C# vs Java is a classic comparison in software development. Both are mature, object-oriented languages with huge ecosystems, excellent tooling, and decades of production use.
Understanding the key differences, pros, and cons of C# vs Java is crucial for companies and teams to make informed decisions about which language to use for their projects.
This article provides a comprehensive comparison of these two languages, highlighting their similarities and differences, and offering insights into their suitability for various software development scenarios.
Introduction to C# and Java
Overview of C#

C#, (pronounced "C sharp") is a modern, object-oriented programming language developed by Microsoft in 2000 as part of its .NET initiative.
Known for its close integration with the Windows operating system, C# is widely used for desktop, web, and mobile applications, especially within the Microsoft ecosystem (Windows, Azure, Office, SQL Server).
While initially Windows-exclusive, C# has evolved into a cross-platform language with .NET Core. This programming language's versatility and efficiency make it a top choice for developers working on enterprise and game development.
One of the key features of C# is versioning, ensuring that programs and libraries can evolve without becoming incompatible.
Overview of Java

Java is a versatile, high-level programming language created by Sun Microsystems in 1995 and now maintained by Oracle.
Known for its "write once, run anywhere" philosophy, Java operates on the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), allowing it to run seamlessly across various platforms.
This programming language is widely used in web, enterprise, and mobile application development, especially for large-scale systems. Java has become one of the most used languages globally.
Originally created to be a small, reliable, portable, real-time operating platform, Java now offers the most reliable solutions for large enterprise backends, mobile apps, big data applications, cloud computing, and IoT development.
With over 90% of Fortune 500 companies employing Java, and consistently ranking among the top ten most popular programming languages in the world, Java is going stronger than ever in 2025.
Java has evolved steadily, and the ecosystem is one of the largest in tech (Spring, Jakarta EE, Maven/Gradle, and a massive open-source community).
Softjourn's Senior Java engineer, Orest Guziy, said that Java has been gaining popularity ever since it changed its release processes to every 6 months.
Popularity of C# and Java Programming Languages
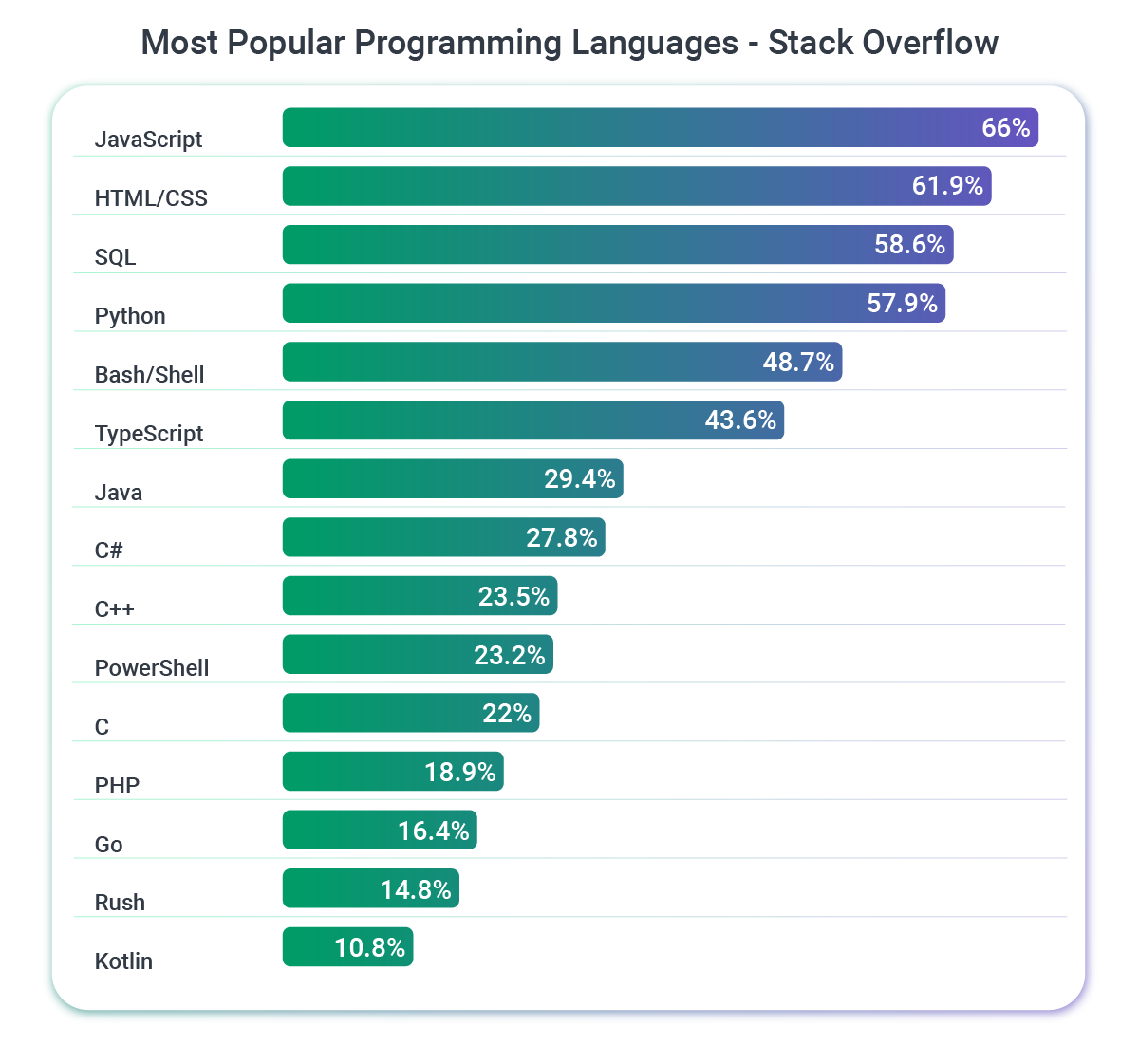
