When building software applications, choosing between Java and Python can significantly impact your project's timeline, budget, and long-term success.
Both programming languages power some of the world's largest applications, but they serve different business needs and excel in distinct scenarios.
This comprehensive guide examines Java vs Python from a business perspective, helping you make informed decisions about technology stack investments, development timelines, and strategic planning.

Executive Summary: Java vs Python at a Glance
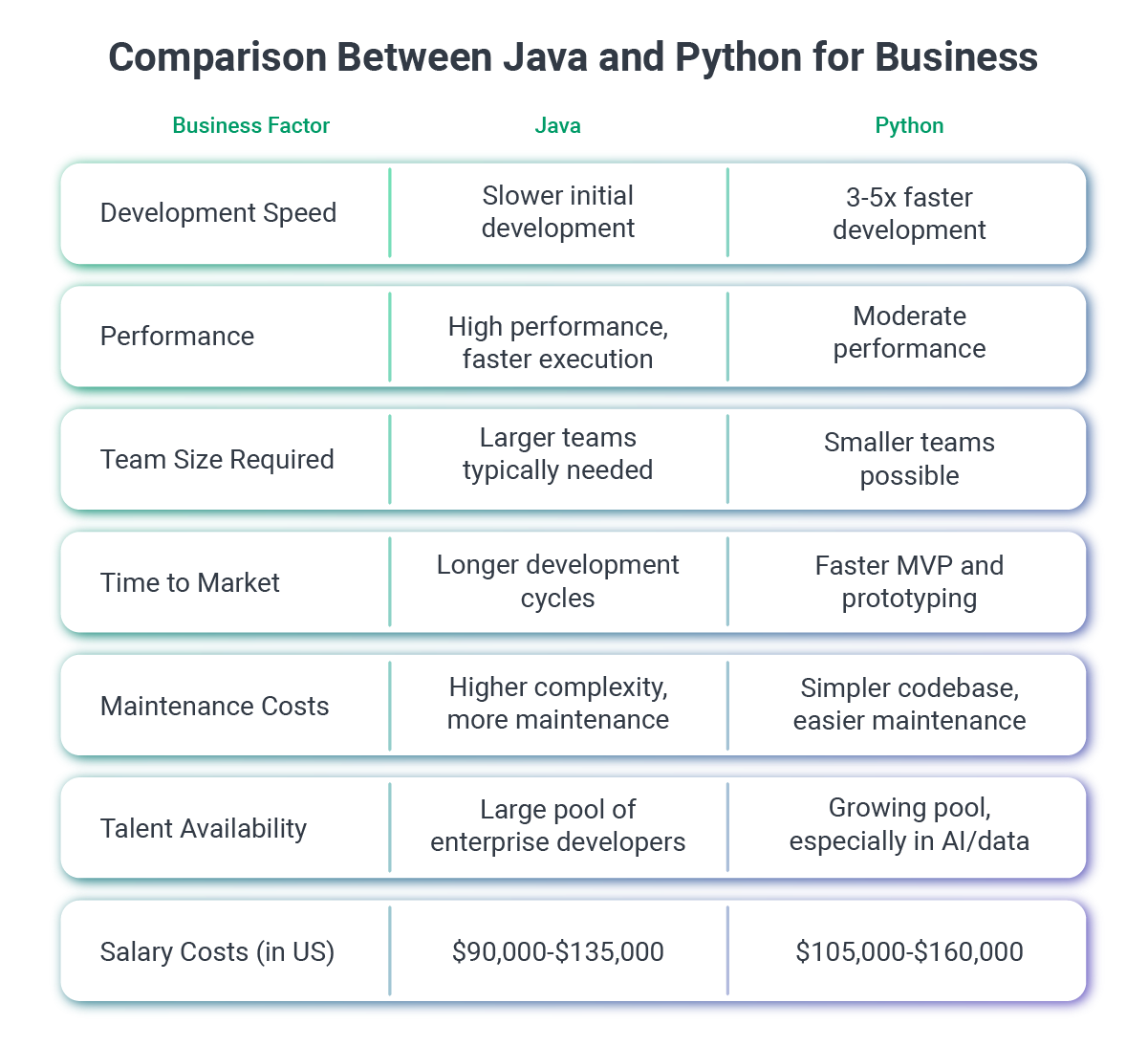
Java is a compiled, statically-typed language that excels in enterprise applications, Android development, and high-performance systems. It offers superior speed, robust security features, and exceptional scalability for large-scale operations.
