Choosing the right mobile app development approach isn’t just a technical decision; it’s a strategic one that impacts your time to market, user experience, maintenance costs, and even team structure.
Understanding the differences between Native, Hybrid, Cross-Platform, and Web app development is the first step toward making an informed decision.
What Are the Differences Between Native, Hybrid, Cross-Platform, and Web Mobile App Development?
We’ll first break down the development types in simple terms before diving deeper into the intricacies of each:
Native Mobile App Development
Native apps are built specifically for a single platform (iOS or Android) using platform-specific programming languages and tools. For iOS, this means Swift or Objective-C; for Android, it’s Kotlin or Java.
- Best for: Performance-heavy apps, complex animations, or apps relying on device-specific features (like GPS, camera, or biometric sensors).
- Downside: You need to build and maintain two separate apps if targeting both platforms, which can double the effort and cost.
Hybrid Mobile App Development
Hybrid apps are built using web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, then wrapped in a native container using frameworks such as Apache Cordova or Ionic.
- Best for: Simple apps that need quick deployment on multiple platforms.
- Downside: While faster to develop, hybrid apps often suffer from performance limitations and limited access to native features.
Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-platform frameworks like React Native, Flutter, and Xamarin allow you to write code once and deploy it across both iOS and Android.
- Best for: Businesses looking to save development time while still delivering a native-like experience.
- Downside: Some platform-specific customization may still be required, and performance may not match pure native apps in very complex use cases.
Progressive Web App (PWA) Development
Web apps are browser-based applications built with web technologies that deliver native app-like experiences without requiring app store downloads. Using frameworks like React, Angular, or Ionic, they offer features like offline functionality and push notifications.
- Best for: Apps needing instant accessibility, cross-platform reach, or lower user acquisition barriers, such as media platforms or e-commerce sites.
- Downside: Limited access to some device features and may not match native performance for graphics-intensive applications.
Now that we have provided a brief overview of the development types, let’s take a closer look at each one to help determine which is the best fit for your next project.
What is a Native App?
![]()
A native app is a mobile application developed specifically for a single operating system (OS), using languages and tools that are native to that platform. For iOS, that usually means Swift or Objective-C using Xcode; for Android, it’s Kotlin or Java with Android Studio.
Key Characteristics of Native Apps
- Platform-Specific: Code written for iOS cannot be reused for Android, and vice versa.
- Full Hardware Integration: Native apps can take complete advantage of device hardware, like GPS, accelerometers, cameras, and biometric sensors.
- Top-Tier Performance: Since native code interacts directly with the OS, the app runs more smoothly and loads faster.
- Better User Experience: Developers can use built-in UI components and follow platform-specific guidelines, resulting in a familiar and responsive interface for users.
Development Tools for Native Apps
| Platform | Language | IDE/Tool |
| iOS | Swift, Objective-C | Xcode |
| Android | Kotlin, Java | Android Studio |

Why Choose Native App Development?
- High Performance: Ideal for games, video streaming, or apps requiring intensive data processing.
- Access to All APIs: You get complete access to the latest device features as soon as they’re released.
- Offline Capabilities: Native apps often perform better without internet connectivity.
- Greater Security: Platform-specific features and native code make it easier to implement advanced security measures.
Drawbacks to Consider
- Higher Cost: Building separate apps for iOS and Android requires more time and resources.
- Longer Development Time: Two codebases mean twice the work for updates and bug fixes.
- Skill Specialization: You need separate teams or developers with platform-specific expertise.
Native development is the gold standard for performance and reliability, but it’s not always the most efficient choice depending on your business goals and budget. That’s where other options might be a better fit.
Examples of Native Apps
- Instagram: Initially built natively to handle high-quality media and real-time interactions.
- Spotify: Uses native code to optimize music playback and background tasks.
- WhatsApp: Ensures fast, secure messaging using native functionality across platforms.

Softjourn Example: Cinewav's Complex Native Solution
Cinewav, a Singapore startup, needed to create an immersive outdoor movie experience where video is projected while audio streams perfectly synchronized to viewers' personal devices - a technically complex challenge requiring precise timing.
The approach: Native iOS (Swift) and Android (Kotlin) development to leverage low-level system APIs for audio processing, real-time synchronization, and minimal latency requirements.
Results:
- Achieved near-perfect audio/video synchronization across varying devices and environments
- Successfully tested at 30+ events with reliable performance
- Handled complex challenges like Bluetooth latency variations and network instability
- Enabled social distancing during pandemic events
- Created a patentable technology solution
What is a Hybrid App?
![]()
As mentioned previously, a hybrid app is a mobile application built using web technologies – HTML, CSS, and JavaScript – that runs inside a native container. This approach enables a single codebase to be deployed across multiple platforms, typically using frameworks like Apache Cordova, Ionic, or Framework7.
In simple terms, a hybrid app is a web app wrapped in a native shell. It behaves like a regular app but renders most of its content using a web view (an embedded browser).
Core Characteristics of Hybrid Apps
- Single Codebase: Write once, deploy to both iOS and Android.
- Web-Based UI: Interfaces are rendered via embedded browsers using HTML/CSS.
- Access to Some Native Features: Through plugins, hybrid apps can access device features like the camera, GPS, and storage.