According to the Stack Overflow 2025 Developer Survey, Java ranks 7th among the most popular programming languages, with C# close behind in 8th place. GitHub’s 2025 State of the Octoverse report tells a similar story, placing Java 4th and C# 5th.
Across most major developer surveys, the two languages remain in a near tie for popularity, reflecting their enduring relevance and broad adoption across industries.
Main Differences Between C# and Java
Syntax Differences
C# and Java share a similar syntax, which makes it easier for developers familiar with one language to adapt to the other.
However, there are also key differences. C# includes advanced features that can simplify complex coding tasks, making web and enterprise development more efficient.
C# is known to have a simpler syntax than Java and is also considered to have a more robust type system, making it easier to write efficient code. C# syntax is similar to the C family of languages and offers improved object-oriented programming support.
With its clean and straightforward syntax, Java is often preferred for larger projects that require easy-to-maintain code. Java's structure is particularly appealing to developers focused on readability and scalability, especially in large codebases.
Platforms and Ecosystems
Java’s JVM makes it platform-agnostic by default, which is why Java vs C sharp often tilts to Java for multi-OS enterprise backends and large distributed systems. Spring Boot, Hibernate, and the broader Java ecosystem offer batteries-included building blocks for microservices and cloud apps.
C# is deeply productive in the .NET world. ASP.NET Core is a fast, modern web framework; Entity Framework Core streamlines data access; Azure integrations are first-class. On the client side, .NET MAUI targets cross-platform apps, and Unity puts C# front-and-center in game development.
C# vs Java Performance
Performance remains essential when selecting a programming language for enterprise application development.
C# offers high performance and is optimized for the .NET framework, which makes it ideal for business-focused applications. C# also offers peak performance in Windows-based systems.
Java, known for its Java Virtual Machine, excels in multi-platform environments, providing flexibility in global projects. Java's platform stability makes it a top choice for cross-platform solutions.
C# code can compile directly into native code, while Java code is compiled into bytecode, which is then interpreted by the JVM. Due to its architecture and optimization, C# sometimes demonstrates better performance compared to Java, depending on the specific use case and environment.