Python is an interpreted, dynamically-typed language known for rapid development, data science capabilities, and ease of maintenance. It enables faster time-to-market, requires smaller development teams, and dominates artificial intelligence and machine learning applications.
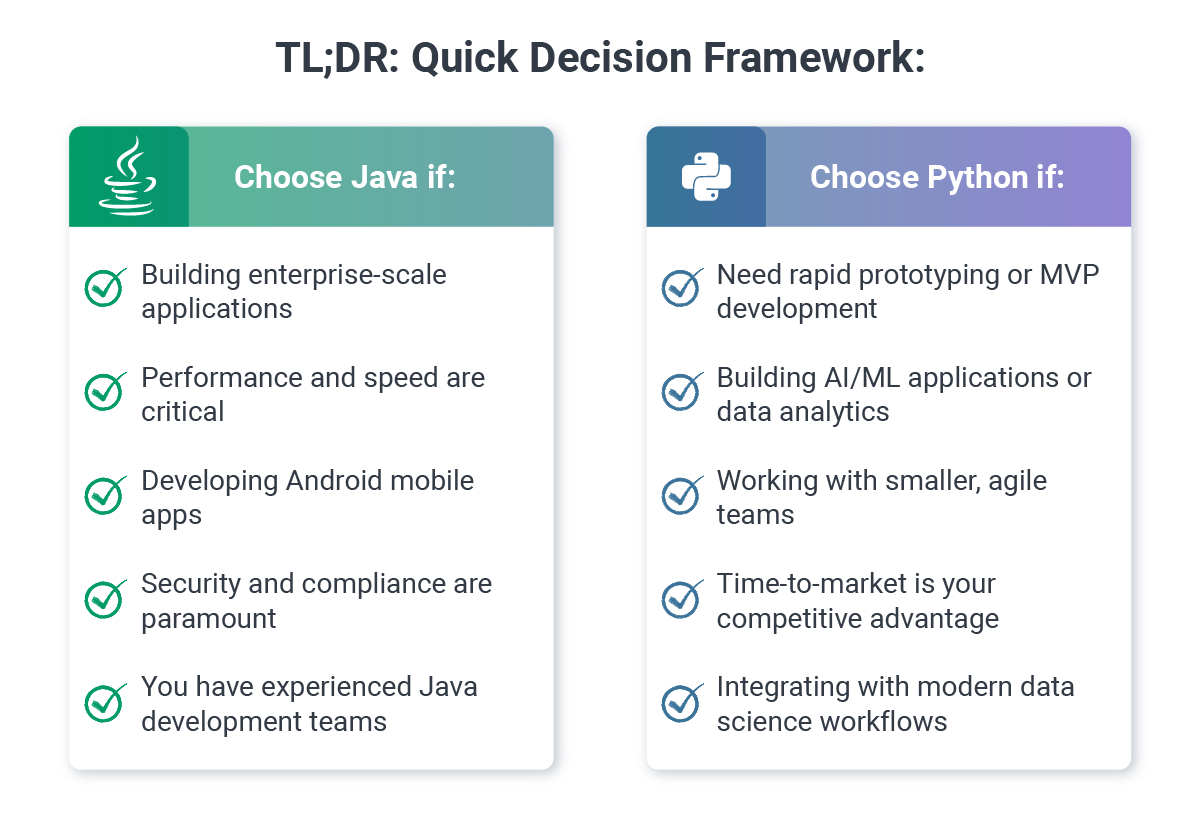
TL;DR: Quick Decision Framework
Choose Java if:
- Building enterprise-scale applications
- Performance and speed are critical
- Developing Android mobile apps
- Security and compliance are paramount
- You have experienced Java development teams
Choose Python if:
- Need rapid prototyping or MVP development
- Building AI/ML applications or data analytics
- Working with smaller, agile teams
- Time-to-market is your competitive advantage
- Integrating with modern data science workflows
Bottom Line: There's no universally "better" choice. Java wins on performance and enterprise stability; Python wins on development speed and innovation capabilities. Many successful companies use both strategically.
