Data-driven decision making (DDDM) is revolutionizing how organizations operate, with measurable benefits in customer acquisition, profitability, and strategic effectiveness across industries. It is an approach that ensures that business decisions made within a company are not based simply on personal observations or instinct, but are backed by hard data from multiple sources.
Data-driven decision-making has become increasingly important for organizations, and the statistics support its benefits. Here are some key statistics that highlight the advantages of data-driven organizations:
- Data-driven organizations are 23 times more likely to acquire customers, six times as likely to retain customers, and 19 times more likely to be profitable
- Highly data-driven organizations are 3 times more likely to report significant improvement in decision-making
- According to a survey of senior executives, highly data-driven organizations are three times more likely to report significant improvement in decision-making
These statistics emphasize the significant advantages that data-driven decision-making can offer to organizations in terms of customer acquisition, retention, profitability, and overall improvement in decision-making processes.
In this article, we will show you how data-driven decision making is applied in various fields, with a special focus on fintech and ticketing.
What is Data-Driven Decision Making?
Data-driven decision making (DDDM) is the practice where data is collected, analyzed, and decisions are made based on the insights derived from the collected information.
DDDM uses past information to predict what is to happen in the future since without necessary and objective data, there is a greater risk of performing on false assumptions and being swayed by biases.
Using data collected from multiple sources requires structured processes including data collection, processing, and data visualization to provide decision-makers with actionable analytics. This enables leaders to understand what the next step in their business should be based on evidence rather than intuition.
Every data-driven decision making process requires setting up Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and other benchmarks that will follow the KPIs. KPIs are quantifiable measures of performance that help businesses to track their progress and see how close they are to achieving business goals. There are a number of different KPIs and value metrics that have the sole purpose of measuring the performance of systems and their business impact.
The success of data-based decision making depends on various factors, such as the methods used for data collection and the quality of the data gathered. Data-based decision management is heavily quantitative, and this usually requires businesses to have powerful machines capable of computing and analyzing large sets of data efficiently.
How to Build a System for Data-Driven Decision Making
Making data-driven decisions depends on creating a robust organizational mindset. It's a process that every affiliated individual needs to understand and apply on a daily basis to create sustainable competitive advantage.
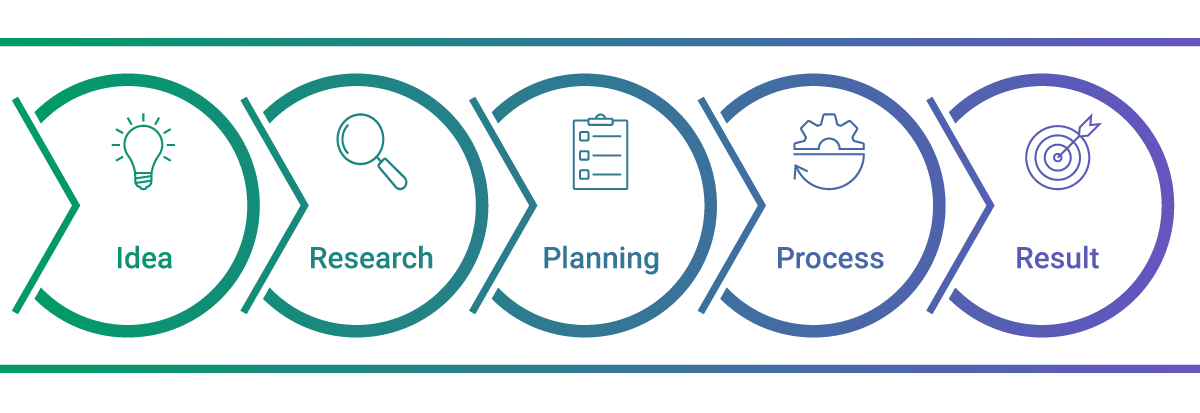
Setting up a data-driven decision making flow is the key to advantageously using all the available information to make informed decisions. Such a system has several stages:
- Identifying a problem
- Collecting and processing internal and external data
- Creating reports, dashboards, and visualizations
- Making informed decisions
- Measuring the outcomes using KPIs
Identifying a problem is the first step toward understanding the type of data necessary to address the issue. Once the problem is defined, the next step is to understand everything surrounding it and find the data necessary to validate assumptions.