Versatility in Application Development
C# excels in several areas, including Windows-based enterprise applications and game development. Java, on the other hand, leads in other domains. Both languages have a strong presence in the following:
C# offers robust libraries and a solid framework within the .NET Framework for enterprise-level applications. C# is often chosen for business application development because it provides stability, security, and scalability.
Java has become a language of choice due to its versatility and cross-platform capabilities, particularly for web application development.
Security, Reliability, and Memory Management
Both languages offer robust security features and memory safety via managed runtimes and garbage collection.
On .NET, you’ll lean on ASP.NET Core Data Protection, built-in cryptography, and role-based auth integrations.
On the JVM, you’ll pair Spring Security with proven crypto libs and container-friendly runtime setups. In either world, reliability comes from good architecture, disciplined testing, and sane GC/runtime tuning more than from the language alone.
Pros and Cons of C# vs Java
Advantages of C#
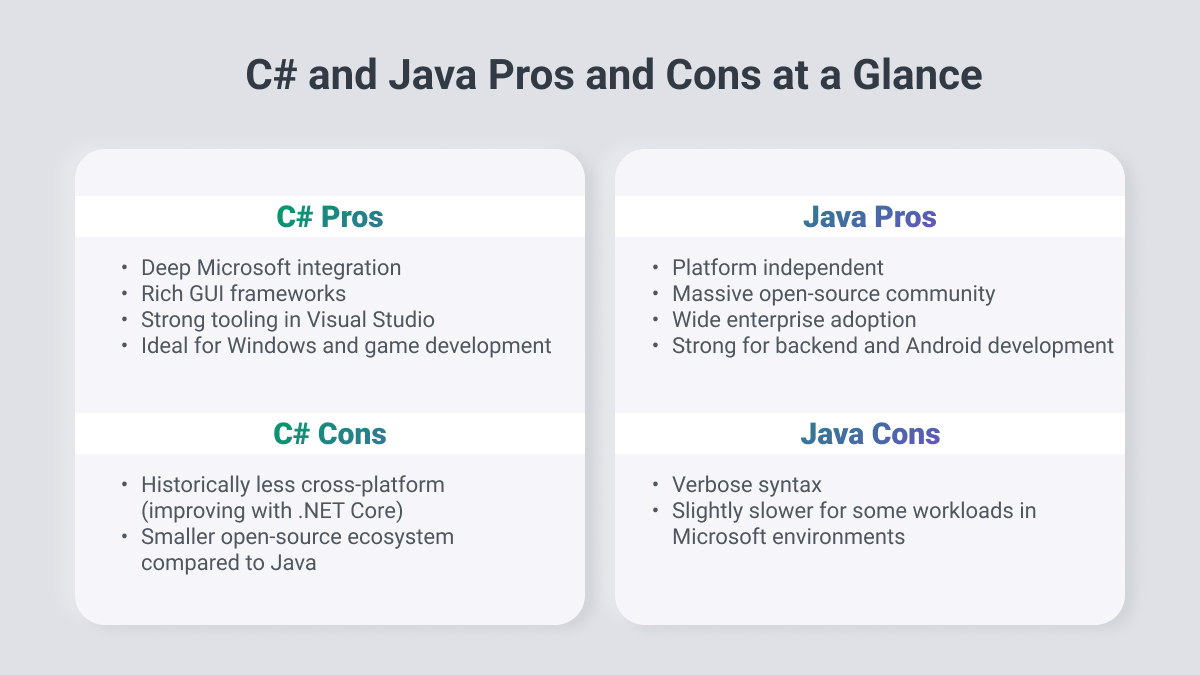
If your stack is Microsoft-heavy or if you’re building Windows clients, services on Azure, or anything in Unity, C# gives you speed of delivery, language ergonomics, and strong performance. Modern .NET is cross-platform and cloud-ready, so you’re not locked in to Windows.
C# benefits significantly from Microsoft’s continued support, offering access to cutting-edge tools, updates, and resources, making it a compelling choice for software development. This backing ensures that developers can leverage the latest advancements in the .NET framework.