Now, let’s dive into the specifics of choosing Python vs Java.
Java vs Python Performance: Impact on Business Operations
Performance differences between Java and Python can significantly affect scalability, infrastructure costs, and user experience.

Java Performance Advantages
- Execution Speed: Java runs many times faster than Python in CPU-intensive use cases.
- Resource Efficiency: Uses less memory and CPU per request, enabling better performance at scale.
- Scalability: Handles high traffic with fewer servers, lowering cloud costs.
- Stability: Fewer crashes due to robust memory management and static typing.
Best Use Cases for Java:
- Financial systems processing real-time transactions
- Gaming apps requiring instant response
- E-commerce platforms handling peak loads
- Video streaming services with large concurrent users

Python Performance Considerations
- Execution Trade-off: Slower runtime, but enables faster development cycles.
- Infrastructure Load: Higher memory and compute usage at scale.
- Acceptable for: Internal tools, data analysis apps, AI/ML workflows, MVPs where runtime speed is less critical.
Difference Between Java and Python: Core Architecture Decisions
Architectural differences between Java and Python directly affect how projects are built, tested, and scaled.
Compiled vs. Interpreted
- Java: Compiled into bytecode before runtime
- Business Impact: Faster execution, better for high-traffic apps
- Development Impact: Slower build cycles, but fewer runtime errors
- Python: Interpreted at runtime
- Business Impact: Faster development and iteration cycles
- Development Impact: Easier debugging and testing, ideal for agile teams
Static vs. Dynamic Typing
- Java (Static Typing):
- Predictable code structure with fewer runtime bugs
- Better suited for large teams and complex applications
- Python (Dynamic Typing):
- Concise, flexible code ideal for prototyping
- Higher risk of runtime issues in large, evolving codebases
Summary of Business Implications
- Java: Best for performance-critical, large-scale, long-lifecycle applications
- Python: Best for rapid development, experimentation, and smaller teams or internal tools
Java or Python for Web Development: Platform Strategy Considerations
Web development represents one of the most common business applications for both Java and Python, but each language serves different strategic purposes in building web-based platforms and services.

Java Web Development: Enterprise-Scale Foundations
When Java Web Development Makes Business Sense
- Building customer-facing platforms that must handle millions of users
- Developing B2B applications requiring integration with existing enterprise systems
- Creating financial services or healthcare applications with strict security requirements
- Building long-term platforms where performance optimization becomes critical over time
Java Web Development Trade-offs
- Advantages: Superior performance, robust security, excellent scalability, mature tooling
- Disadvantages: Longer development cycles, larger team requirements, higher initial costs
- Best For: Large organizations with complex requirements and resources for thorough development processes

Python Web Development: Agility and Innovation
When Python Web Development Drives Business Value
- Launching MVP web applications to validate business models quickly
- Building content-heavy websites with dynamic data requirements
- Creating data-driven web applications with analytics and reporting features
- Developing internal business tools and admin interfaces
Python Web Development Benefits
- Advantages: Rapid development, smaller teams, easier maintenance, excellent data integration
- Disadvantages: Performance limitations at scale, higher server costs for high-traffic applications
- Best For: Startups, content-driven sites, data-heavy applications, rapid prototyping scenarios
Performance and Scalability Considerations
- Low-Medium Traffic (< 100,000 monthly users): Python's development speed advantages typically outweigh performance concerns
- High Traffic (> 1 million monthly users): Java's performance benefits become significant for infrastructure costs
- Enterprise Traffic (> 10 million monthly users): Java's scalability advantages are often essential
Development Cost Analysis: Java vs Python Project Economics
Choosing between Java and Python impacts more than just salaries as they both have advantages and disadvantages. What you choose will shape your timeline, team structure, infrastructure spend, and maintenance budget. Here’s how each stacks up.