Collection and processing of necessary data enable deeper analysis. Using data pipelines, data lakes or warehouses ensures that data is captured without any bias that favors a particular outcome. The collected data is typically analyzed using programming languages like Python or R for statistical modeling and insight generation.
Creating reports, dashboards and visualizations ensures that complex data is visualized in a way that makes it easily understandable for everyone involved in the decision-making process. In the end, stakeholders are presented with the data captured by various charts, graphs, and dashboards.
Making informed decisions becomes more systematic when there is a decision model in place. Without such a framework, making programmed and unprogrammed decisions often takes more time as it requires extensive data to support certain conclusions.
Measuring outcomes with KPIs is essential for assessing the performance of any decision. Developing good KPIs, targets, and goals takes time, but once they have been created, the decision-making process outcomes and the success of every decision become measurable.
Advantages of Using a Data-Driven Decision Making
1. Greater Transparency and Accountability
Data-driven decision making, along with clear and concrete goals, improves transparency in companies, especially when all data is considered without bias and overall results are measured accordingly.
An organization-wide approach that focuses on data allows employees to better understand the importance of data-backed decisions and encourages staff to adopt data-driven decision making in their daily work. This, in turn, helps the organization mitigate risks and enhance its overall performance while boosting employee morale through increased clarity and purpose.
Organizations are seen as more accountable when they collect and properly manage objective data and use it for record keeping and compliance.
2. Continuous Improvement and Innovation
Data-based decision management indirectly opens up space for improvement and innovation. Organizations can implement incremental changes, monitor vital metrics, and make further changes based on captured data. Client feedback can push a business in the right direction.
3. Faster Decision Making Process
Precise analytical insights help solve multiple problems for business. Data-based decision management often calls for entrepreneurs to mine data to obtain predictive and prescriptive insights.
When an organization bases decisions on data and facts rather than intuition, the speed of decision making dramatically increases. Through the analysis of real-time data and historical patterns, the decision making process becomes not only faster and more reliable, but also gives leaders confidence that they're making strategically sound choices.
4. Clear Feedback for Market Research
The data-driven decision making approach helps organizations formulate new products, services, workplace initiatives, and identify emerging trends. By analyzing historical data, companies can better anticipate market changes and make proactive adjustments to their strategies, products, and operations based on data.
Businesses can analyze client feedback to understand how to maintain a great relationship with their customers and discover smart ways to introduce new products and services to move their brand forward.
Challenges of Data-Driven Decision Making
Data-based decision making is a model that helps organizations improve the accuracy of their decision making process, but it does come with its own set of challenges.
1. Low Quality of Collected Data
When collecting data, the goal is to gather information that has relevance and accuracy. However, if the data collected is of low quality, incomplete, or doesn't contribute to understanding the problem at hand, it may be counterproductive to use. High-quality data is easier to process and leads to more accurate insights.
2. Different Data Formats
Collecting different types of data to support DDDM is a necessary part of the process. However, if the data is saved in JSON, CSV, or XML formats, you’ll likely need scripts to convert it into one format. An easier approach is to use data management tools to collect and format everything using one universal standard.
3. Learning Curve for Interpreting Data
Gathering and interpreting data require different skillsets. It is important to educate teams so they understand both processes to ensure quality insights. Since every employee is in some way involved in DDDM, providing training on data literacy and analysis best practices is essential for building a true data-driven culture.