As an object-oriented programming language, C# promotes efficient, flexible, and scalable code, enabling developers to create robust applications that are easier to maintain.
C# is also designed to be relatively easy to learn; even new developers can quickly grasp its core concepts. The readability of C# is also noteworthy, making it simpler to understand and debug compared to some other programming languages.

Advantages of Java
There are many advantages of Java, since it's a simple programming language, it's easy to write, compile, and debug, facilitating a smoother development process.
It offers extensive libraries and frameworks specifically for web development, including Java EE and Spring, making it a robust choice for enterprise-level applications. Additionally:
- Its object-oriented programming language nature allows developers to create modular programs and code that can be easily reused, promoting efficiency and reducing redundancy.
- Java's "write once, run anywhere" capability, enabled by the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), means it can run on any operating system, making it platform-independent.
For cross-platform enterprise backends, large distributed systems, and organizations that value portability and an enormous open-source ecosystem, Java is a safe bet. Spring accelerates common patterns, and the JVM’s maturity at scale is a big reason financial services and telecoms stick with Java.
Additionally, Java is known for its stability and offers automatic garbage collection, where stale objects are automatically removed, further simplifying memory management.

Disadvantages of C#
- Platform Bias: While .NET Core has expanded C#’s reach, it’s still most optimized for Windows environments, which may limit options if your target audience is on other operating systems.
- Licensing Costs: Some Microsoft tools and enterprise features may involve licensing fees, making it less appealing for budget-conscious teams.
- Smaller Open-Source Ecosystem: Although growing, C#’s community-driven libraries and tools are less extensive than Java’s long-established open-source base.
- Learning Curve for Non-Microsoft Developers: Developers without prior .NET experience may take longer to adapt.
Disadvantages of Java
- Performance Overhead: Java applications can have slower startup times and higher memory usage compared to some compiled languages.
- Verbose Syntax: While clear, Java code often requires more lines to accomplish tasks compared to newer languages, which can slow development.
- UI Development Limitations: Java’s native UI frameworks (like Swing) are considered outdated compared to modern options.
- Slower Evolution: Java is stable but often slower to adopt new language features compared to other modern languages.

Industry Considerations for C# and Java
In industries where data security is mission-critical, such as banking, healthcare, and government, both C# and Java are proven, trusted choices.
- C# — Backed by Microsoft’s .NET framework, C# offers layered security features that make it a natural fit for enterprise systems requiring strict compliance and secure integrations, particularly in finance, insurance, and large-scale corporate environments.
- Java — With its JVM-based security model, Java has long been favored by government agencies, global banks, and large-scale payment processors, where stability, platform independence, and advanced access controls are essential.
In consumer-facing applications, such as e-commerce, ticketing, and media platforms, both languages’ automated memory management (garbage collection) helps reduce bugs, optimize performance, and ensure a smooth user experience at scale.
For industries with fast-moving project timelines, C#’s close integration with the Microsoft ecosystem can accelerate development for Windows-based solutions, while Java’s broad platform compatibility makes it ideal for products that must run seamlessly across multiple operating systems and devices.