The Cost of Using Python
Initial Investment
- Smaller teams (2–4 devs)
- Shorter development cycles
- Mid-level developers ramp up quickly
Infrastructure Costs
- More compute resources for similar performance
- Higher cloud costs at scale
- Extra monitoring tools often needed
- Scaling = linear cost increase
Maintenance Profile
- Less code to maintain
- Frequent small updates
- Faster bug fixes and new feature rollouts
Hidden Costs
- May require refactoring as traffic grows
- Higher infrastructure spend during rapid scaling
- Extra security reviews due to dynamic typing
- Talent is competitive and retention can be costly

The Cost of Using Java
Initial Investment
- Larger teams (4–8 devs)
- More detailed planning and longer development cycles
- Senior developers needed for complex functionality
Infrastructure Costs
- Better performance per server = fewer resources
- Lower CPU/memory usage at scale
- Often leverages enterprise licenses/tools already in place
Maintenance Profile
- Stable, predictable code
- Less frequent but more comprehensive updates
- Stronger QA processes, ideal for complex systems
Hidden Costs
- Licensing fees (e.g., Oracle)
- Higher upfront training and onboarding
- More expensive integration with legacy systems
- Risk of over-engineering for simple projects
ROI Considerations & Budget Strategy
Python accelerates time-to-market and reduces risk: perfect for MVPs, internal tools, and cash-conscious projects. It supports iterative delivery and early revenue generation.
Java pays off over time. It’s built for high-performance, enterprise-grade apps that require stability, long lifecycles, and complex integrations.
Budget Recommendations:
- Use Python for: Fast launch, small teams, agile development
- Use Java for: Enterprise growth, high user volume, long-term ROI
- Hybrid Approach: Prototype in Python → scale in Java
Cost Analysis: The Hidden Economics
- Java’s Long-Term Advantage: Higher dev cost upfront, but potential cost savings in annual infrastructure savings for traffic-heavy apps.
- Python’s Short-Term Advantage: Lower initial spend and faster launch help businesses generate revenue sooner, making it a great choice for early-stage growth.

Is Python Easier Than Java? The Learning Curve That Affects Your Hiring
The complexity of a programming language directly affects how quickly you can hire, train, and scale your development team. Choosing between Java and Python isn’t just a technical decision but a strategic one that impacts agility, cost, and team growth.
Python’s Accessibility Advantage
Faster Onboarding
New developers can learn Python in 2–3 months or less – far quicker than the 6-12 months often needed for Java.
Benefits:
- Lower training costs
- Faster team expansion
- Reduced knowledge loss when team members leave
- Easier to hire from bootcamps or non-traditional backgrounds
Simplified Maintenance
Python codebases are typically smaller, which means:
- Fewer bugs
- Easier code reviews and QA
- Lower long-term maintenance effort
- Faster feature delivery
Java’s Structured Approach Benefits
Built for Enterprise
Java enforces structure through strict syntax and static typing, which is ideal for maintaining consistency across large teams and complex systems.
Business Impact:
- Fewer runtime errors
- Predictable, stable code
- Easier collaboration in enterprise environments
Developer Growth
Java’s complexity builds deep technical expertise:
- Stronger grasp of core CS concepts
- Familiarity with memory management and performance optimization
- Readiness for working with legacy and enterprise tech stacks
Talent Market Implications
Python Developers
- Broad, growing pool
- Especially common in data science and AI
- Accessible to career changers and bootcamp grads
- Salary range: ~$105K–$160K
Java Developers
- Large, experienced enterprise-focused talent pool
- Strong foundations in backend systems and integration
- Salary range: ~$90K–$135K
Strategic Hiring Considerations
- Choose Python if you need:
- Fast team scaling
- Agile development and quick pivots
- Collaboration with data/AI teams
- A lower barrier to entry for new devs
- Choose Java if you require:
- Long-term code maintainability
- Integration with legacy or enterprise systems
- High performance and strict QA standards
- Developers with deep technical specialization

Security and Compliance: Java vs Python for Regulated Industries
When handling sensitive data or operating in regulated sectors like finance, healthcare, or government, the language you choose can impact both your security posture and compliance readiness.