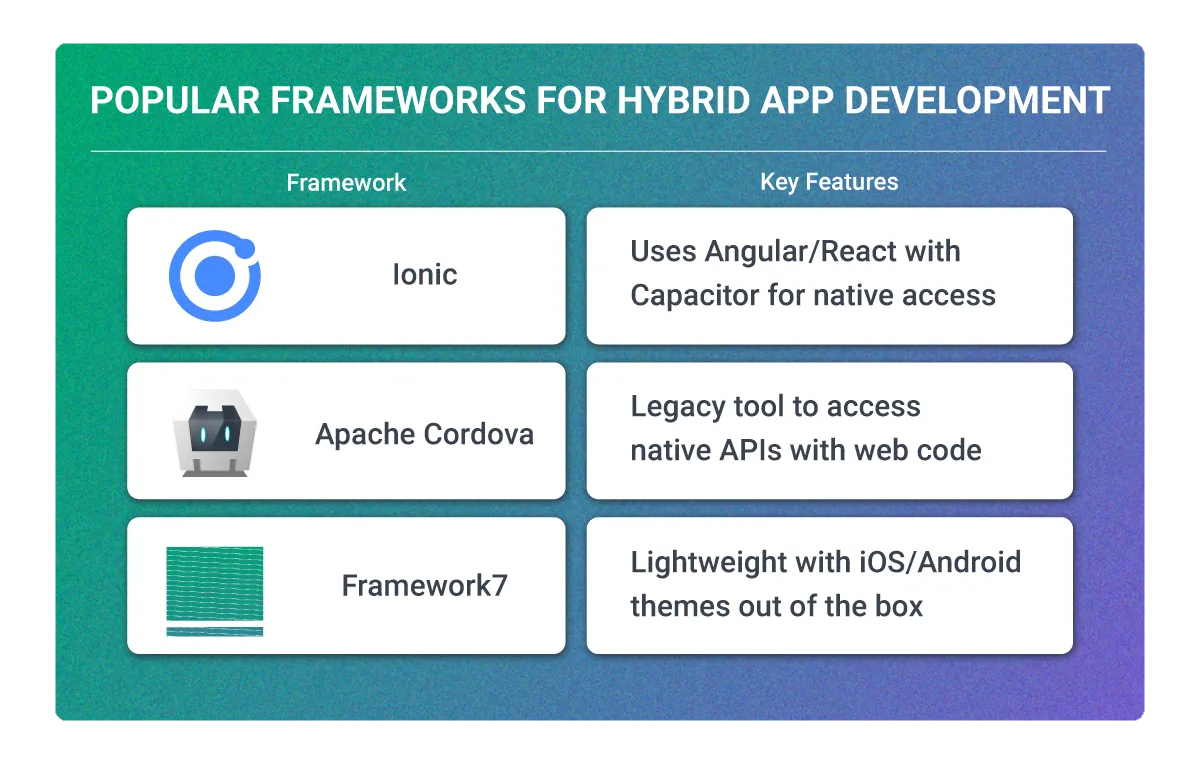
Popular Frameworks for Hybrid App Development
| Framework | Key Features |
| Ionic | Uses Angular/React with Capacitor for native access |
| Apache Cordova | Legacy tool to access native APIs with web code |
| Framework7 | Lightweight with iOS/Android themes out of the box |
When to Consider a Hybrid App
- Rapid MVPs: If you need to validate your idea quickly on multiple platforms.
- Budget Constraints: One team, one codebase, faster delivery.
- Content-Driven Apps: Ideal for apps that primarily display information or use minimal device hardware.
Pros of Hybrid Apps
- Faster and cheaper to develop.
- Easy maintenance, since a single codebase means updates apply to all platforms.
- You can leverage existing web development skills.
Cons of Hybrid Apps
- Performance limitations mean that a hybrid solution will be slower than native or optimized cross-platform solutions.
- UI inconsistencies mean that your app may not feel fully “native” to users.
- Plugin dependencies, so you’ll need third-party tools to access device features, which may become outdated and need replacement over time.
Hybrid apps strike a balance between affordability and functionality, especially for startups or internal-use apps. However, for apps where speed, performance, or a seamless UI are critical, or potentially an app you plan to use for many years, other options like cross-platform or native might be a better fit.
Real-World Examples
- Untappd (beer rating app): Initially hybrid to accelerate cross-platform reach.
- JustWatch: Used Cordova for faster deployment across Android and iOS.
- Many early-stage apps start as hybrids to reduce time-to-market.

Softjourn Example: PEX's Cost-Effective Hybrid Solution
Before their Xamarin rebuild, PEX initially chose hybrid development using HTML5 and PhoneGap for their expense management mobile apps, prioritizing speed to market and cost efficiency.
The approach: Single codebase in HTML5 deployed to both iOS and Android, acknowledging performance trade-offs for business benefits.
Results:
- Delivered both iOS and Android apps from one development team
- Significantly reduced initial development costs
- Enabled rapid feature updates across both platforms
- Eventually migrated to cross-platform when scaling needs grew
What is a Cross-Platform App?
![]()
A cross-platform app is a mobile application developed using a single codebase that works across multiple operating systems (most commonly iOS and Android). Unlike hybrid apps, which run inside a web view, cross-platform apps are compiled into native code, offering better performance and a more “native-like” user experience.
Cross-platform development uses advanced frameworks like React Native, Flutter, and Xamarin, which allow developers to write shared code while still delivering apps that feel and behave like native applications.
Key Characteristics of Cross-Platform Apps
- Shared Codebase: Developers write once and deploy to multiple platforms.
- Native Rendering: Uses native UI components for better performance and appearance.
- Component-Based Architecture: Frameworks like React Native and Flutter offer reusable components, streamlining development and maintenance.