The Influence of Big Data on Business
Data-driven decision making already has a significant impact on different types of businesses, including Fortune 500 companies, across every industry. According to research from the IDC, global spending on big data reached $215 billion in 2021, which was an increase of 10% from the previous year.1
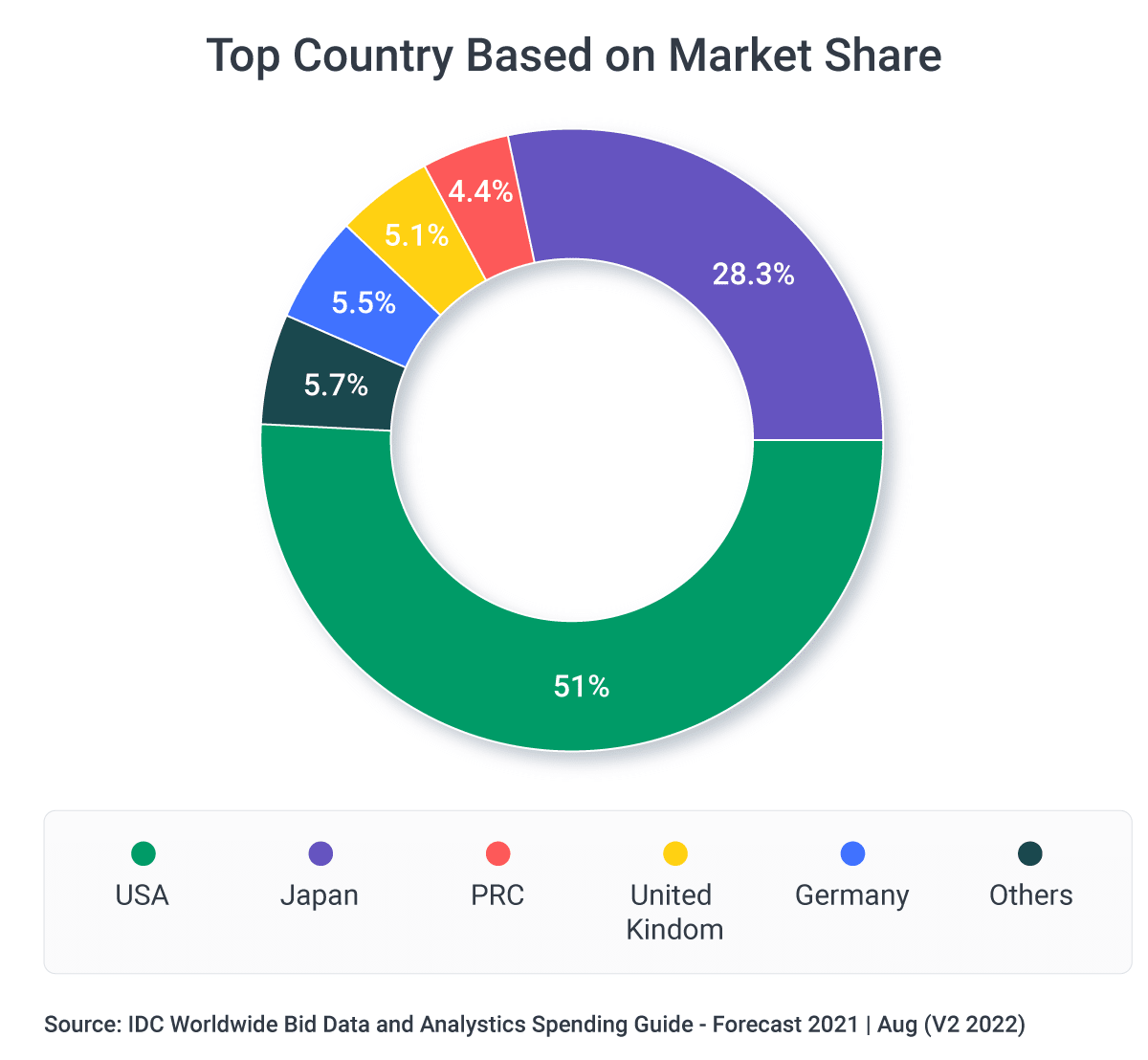
The industries that are currently making the biggest investments in big data and analytics are banking, IT, discrete manufacturing, professional services, process manufacturing, and telecommunications. The biggest markets, when it comes to big data and analytics, are the United States, Japan, China, and the United Kingdom.
But investing in DDDM doesn't automatically guarantee successful implementation; it requires creating the right environment for smart decision making to thrive. Similarly, optimizing operations requires both robust data infrastructure and a culture that values and understands data analysis.