When to Use Java
Situations where Java stands out:
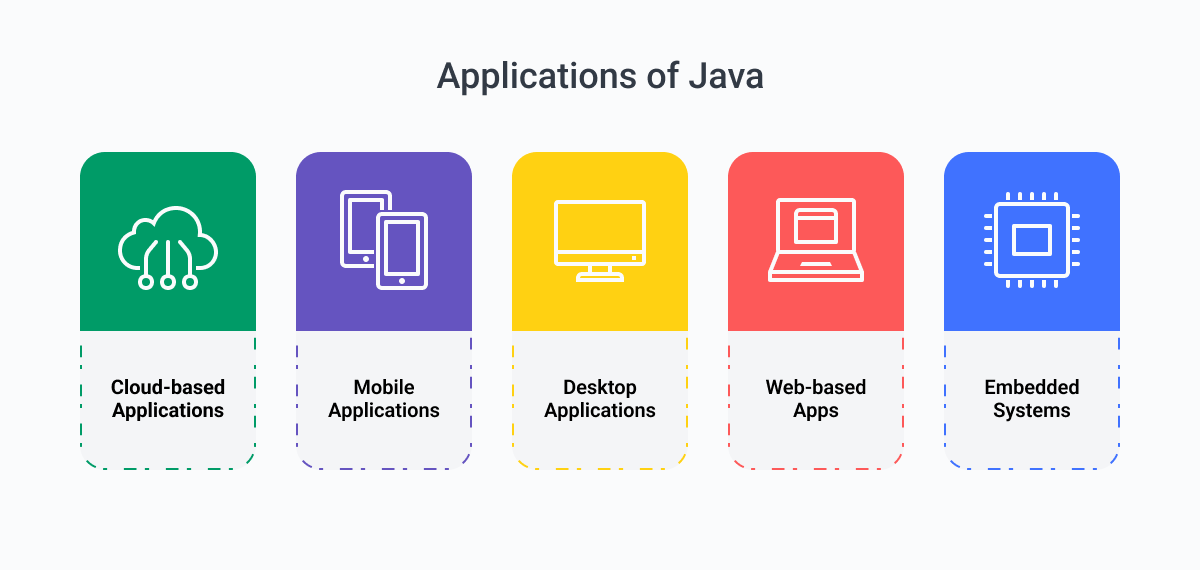
- Cross-Platform Applications: Runs reliably across multiple operating systems, ideal for reaching a wide audience with a single codebase.
- Enterprise Solutions: Frameworks like Spring and Hibernate make it a strong choice for secure, large-scale applications in finance, healthcare, and government.
- Android Development: As the original Android language, Java remains a go-to for building Android apps with Android Studio and Google’s support.
- Cloud & Web Applications: Offers robust libraries and frameworks (Java EE, Spring) for scalable, distributed cloud-based solutions.
- Long-Term, Complex Projects: Clear, structured code and a massive developer community make it easy to maintain and scale over time.
- High-Security Applications: JVM-based security and proven reliability make it trusted for banking, e-commerce, and other sensitive sectors.
When to Use C#
Scenarios where C# is the better fit:
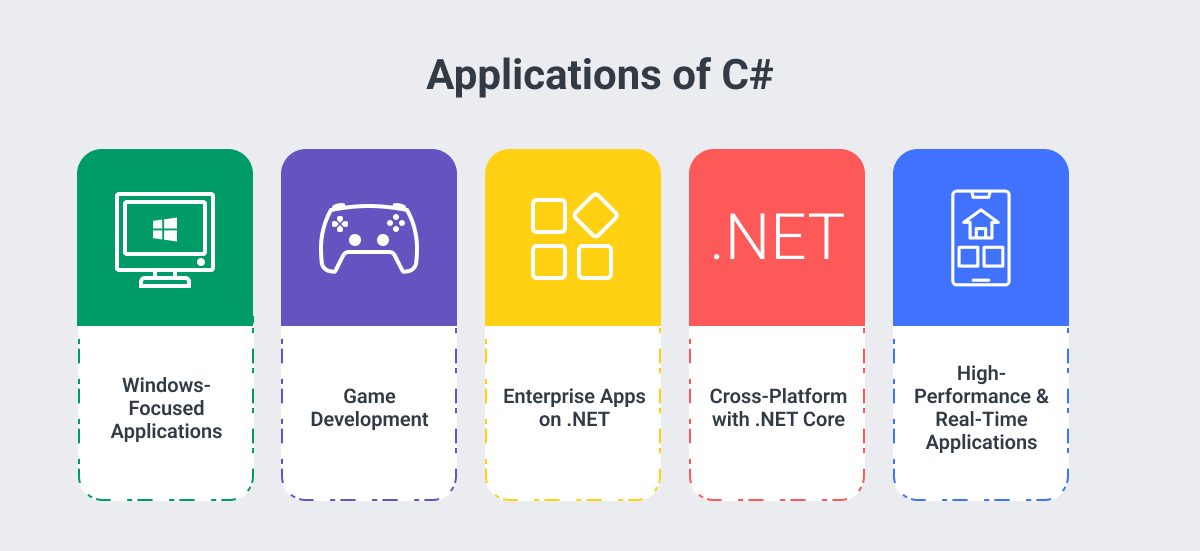
- Windows-Focused Applications: Seamless integration with Microsoft technologies for desktop, enterprise, and Azure-based solutions.