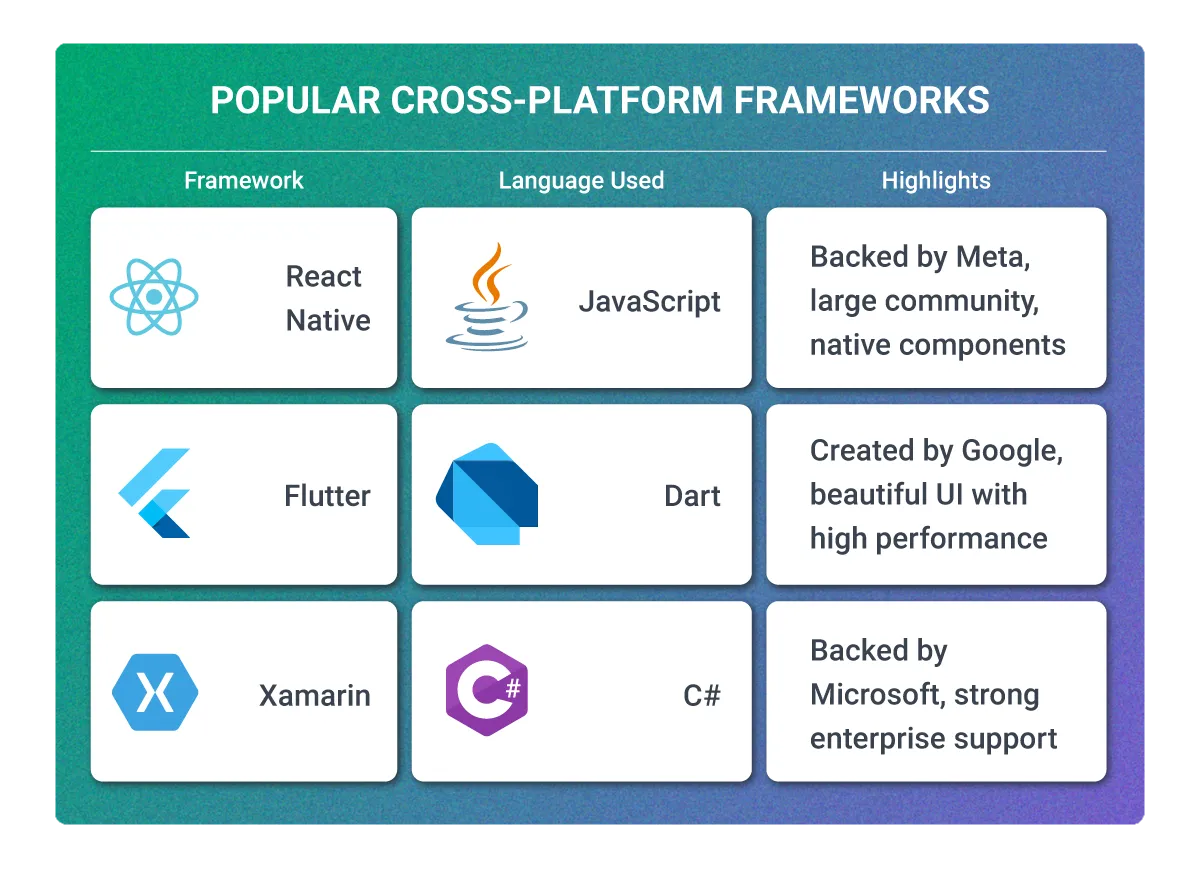
Popular Cross-Platform Frameworks
| Framework | Language Used | Highlights |
| React Native | JavaScript | Backed by Meta, large community, native components |
| Flutter | Dart | Created by Google, beautiful UI with high performance |
| Xamarin | C# | Backed by Microsoft, strong enterprise support |
When to Choose Cross-Platform Development
- You want to reduce development costs without sacrificing performance.
- You need faster time-to-market for both iOS and Android.
- Your app relies on shared business logic but still demands a native-like interface.
Advantages of Cross-Platform Apps
- Cost efficiency: Single development team and codebase.
- Faster updates and bug fixes across platforms.
- Near-native performance, especially with optimized framework.
Limitations of Cross-Platform Apps
- Requires platform-specific code for advanced features or UI fine-tuning.
- Third-party dependency risks, especially with native module integrations.
- Can lead to larger app sizes compared to native counterparts.
Cross-platform apps offer a smart middle ground – faster development and deployment without compromising significantly on quality. They’re especially appealing to startups, growing businesses, and organizations with tight development timelines.
Real-World Examples
- Airbnb (initially used React Native for faster feature rollout)
- Alibaba (uses Flutter for some mobile interfaces)
- Skype (built with Xamarin for unified user experience)
Softjourn Example: Ticketmaster's Strategic Move to Xamarin
Ticketmaster was maintaining expensive native iOS and Android ticket-scanning apps with separate codebases and development teams. Rising maintenance costs and difficulty finding specialized developers prompted them to explore cross-platform solutions.
The approach: Xamarin development allowing shared code across platforms while maintaining native performance for critical barcode scanning functionality.
Results:
- 200,000 tickets scanned within the first months of beta testing
- Significant reduction in maintenance overhead from dual codebases
- Leveraged existing .NET team skills, reducing hiring needs
- Enhanced performance compared to previous native solutions
- Added offline scanning capabilities for unreliable venue connectivity
What is a Web App (Progressive Web App)?

A web app, specifically a Progressive Web App (PWA), is a mobile application built using web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript that delivers a native app-like experience directly through a web browser.
Unlike traditional apps, PWAs don't require installation from app stores and can be accessed instantly via any modern browser while offering features like offline functionality, push notifications, and home screen installation.
PWAs combine the accessibility and reach of websites with the performance and user experience of native mobile apps, using technologies like Service Workers, Web App Manifests, and responsive design to bridge the gap between web and mobile.
Key Characteristics of Web Apps
- Browser-Based: Accessible from any modern web browser without app store downloads
- App-Like Experience: Full-screen interface with native app behaviors and animations
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Single codebase works on iOS, Android, and desktop
- Offline Functionality: Service workers enable use without internet connectivity
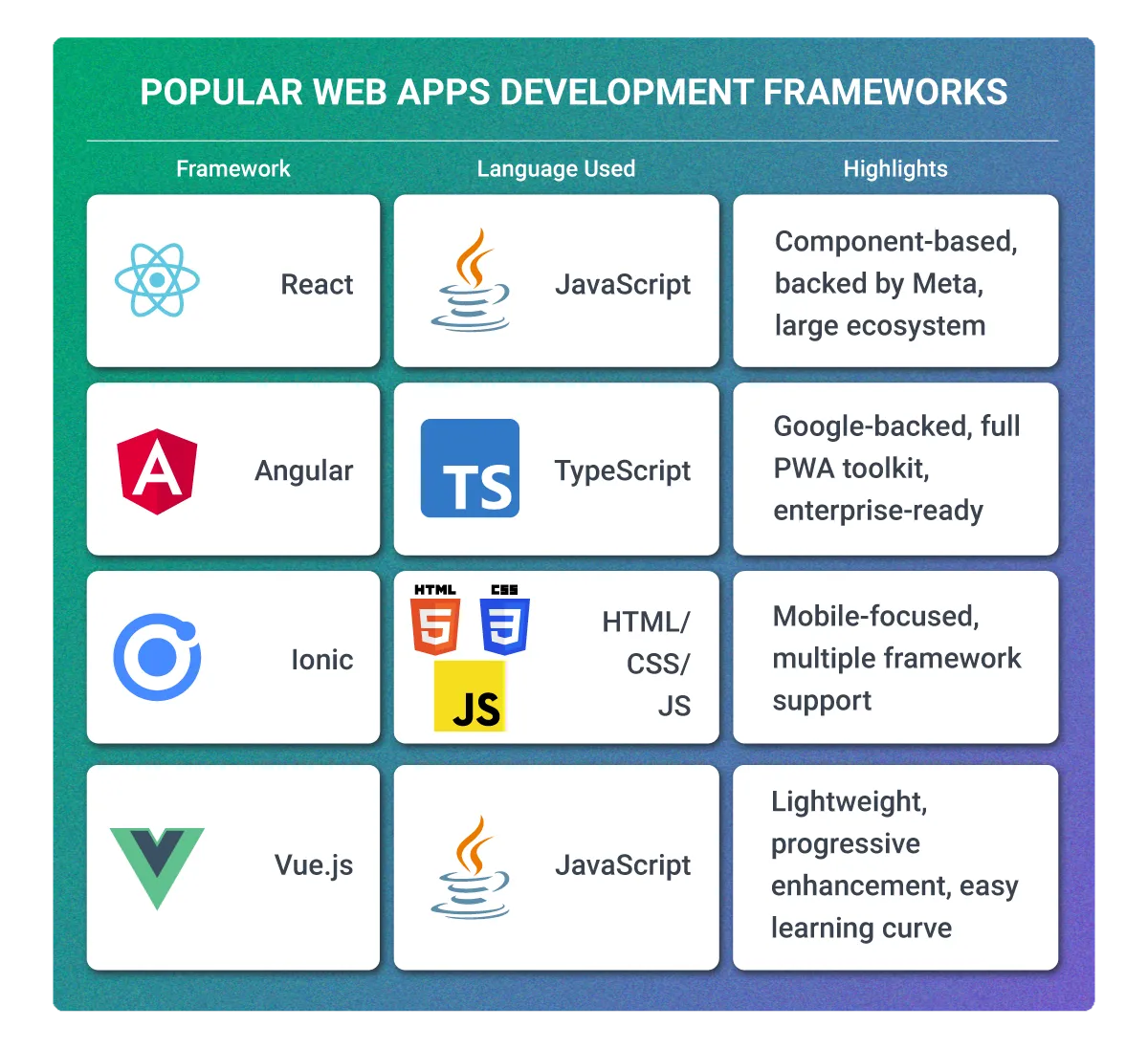
Popular Web App Development Frameworks
| Framework | Language Used | Highlights |
| React | JavaScript | Component-based, backed by Meta, large ecosystem |
| Angular | TypeScript | Google-backed, full PWA toolkit, enterprise-ready |
| Ionic | HTML/CSS/JS | Mobile-focused, multiple framework support |