Java was built with enterprise security in mind. Its static typing, bytecode verification, and robust built-in tools (like Spring Security and JVM access controls) make it a strong fit for industries requiring formal audits, long-term support, and tight access control.
This is why banks, government agencies, and healthcare systems often default to Java for core infrastructure.
Python, by contrast, relies more on developer best practices and third-party libraries. While it lacks Java’s built-in security layers, it offers flexibility and speed, which are valuable for developing security automation, analytics, or tools powered by AI.
However, Python apps demand stricter vigilance around dependencies and runtime vulnerabilities. Strong community tooling (e.g. Bandit, safety) helps mitigate risks, but success depends on process maturity and architecture design.
Strategic Guidance:
- Use Java when security certifications, long-term compliance, and operational stability are top priorities.
- Use Python for fast-moving security features, cloud-native environments, or AI-based threat detection.
- Hybrid Approach: Java for core systems; Python for monitoring, analytics, and automation.
What is Java Used For? Business Applications That Drive Revenue
Java has powered enterprise software for over 25 years, making it one of the most trusted technologies for mission-critical business applications.
When companies need software that handles millions of transactions, processes sensitive financial data, or operates 24/7 without downtime, Java is often the foundation.

Enterprise Software Systems
Financial Services and Banking - Major banks like Goldman Sachs, JPMorgan Chase, and Bank of America rely on Java for core banking systems, trading platforms, and risk management applications. Java's robust security features and performance make it ideal for handling millions of financial transactions daily while maintaining regulatory compliance.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) - Salesforce, the world's leading CRM platform, is built primarily on Java. The language's scalability allows CRM systems to manage millions of customer records, automate complex business processes, and integrate with hundreds of third-party applications.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) - Companies like SAP and Oracle use Java to build ERP systems that manage supply chains, inventory, human resources, and expense management for Fortune 500 companies. These systems often handle billions of data points and require the stability that Java provides.
Mobile Application Development
Android Ecosystem - Java remains the primary language for Android development, powering applications used by over 3 billion devices worldwide. For businesses targeting mobile users, Java provides direct access to Android's native features and optimal performance.
Cross-Platform Solutions - Many companies use Java-based frameworks to build applications that work across multiple mobile and desktop platforms, reducing development costs while maintaining consistent user experiences.
Web Applications and APIs
High-Traffic Web Platforms - Netflix streams content to over 300 million subscribers worldwide using Java-based microservices. The platform handles billions of requests daily, demonstrating Java's capability to scale with business growth.
E-commerce Platforms - Amazon's core e-commerce platform relies heavily on Java for inventory management, order processing, and payment systems. During peak shopping periods like Black Friday, these Java applications process millions of transactions per hour.
Big Data and Analytics
Real-Time Data Processing - Apache Kafka, Apache Spark, and Hadoop – three of the most important big data technologies – are built with Java. Companies like LinkedIn and Twitter use these tools to process and analyze massive data streams in real-time, enabling instant insights and automated decision-making.
What is Python Used For? The Engine of Modern Innovation
While Java dominates traditional enterprise software, Python has become the language of choice for companies driving digital transformation, artificial intelligence, and data-driven decision making.
Python's strength lies not in raw performance, but in enabling businesses to innovate faster, extract insights from data, and build intelligent applications that create competitive advantages.

Data Science and Business Analytics
Customer Intelligence and Personalization - Netflix uses Python to analyze viewing patterns and preferences of its 300 million subscribers, powering their recommendation algorithm that drives the majority of content watched. Spotify leverages Python for their Discover Weekly feature, which analyzes billions of songs and user interactions to create personalized playlists for 100+ million users.