For those companies that manage to balance strong data and a smart decision making process, they must also cultivate an effective culture that promotes the value of data to their team members.
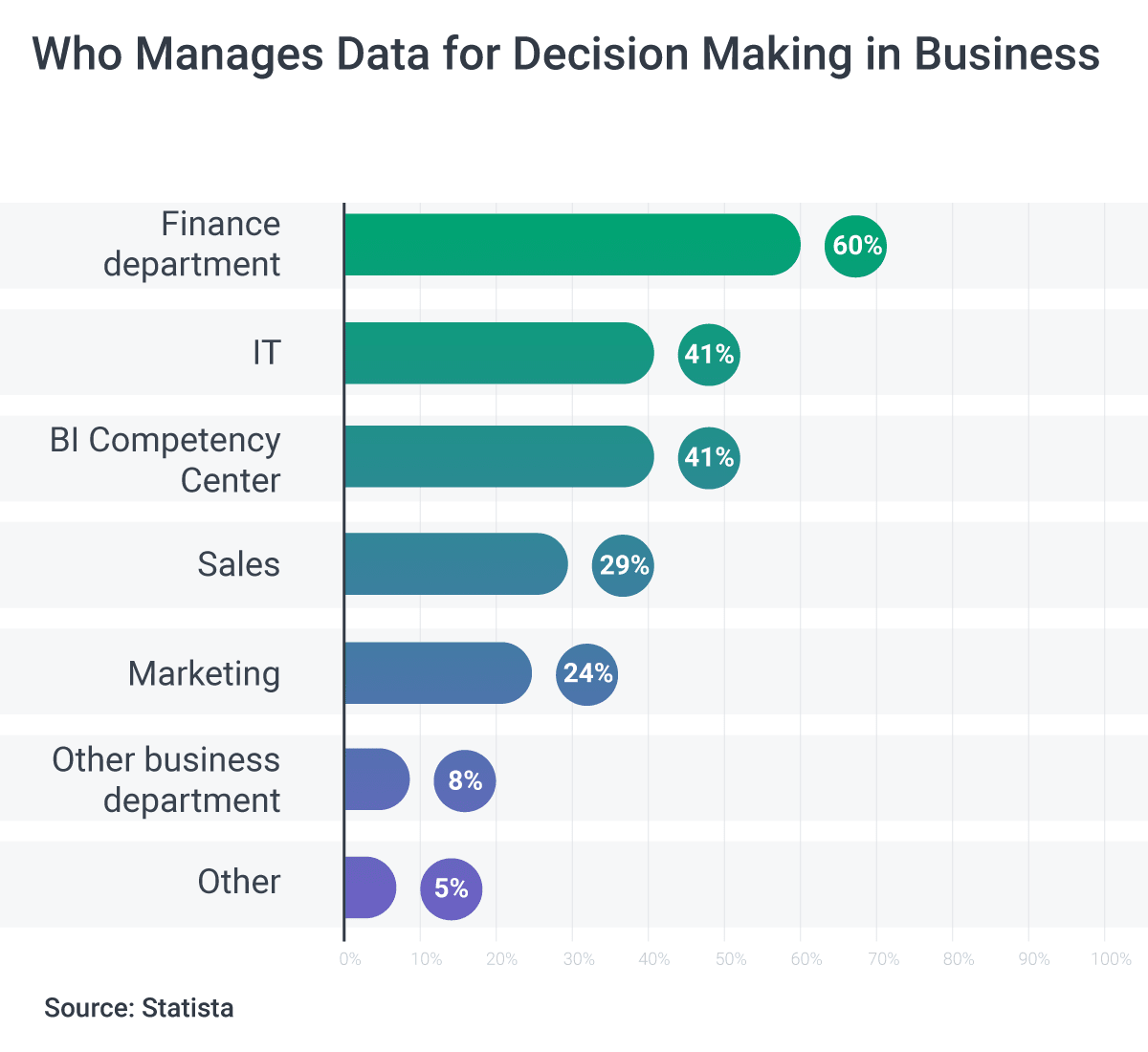
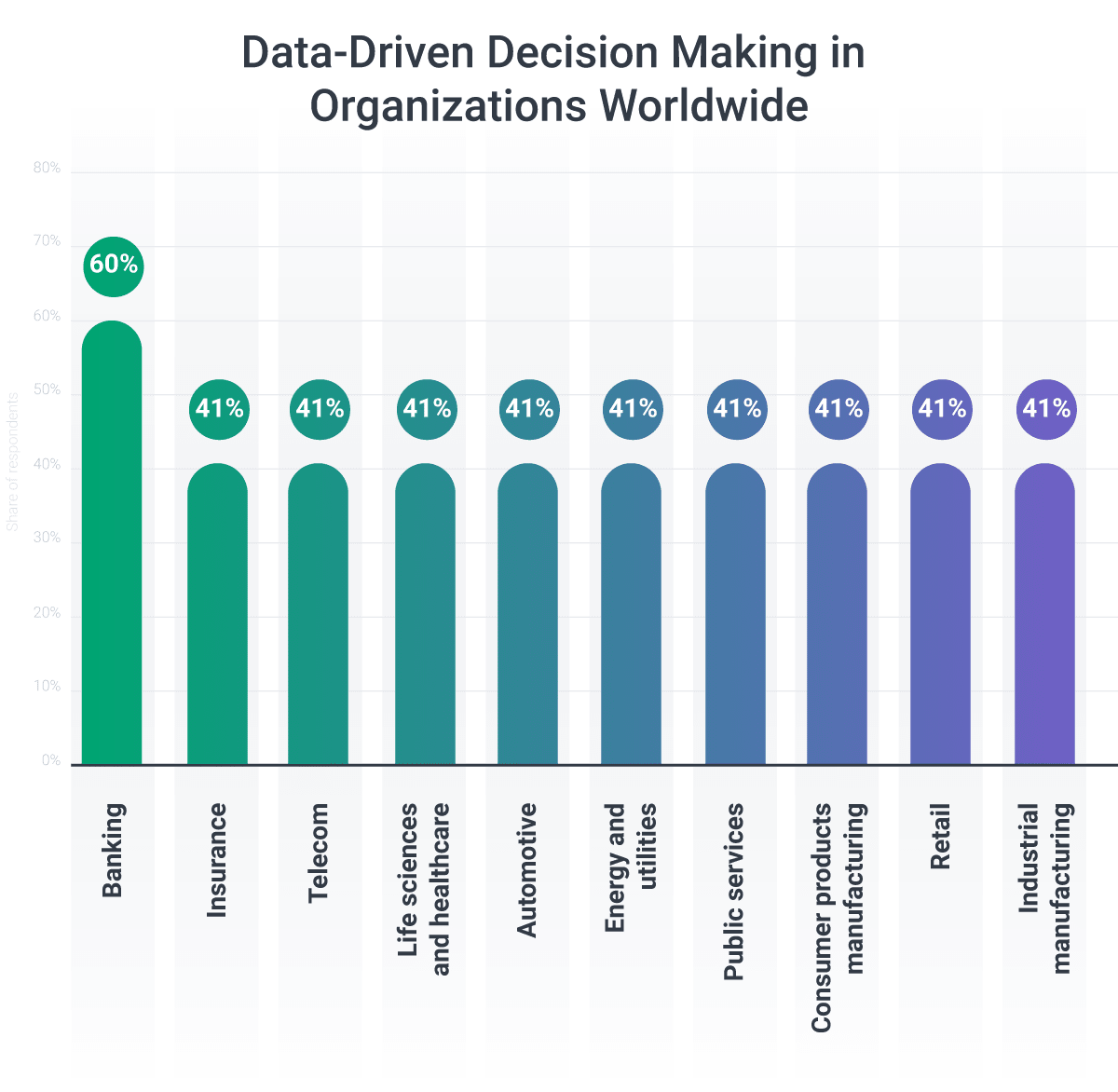
When it comes to industries leading the adoption of data-driven decision making, finance, IT, and sales are at the forefront. Data-driven decision making has evolved from being optional to absolutely necessary for various industries to navigate unplanned changes in their business environment. Every sector, from banking and insurance to healthcare, transportation, and entertainment, can benefit from understanding and utilizing data to make strategic decisions.