| Vue.js | JavaScript | Lightweight, progressive enhancement, easy learning curve |

When to Choose Web App Development
- You need instant accessibility without app store barriers or approval processes
- You want to reach users across all platforms with a single codebase
- Your app benefits from web discoverability and SEO optimization
- You're targeting users who are hesitant to download large native apps
Advantages of Web Apps
- Instant Access: No download required, accessible via URL sharing
- Lower User Acquisition Cost: Eliminates app store download friction
- Automatic Updates: Changes deploy instantly without user action
- SEO Benefits: Discoverable through search engines unlike native apps
- Storage Efficient: Much smaller than native apps (often under 1MB vs 15-38MB)
Limitations of Web Apps
- Internet Dependency: Limited offline capabilities compared to fully native apps
- Platform Restrictions: Some device features may have limited browser access
- Performance Constraints: May not match native apps for graphics-intensive applications
- App Store Absence: Harder to discover without traditional app store presence
Web apps represent the future of accessible, cross-platform development, offering businesses a way to deliver sophisticated mobile experiences without the complexity and cost of maintaining separate native applications.
Real-World Examples
- Starbucks (offline ordering, menu browsing, loyalty features)
- Spotify Web (music streaming without app installation)
- Financial Times (news consumption with offline reading)
Softjourn Example: Project Admission's Emergency PWA Solution
Project Admission needed an access control app in just two weeks before a major event, with functionality for ticket scanning, access control, and data management.
The approach: Progressive Web App using React and Ionic, chosen specifically for development speed and instant deployment.
Results:
- Delivered a fully functional app in exactly 2 weeks
- No app store approval delays - instant deployment
- Offline functionality for events with poor connectivity
- Automatic updates without user intervention
- Significant cost savings compared to native development
Which Mobile App Development Approach Should You Choose?
Selecting the right mobile app development approach – whether native, hybrid, cross-platform, or web app – depends on your project’s specific goals, timeline, budget, technical complexity, and target audience.
There’s no one-size-fits-all solution; instead, each approach has its own advantages based on context.
Key Factors to Consider
- Performance Requirements
If your app needs to process a lot of data, work offline, or deliver high responsiveness (e.g., gaming, video streaming, financial apps), native development is typically the best choice. - Speed to Market
For projects with tight deadlines or limited initial budgets, hybrid or cross-platform approaches offer quicker deployment and reduced time-to-market. - User Experience Expectations
Apps that must deliver seamless, highly-polished, and platform-consistent user experiences are best served by native or high-quality cross-platform frameworks like Flutter. - Maintenance and Scalability
If your app will evolve with frequent updates or shared business logic across platforms, cross-platform or web app development makes long-term maintenance easier and more cost-effective. - Access to Native APIs
If your app heavily relies on device features (e.g., camera, GPS, push notifications), native or robust cross-platform solutions (like React Native with native modules) are essential. - Team Skills and Resources
Your in-house team’s familiarity with certain frameworks or programming languages may naturally influence the development path.