Financial Modeling and Risk Assessment - JPMorgan Chase employs Python for quantitative analysis, portfolio optimization, and fraud detection systems. The bank's Python-based models process millions of transactions daily, identifying suspicious patterns and preventing financial losses worth millions of dollars annually.
Enterprise Software - Uber relies on Python for pricing algorithms, driver matching, and data analytics that optimize their global transportation network. Airbnb uses Python for their booking platform, pricing optimization, and fraud detection systems that process millions of transactions annually.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Automated Decision Making - Tesla's autopilot system relies heavily on Python for processing sensor data, computer vision, and neural network training. The company's Python-based AI systems make millions of driving decisions daily across their global fleet.
Natural Language Processing - OpenAI built ChatGPT using Python frameworks like PyTorch. The model's training and inference systems process billions of conversations, demonstrating Python's capability in handling complex AI workloads at scale.
Predictive Maintenance - General Electric uses Python to analyze sensor data from jet engines, wind turbines, and industrial equipment. Their Python-based predictive models prevent equipment failures, saving millions in maintenance costs and preventing costly downtime.
Web Development and Digital Platforms
Social Media Platforms - Instagram, with over 2 billion users, was built primarily in Python using the Django framework. Despite handling billions of photos and interactions daily, Instagram's Python foundation enabled rapid feature development and scaling.
Content Management - Pinterest uses Python for their core platform, recommendation engine, and spam detection systems. The platform serves 550+ million users, processing billions of pins and searches using Python-based infrastructure.
Business Automation and Operations
DevOps and Infrastructure Management - Dropbox built their file synchronization and storage platform primarily in Python, serving over 700 million users. Python's automation capabilities enable Dropbox to manage massive server infrastructure with relatively small operations teams.
Scientific Research and Development - NASA uses Python for data analysis, mission planning, and equipment control. The Mars Rover missions rely on Python scripts for image processing, navigation, and scientific data collection, demonstrating Python's reliability in mission-critical applications.

Java vs Python: Which is Better for Future Business Growth?
The technology choices you make today will determine your company's ability to adapt, scale, and compete in an increasingly digital marketplace.
Both Java and Python are positioned strongly for the future, but they serve different strategic purposes in modern business technology stacks.
Market Trends and Industry Adoption
Python's Rapid Growth Trajectory - Python has become the fastest-growing programming language globally, driven by several business megatrends:
- Artificial Intelligence Boom: the majority of machine learning frameworks are built in Python
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Python dominates data science with 68% market share
- Cloud-First Development: Major cloud platforms offer extensive Python support
- Financial Technology: Banks and fintech companies increasingly adopt Python for quantitative analysis
Java's Established Enterprise Position - Java maintains its dominance in traditional business applications while evolving for modern needs:
- Enterprise Software: 90% of Fortune 500 companies use Java in their core systems
- Mobile Development: Android's continued growth keeps Java relevant for mobile-first strategies
- Microservices Architecture: Java's Spring framework leads enterprise microservices adoption
- Cloud Migration: Mature Java applications transition well to cloud environments
Emerging Technology Alignment
Python's Strategic Advantages for Innovation
- AI Integration: Businesses implementing AI/ML capabilities find Python essential
- IoT and Edge Computing: Python's simplicity makes it ideal for connected device management
- Automation and Process Optimization: Python excels at business process automation
- Research and Development: Universities and research institutions standardize on Python
Java's Strengths for Digital Transformation
- Legacy System Modernization: Java provides smooth migration paths for existing systems
- Scalable Cloud Architecture: Proven performance for high-load, distributed systems
- Security Compliance: Enterprise-grade security features meet regulatory requirements
- Integration Capabilities: Mature ecosystem for connecting diverse business systems

When to Use Java vs Python: Strategic Decision Making
The choice between Java and Python shouldn't be made in isolation. It requires careful analysis of your specific business context, technical requirements, and strategic objectives. Here's a framework to guide your decision-making process.