- Game Development: Primary language for Unity, enabling both indie and AAA games with high performance and cross-platform support.
- Enterprise Apps on .NET: Extensive .NET libraries provide stability, security, and scalability for business-critical systems.
- Cross-Platform with .NET Core: Build apps for Windows, Linux, and macOS without rewriting the codebase.
- Real-Time & Responsive Applications: Asynchronous programming support enables smooth, fast performance for apps requiring instant updates.
- High-Performance Desktop Software: Optimized for processing-heavy applications with complex data handling, especially in Windows environments.

C# in Action: Real-World Examples of Softjourn Clients
- Gift Card Personalization – iCARD: Used C# and Xamarin to redesign and expand iOS and Android apps, letting users create custom gift cards with photos, greetings, and automated reminders—boosting engagement and market reach.
- Festival Fan Experience – Datahove: Updated and enhanced a C# sports event app with offline access, push notifications, maps, and search—improving communication with fans and speeding feature rollouts without expanding the client’s in-house team.
- Social TV Viewing – ClipSync: Built a C# interactive platform integrated with TV.com that revived “watch together” experiences online, combining real-time chat with synchronized streaming for events and shows.

Java in Action: Real-World Examples of Softjourn Clients
- Architecture & Sustainability – FenestraPro: We developed a Java-based cloud tool that helps architects design energy-efficient facades by providing real-time guidance on daylight, thermal performance, and cost, reducing design time and supporting greener buildings.
- Fintech Migration – Tribal Credit: Maintained the client’s 1.0 system while building a fully documented, optimized 2.0 Java platform. Delivered on time, eliminated blockers, and improved database performance for a smoother transition.
- Low Code for Remote Work – Powwow Mobile: Evolved a Java-powered low-code platform over nearly a decade, enabling companies to transform legacy desktop apps into mobile-friendly tools—critical during the shift to remote work.
Choosing Between C# or Java (Practical Guidance)
In 2025, the choice between C# and Java remains a pivotal decision for developers and businesses alike, as both programming languages offer distinct advantages suited to various software development scenarios.
Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed decisions that align with project requirements and business goals. Both C# and Java are robust, versatile languages that can handle complex tasks and deliver high-quality software solutions.
The decision should be based on factors such as platform preference, integration needs, and the specific requirements of the project. Both programming languages remain relevant for software development, and developers should be familiar with them.
Keep your needs in mind when deciding on which language to use for your next project:
- Platform & Ecosystem Needs: Deep Microsoft integrations, Office/SharePoint, Windows desktop, or Unity → C#. Heterogeneous OS fleets, existing JVM infrastructure, or broad OSS library needs → Java.
- Team Skills: Lean into what your team knows—developer ramp time is real.
- Runtime Constraints: If cold starts and memory are critical, evaluate AOT options on both sides (NativeAOT vs GraalVM).
- Hiring & Community: Both have huge talent pools; availability in your region or specialty may tip the scale.

Future Trends in Software Development
C# and Java remain two of the most reliable and versatile programming languages in modern software development.
Each offers a proven track record, strong community support, and the ability to power everything from small-scale apps to global enterprise systems.
The best choice ultimately depends on your project’s requirements, technical environment, and long-term growth plans.
If you’re deciding between C# and Java, the right technology partner can guide you through the trade-offs, align the choice with your business goals, and deliver a solution that performs today and scales for tomorrow. Our team includes seasoned C# and Java developers ready to bring your next project to life.

