Example Scenarios
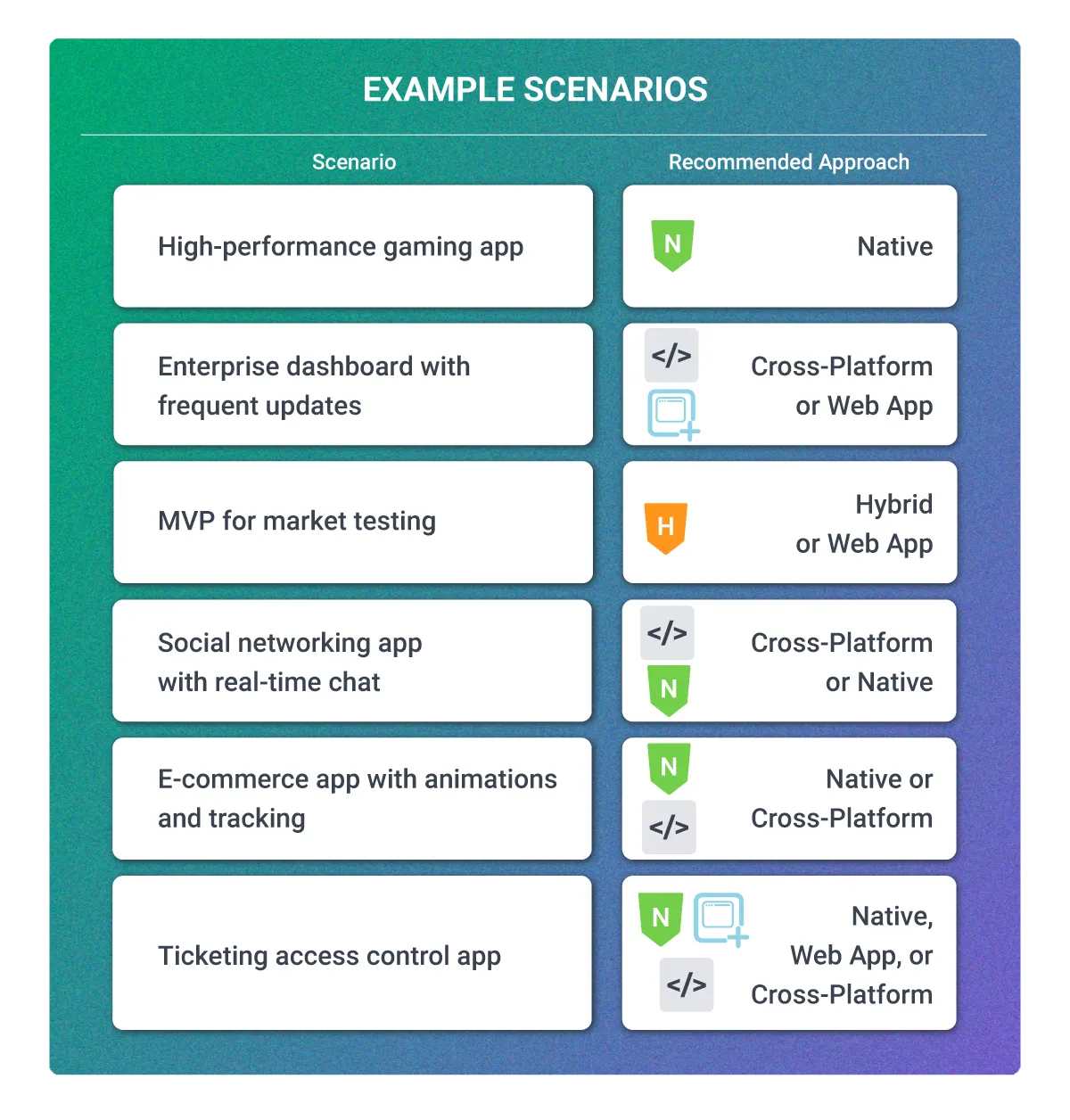
Balancing Cost vs. Experience
- Startups and MVPs often choose hybrid or cross-platform to save time and cost.
- Established businesses or apps with high user expectations often invest in native for performance and branding control.
- Web apps are excellent for apps needing instant user access and cross-platform reach, like media streaming or productivity tools.
Choosing the right mobile app development strategy isn’t about picking the "best" option overall, but about selecting the most aligned option for your product vision, user needs, and resource constraints.
Still unsure which approach fits your project best? Let's chat about your specific needs and help you make the right choice.
What Are the Cost Implications of Each Mobile App Development Type?
The choice between native, hybrid, cross-platform, or web app doesn’t just affect performance or user experience; it significantly impacts your budget. Each method requires different levels of investment in tools, teams, testing, and long-term maintenance.
Understanding the financial implications helps project managers, CTOs, and business leaders align development strategy with budget realities.
Let’s break down how costs vary and what factors influence them:
Is Native App Development More Expensive?
Yes, native app development is typically the most expensive option. That’s because developing for iOS and Android separately requires:
- Two specialized development teams (Swift for iOS, Kotlin/Java for Android)
- Double the effort in coding, testing, and maintaining each platform
- Separate timelines, which can delay synchronized releases
While the end product often delivers the best performance and user experience, these benefits come at a premium, making native apps better suited for organizations that need high-end functionality, long-term scalability, and complete control over platform-specific features.
Typical Budget Range (per platform)1:
- Simple native app: $25,000 – $50,000
- Mid-range app with integrations: $55,000 – $100,000
- Complex, enterprise-level app: $100,000+
How Do Costs Compare for Hybrid vs Cross-Platform Development?
Both hybrid and cross-platform options reduce costs by using a single codebase across platforms, but they differ in trade-offs and long-term value.
Hybrid App Costs
- Lower initial costs: Hybrid apps are often the cheapest to build upfront, especially when using lightweight tools like Ionic or Cordova.
- Limitations: Hybrid apps may require costly rewrites later if scalability or performance become issues.
- Plugin reliance: You may need to pay for third-party plugins to access native features.
Cross-Platform App Costs
- Moderate cost savings: Development costs are higher than hybrid but still 30–40% lower than native in most cases.
- Higher quality: Frameworks like Flutter or React Native reduce long-term tech debt by offering better performance and native-like features.
- Reusable business logic: Ideal for apps that evolve over time with shared features across platforms.
How Do Web App Development Costs Compare?
Web apps (PWAs) often offer the most cost-effective development approach, especially for businesses prioritizing reach and accessibility over platform-specific features.