Data-Based Decision Making in Banking
To remain competitive in the financial sector, institutions must prioritize customer experience. Banks and financial organizations have recognized that their success largely depends on customer satisfaction and retention, and are now leveraging large volumes of customer data to gain deeper insights into preferences, behaviors, and loyalty factors.
Millennials and GenZ mobile banking customers expect banks to create hyper-personalized experiences that are engaging, easily understandable, and consistent on all channels.
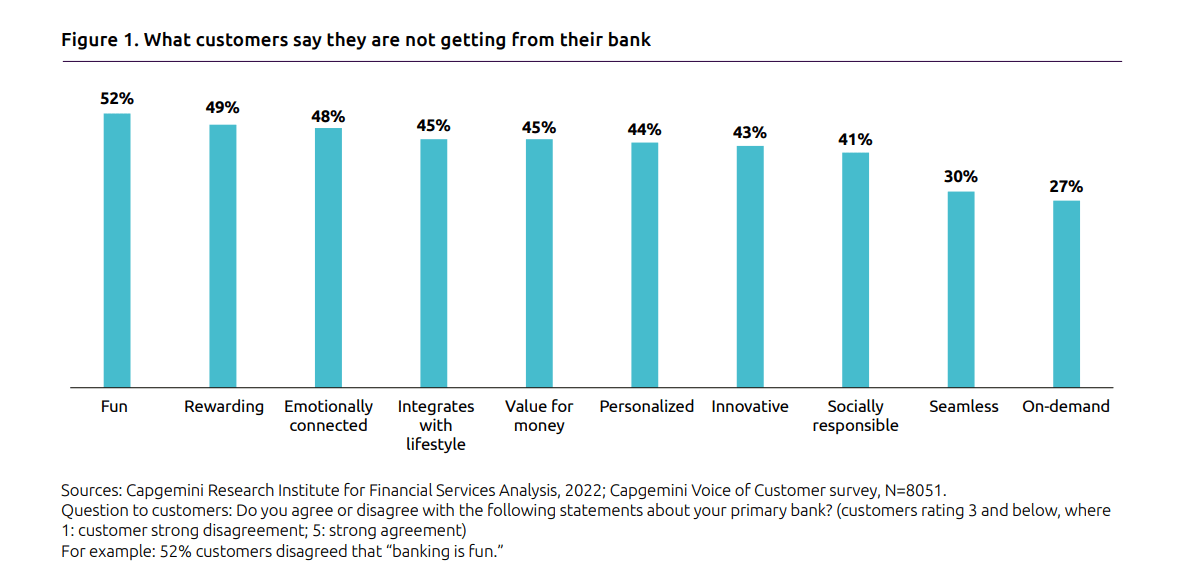
According to a 2022 financial services survey, approximately 75% of traditional bank customers report being attracted to FinTech competitors primarily because they offer faster processing times and more intuitive user interfaces.
Fintech companies are actively using DDDM to create new experiences and specialized customer journeys on their platforms, and traditional banks are falling behind. Many of them are still struggling just to identify what their clients want and how to deliver it, much less develop interesting and innovative solutions.
Banking is moving from real-time and in-person communication to online platforms and apps. Platform-based models come with many challenges, but they can also create a chance for huge gains if implemented in the right way. Options for procuring new revenue are there, but they depend greatly on instituting data-driven decision making processes and straying away from a traditional mindset.
Fintechs are rapidly making waves in the industry due to their use of innovative tech and simply because they approach the market with different mindsets than banks. They have been accelerating customers’ expectations, especially when they relate to convenience and simplicity. Competing in this platform-based sphere requires a different mindset, willingness to change, and a new set of skills to unlock the potential rewards.
Advantages of Date-Based Decision Making in Banking and Finance
Innovative and data-driven approaches have enabled fintechs to acquire clients rapidly, while many traditional financial institutions struggle to keep pace with digital offerings that customers increasingly demand.
