product. Both are essential parts of the QA process.
What are the key steps to validate the effectiveness of the QA process?
To validate the effectiveness of the QA process, you can use KPIs, conduct regular reviews, implement checklists, and gather feedback from the quality assurance testing team. This helps ensure that the process meets its objectives.
How can implementing a QA process help in early stages of development?
Implementing a QA process in the early stages of development allows the QA team to identify potential issues before they escalate, ensuring that quality is built into the product from the ground up. This proactive approach can save time and resources later in the project.
What is the role of QA engineers in the QA process?
QA engineers play a critical role in the QA process by designing test cases, executing tests, and analyzing results. They ensure that the product meets quality standards and provide valuable feedback for continuous improvement.
What elements are essential for a robust quality assurance process?
A robust quality assurance process includes a clear methodology, defined roles and responsibilities, effective communication, comprehensive test cases, and regular reviews. These elements help ensure the effectiveness of the QA process.
What is the importance of assurance testing in the QA process?
Assurance testing is crucial in the QA process as it verifies that the product meets specified requirements and functions as intended. It provides confidence to stakeholders that the product is ready for release.
How does the QA process help identify risks?
The QA process helps identify risks by conducting thorough testing and analysis at various stages of development. This early identification allows the QA team to implement controls to mitigate potential issues before they affect the final product.
What practices can enhance the effectiveness of the QA process?
To enhance the effectiveness of the QA process, teams can adopt best practices such as continuous integration, automated testing, regular training for QA engineers, and effective communication between development and QA teams. These practices ensure a more efficient and effective quality assurance process.