Web App Cost Advantages:
- Single Development Cycle: One codebase serves all platforms, browsers, and devices
- No App Store Fees: Eliminates ongoing platform fees and approval processes
- Faster Deployment: Instant updates without waiting for app store approvals
- Lower Hosting Costs: Standard web hosting vs. specialized mobile backend infrastructure
Estimated Budget Comparison (for two platforms)1:
| App Type | Development Cost Estimate |
| Native (2 apps) | $80,000 – $150,000+ |
| Cross-Platform | $40,000 – $100,000+ |
| Web App (PWA) | $15,000 – $80,000+ |
| Hybrid | $20,000 – $100,000+ |
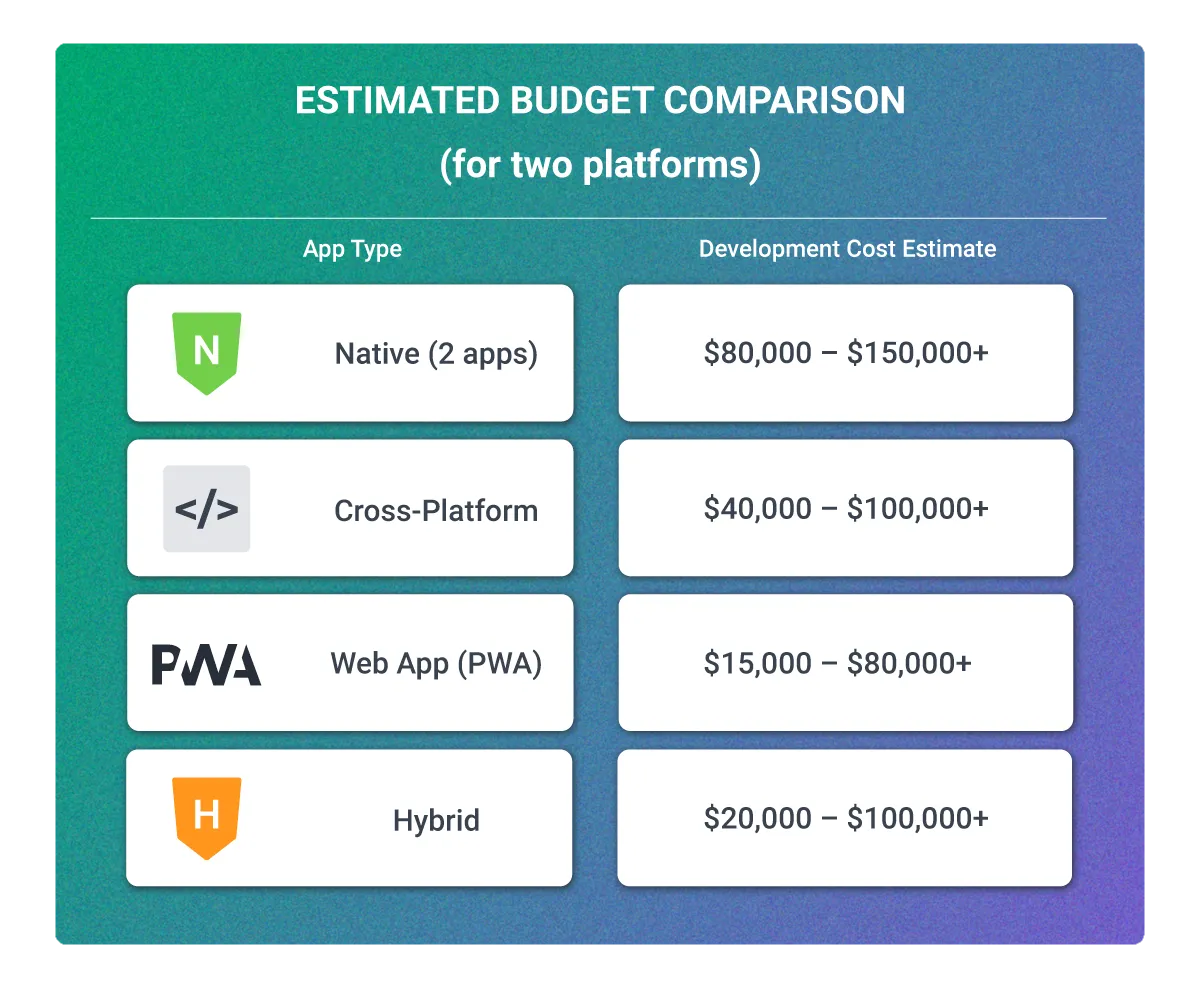
What Budget Considerations Should You Keep in Mind?
Regardless of your technical choice, the real cost of app development includes more than just writing code. You’ll also need to account for:
- Ongoing Maintenance
- Native apps: double the workload
- Cross-platform: streamlined but still needs platform-specific QA
- Hybrid: fewer updates but may face compatibility issues over time
- Web app: minimal maintenance overhead, hosting and domain costs only
- Third-Party Integrations: Costs vary depending on whether you need APIs for payments, maps, social logins, analytics, etc.
- UI/UX Design Complexity: Platform-specific customizations increase costs for cross-platform and hybrid apps.
- Testing and Quality Assurance: Cross-platform frameworks reduce testing overhead compared to native.
- Developer Availability and Expertise: Cross-platform skills (React Native, Flutter) are increasingly common, while native devs command higher rates.
Cost efficiency shouldn't come at the expense of long-term sustainability. If your app is mission-critical, a slightly higher upfront investment in cross-platform or native may pay off in fewer performance issues and reduced technical debt later.
How Do User Experience and Design Differ in Native, Hybrid, Cross-Platform Apps, and Web Apps?
User experience (UX) and interface design (UI) are key factors that can determine whether your mobile app succeeds or fails. While functionality is essential, it’s the design and usability that shape how users feel when interacting with your app.
Each development approach handles UX and UI differently based on how the app is built and how it interacts with device-specific features and design conventions.

What User Experience Can You Expect from Native Apps?
Native apps provide the most refined and responsive user experience because they are designed specifically for a single platform using that platform’s tools, design patterns, and UI components.
Advantages of Native UX:
- Platform Consistency: Users are familiar with how apps behave on iOS or Android. Native apps align with these expectations using built-in design libraries like Apple’s Human Interface Guidelines or Google’s Material Design.
- Smooth Animations and Transitions: Native apps handle UI animations natively, ensuring fluid performance without lags or dropped frames.
- High Responsiveness: Gestures, scrolling, and touch inputs feel natural because native apps can access lower-level system APIs.
- Offline Functionality: Native apps can offer better offline support, allowing for continuous access even without a stable internet connection.
Use Case Example: A fintech app requiring instant touch responses and secure biometric authentication benefits from native UX due to its speed and trust factor.
How Does Hybrid Mobile App Design Impact User Experience?
Hybrid apps, built with web technologies, often struggle to match the fluidity and polish of native apps. Since the UI is rendered through a web view, there's an additional layer between the user and the device’s native interface.
Hybrid UX Limitations:
- Inconsistent Platform Behavior: Users may notice that buttons, icons, and transitions don’t fully align with their OS’s native feel.
- Performance Lag: Because UI interactions are rendered via an embedded browser, animations or gesture responses may feel delayed or less fluid.
- UI Customization Constraints: Complex animations or highly customized designs can be difficult to implement without performance penalties.
Use Case Example: A simple business expense tracking app benefits from hybrid development for quick deployment across platforms, but users may notice slower transitions when navigating between expense categories compared to native alternatives.
While hybrid apps can look decent and serve their purpose, they often don’t deliver the intuitive, responsive feel users expect from modern apps.
What is the User Interface Like for Cross-Platform Apps?