Java is the Strategic Choice When:
Performance is Mission-Critical
- Your application will serve millions of concurrent users
- Response times directly impact revenue (e.g., trading systems, gaming platforms)
- Infrastructure costs become significant at scale
- Real-time processing requirements with minimal latency
Example: An e-commerce platform expecting Black Friday traffic of 10+ million users should prioritize Java's performance advantages to avoid costly downtime and lost sales.
Enterprise Integration is Essential
- Your organization has existing Java-based systems
- You need seamless integration with enterprise software (SAP, Oracle, IBM)
- Compliance and security requirements are stringent
- Long-term maintenance and stability are priorities
Example: A Fortune 500 company implementing a new CRM system should consider Java for better integration with existing enterprise infrastructure and proven security standards.
Mobile-First Strategy
- Android development is central to your business model
- You're building consumer-facing mobile applications
- Cross-platform mobile solutions are required
- Native mobile performance is crucial
Example: A fintech startup focusing on mobile banking should leverage Java's Android development advantages and performance benefits for financial transactions.
Large Development Teams
- You manage teams of 10+ developers
- Code quality and consistency across team members is challenging
- You need strict development standards and error prevention
- Long-term maintainability by different developers is important
Python is the Strategic Choice When:
Speed to Market is Critical
- You're in a competitive market requiring rapid innovation
- MVP development and user feedback cycles are essential
- Budget constraints require efficient development resources
- Time-to-market determines competitive advantage
Example: A startup building a SaaS product should choose Python to validate their business model quickly and iterate based on customer feedback.
Data-Driven Business Model
- Customer analytics and insights drive business decisions
- Machine learning and AI capabilities provide competitive advantages
- You need to process and analyze large datasets regularly
- Integration with data science workflows is essential
Example: A marketing technology company building customer segmentation and recommendation systems should leverage Python's dominant data science ecosystem.
Innovation and Experimentation
- Your business model relies on continuous experimentation
- A/B testing and rapid feature deployment are routine
- Research and development activities are core to your strategy
- Collaboration with academic or research institutions is common
Example: A healthcare technology company developing diagnostic AI tools should use Python for faster research iteration and access to cutting-edge ML frameworks.
Resource Constraints
- Limited development budget requires maximum efficiency
- Small, agile development teams (2-5 developers)
- Rapid scaling of development capabilities is needed
- Lower complexity and maintenance overhead is preferred
Hybrid Approaches: Best of Both Worlds
Many successful companies use both languages strategically:
Common Hybrid Patterns
- Core System in Java + Analytics in Python: Use Java for user-facing applications and Python for data processing and insights
- MVP in Python + Scale in Java: Prototype and validate with Python, then rebuild performance-critical components in Java
- Microservices Architecture: Use Java for high-performance services and Python for rapid feature development
- API-First Integration: Build Java backend systems with Python-based tools and automation
When Hybrid Makes Sense
- Large organizations with diverse technical requirements
- Companies transitioning from traditional enterprise to data-driven approaches
- Businesses with both performance-critical and innovation-focused initiatives
- Organizations with separate teams specializing in different technologies
Making the Strategic Choice Between Java and Python
The most successful technology leaders don't ask "Which language is better?" Instead, they ask "Which language best serves our specific business goals?"
Both Java and Python are mature, well-supported technologies that can power successful businesses. Your choice should align with your company's competitive strategy, operational constraints, and long-term vision.
Whether you choose Java, Python, or a strategic combination of both, success depends on execution, team expertise, and alignment with your broader business strategy.
Need Expert Guidance?
Choosing the right technology stack is a critical decision that impacts your entire development trajectory. At Softjourn, our experienced Java and Python engineers have helped hundreds of companies make informed technology decisions that align with their business objectives.
Whether you need deep technical expertise in Java enterprise development, Python AI/ML implementations, or strategic consulting to evaluate the best tech stack for your specific requirements, our team will provide the guidance and execution capabilities to ensure your technology choices drive business success.
Contact our friendly consultants to discuss your project requirements and get expert recommendations tailored to your business goals.