Cross-platform apps aim to deliver native-like user experiences while using shared code. With modern frameworks like Flutter and React Native, developers can create custom interfaces that mimic native behavior closely, and in many cases, users can’t even tell the difference.
Strengths of Cross-Platform UX:
- Near-Native UI Components: React Native and Flutter both allow developers to use widgets that behave like native elements.
- Custom Design Systems: Flutter offers complete control over every pixel, enabling beautiful, custom UIs with consistent behavior across platforms.
- Consistent UX Across Platforms: Developers can implement design systems once and maintain parity between iOS and Android.
Use Case Example: A social media app like Instagram benefits from cross-platform development to maintain consistent branding and user experience across iOS and Android while reducing development time for new features.

What User Experience Do Web Apps Deliver?
Web apps provide increasingly sophisticated user experiences that rival native apps, while offering the unique advantage of instant accessibility through any modern browser without installation barriers.
Advantages of Web App UX:
- Instant Access: Users can start using the app immediately via URL sharing without download delays or storage concerns.
- Cross-Platform Consistency: Single codebase ensures identical experience across all devices and operating systems.
- Automatic Updates: Users always access the latest version without manual app updates or approval delays.
- Responsive Design: Adapts seamlessly to different screen sizes from mobile to desktop without separate development.
Use Case Example: A collaborative project management tool like Notion benefits from web app architecture because team members can instantly access shared workspaces via links, regardless of their device or operating system, without requiring IT approval for app installations.
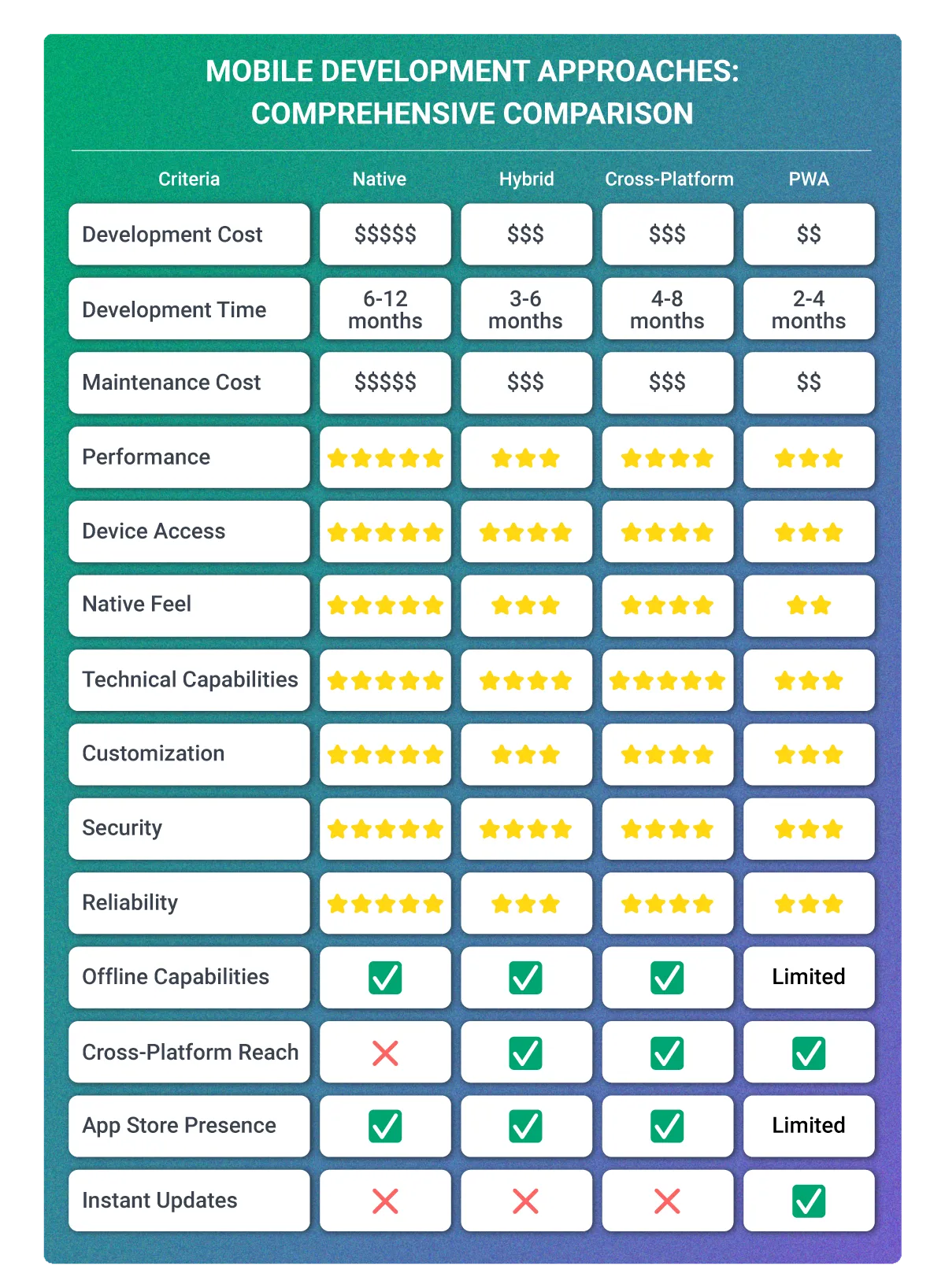
The Best Development Approach for Your Mobile Application
Choosing the best development approach for your mobile application isn’t just a technical decision; it’s a strategic one that directly impacts your product’s success, user satisfaction, and long-term ROI.
Native development is ideal when performance, responsiveness, and deep device integration are top priorities. It’s the best choice for high-end apps, complex UIs, or industries with stringent security requirements, such as finance, healthcare, or media streaming.
Hybrid development works best for startups or internal business tools where time-to-market and budget are major constraints. It's a good starting point for MVPs or simple apps that don’t require complex interfaces or animations.
Cross-platform development offers a balanced solution for businesses aiming to launch apps on multiple platforms without doubling the workload. With modern frameworks like Flutter and React Native, it's possible to achieve near-native performance while accelerating development timelines and reducing costs.
Web app development is an excellent fit for applications needing instant accessibility, cross-platform compatibility, and lower barriers to user adoption.
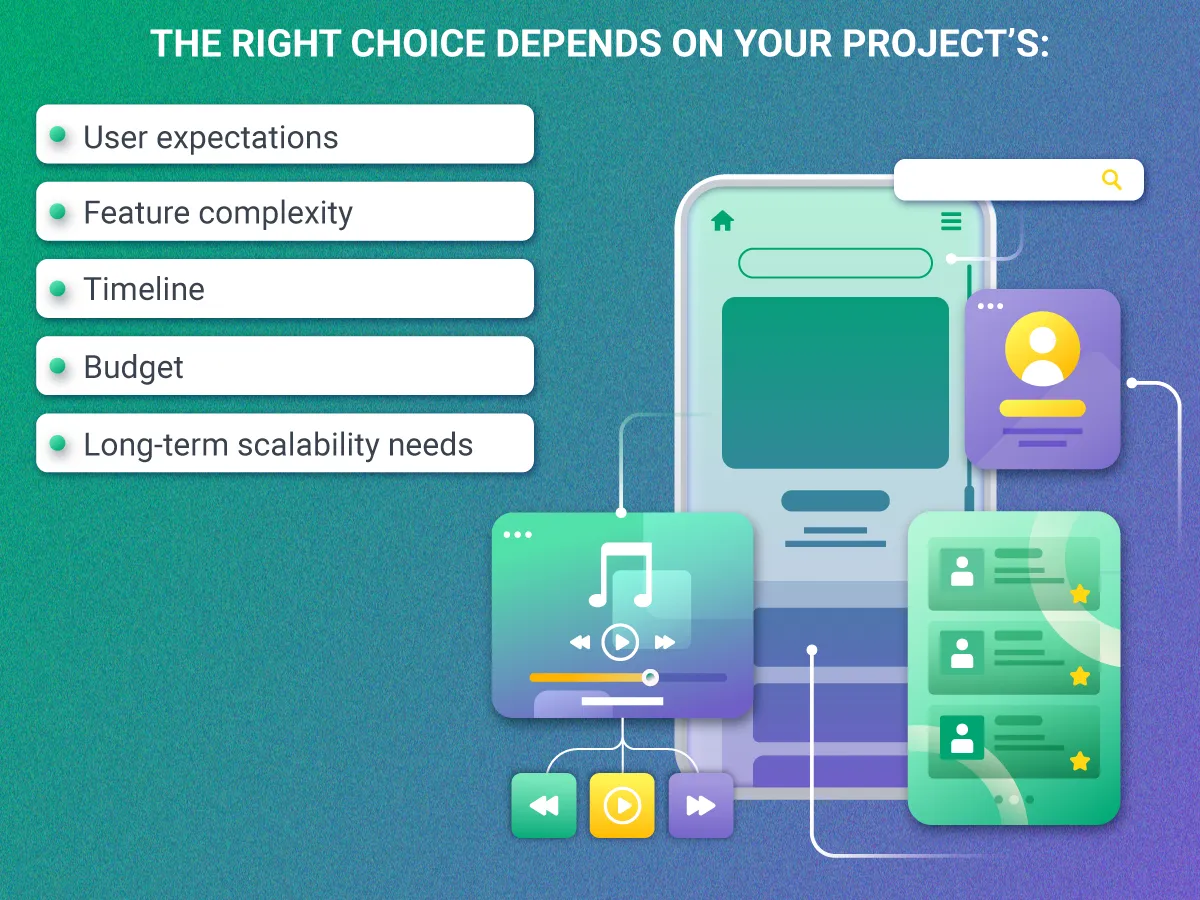
The Bottom Line
The right choice depends on your project’s:
- User expectations
- Feature complexity
- Timeline
- Budget
- Long-term scalability needs
There’s no universal “best” approach, only the best fit for your business goals.
At Softjourn, we’ve helped startups, enterprise teams, and global brands choose and implement the right mobile strategy, whether native, hybrid, cross-platform, or web app.
If you're exploring the best path for your next app, our team is here to help you evaluate your options, avoid costly missteps, and bring your vision to life with precision and performance.
Let’s talk about your mobile app idea – and make it a reality.
FAQ
What is the difference between native vs hybrid vs cross-platform mobile apps?
A: Native apps are developed specifically for a single platform (like native iOS or native Android) using platform-specific development languages. Hybrid apps combine elements of both native and web apps, allowing for some cross-platform compatibility but often sacrificing performance. Cross-platform mobile apps are built to run on multiple platforms with a single codebase, which can streamline development but may limit access to device-specific features.
What are the advantages of using a native mobile application?
A: Native mobile applications typically offer the best performance and user experience as they are optimized for specific platforms. They can leverage the full capabilities of the device, including access to hardware features, and are often more responsive and faster than other types of apps.
How does cross-platform mobile app development work?
A: Cross-platform mobile app development allows developers to build apps that can run on multiple operating systems from a single codebase. This approach uses frameworks that enable the app to function on different platforms while still providing a native-like user experience.
What are progressive web apps and how do they differ from native apps?
A: Progressive web apps (PWAs) are web applications that use modern web capabilities to deliver an app-like experience to users. Unlike native apps, PWAs are accessed via a web browser and do not need to be downloaded from an app store. They are designed to be fast, reliable, and engaging, but may not have full access to device features like native apps.
Which type of app is best for my project: native, hybrid, or progressive web app?
A: The best type of app depends on your project requirements. If you need high performance and full access to device features, a native application is ideal. If you want to reach a broader audience quickly, hybrid or cross-platform apps may be more suitable.
Can I use a single codebase for both iOS and Android with cross-platform app development?
A: Yes, cross-platform app development allows you to use a single codebase to build applications for both iOS and Android. This approach can save time and resources in the development process while ensuring a consistent user experience across platforms.
What are the main considerations when choosing between native and web apps?
A: When choosing between native and web apps, consider factors such as performance, user experience, development cost, and time to market. Native apps provide better performance and access to device features, while web apps are easier to maintain and update, as they do not require app store approvals.
How do I protect my app's data if I choose a cloud-based solution?
A: To protect your app's data in a cloud-based solution, implement strong encryption for data at rest and in transit, use secure authentication methods, and ensure compliance with data protection regulations. Additionally, choose reputable cloud service providers with robust security measures in place.
What is the future of application development with the rise of cloud technology?
A: The future of application development is likely to see a greater shift towards cloud-based solutions, as they offer scalability, flexibility, and easier updates. Developers will increasingly focus on creating applications that can leverage cloud computing capabilities, including machine learning and big data analytics, to enhance user experiences.