Neobanks and fintechs are investing heavily in digital products and services, but to make them successful, they need big data analytics, machine learning, and other tools to provide them with actionable insights. Here are the top advantages of DDDM for banking and why all banks should jump on the bandwagon before it is too late.
Source
1. Strengthens Banking Capabilities
With data-driven decision making, brick and mortar banks are adapting their business models to the new business landscape. By embracing digital tools to assist them in collecting, analyzing, and using data to make informed decisions, banks learn about their customers and resolve their pain points much faster and easier than before.
2. Provides a Better Understanding of Customers’ Needs
Understanding customers' demographics, income, spending habits, and behavioral patterns offers valuable insights into financial management preferences. Banks can provide their customers with targeted offers by using insights generated from data analysis. Whether it's BNPL, a digital wallet app, or really any type of digital service, DDDM allows management to understand what products they need to develop to compete in the digital market.
3. Builds Stronger Relationships with Customers
User-personalization offers a way for banks to engage with customers and anticipate their needs - this keeps customers satisfied to use your service time and again. Banks have the opportunity to use data to identify customer groups and create new products with a client-focus.
DBS Bank: Better Services Thanks to Advanced Analytics
One of Singapore's largest banks, DBS, recognized that fintech competitors would attract their clients if they didn't match innovative digital offerings. DBS invested in DDDM and advanced AI systems to develop deeper understanding of their customer base. This helped them to create hyper-personalized financial advice and promote new product offers tailored to their patrons.
Using intelligent banking, the bank started offering stock recommendations, notifications on favorable FX rates, and new products customers might enjoy using. Today, employees across DBC Banks are able to use all data to help clients address problems, understand their pain points, and serve them better than ever before.
CIBC Bank; Using Data-Driven Personalization
CIBC, a Toronto-based bank, started working on a robust customer-centric platform to deliver a more customized experience for their customers. Using a third-party solution, they acquired new information about their customers, made customer profiles, and created specialized strategies to answer their specific needs.
A data-driven approach gave CIBC the capability to deliver targeted mobile promotions to customers and dynamically update product pages based on user behavior and preferences. It offers advantages for busy customers, such as the ability to set up deposit payments, send requests, or apply for mortgage payment adjustments in just a few seconds.
The benefits of this approach were quickly visible with CIBC’s acquisition rate rising by 65%. The bank is continuing to invest and think innovatively, and its next objective is to enable its clients to set goals and receive help and information from bank advisors on their requests.
Data-Based Decision Making in the Ticketing Industry
Creating exciting and one-of-a-kind events has never been as hard as it is now. Exceedingly, the majority of event organizers are adopting attendee-centric ways to strategize event planning. It has become essential to focus on engaging audiences, and luckily data can be leveraged to ensure event success.
Ticketing systems are able to process incredible amounts of data about ticket holders and events. If you currently use a modern ticket system, you may already have all of the data and analytical tools you need to get started on making smarter decisions for your company.
When set up correctly, a ticketing system can help your company save a considerable amount of time and money, making it a worthy investment. Ticketing platforms play an essential role in business industries with a substantial amount of data, as they can easily deal with bulk requests that require fast speeds.
However, collecting excessive or irrelevant data can obscure meaningful insights into participant behavior during events. Focus on gathering the most relevant metrics for decision making to simplify data interpretation. Starting with basic data collection and analysis provides foundational knowledge about which metrics deliver the most value for your specific needs.
Advantages of Data-Based Decision Making for the Ticketing Industry
While it is clear that too much and unrelated data or an unclear focus can be problematic, if used correctly, data-based decision making has huge potential for success in the ticketing industry. Here are ticketing-specific advantages of DDDM and how you can utilize data sources at your next event:
1. Create personalized Attendee Experiences
Personalized event experiences are within reach when fans use RFID, iBeacon, or VR, because these technologies enable customized interactions based on individual preferences and behaviors.
For example, sending fans on a scavenger hunt using a digital map marked with interactive checkpoints, where certain items become downloadable, is a fun way for fans to explore a venue. Another fun activity is to use RFID-enhanced chips, which can be embedded in badges, labels, and lanyards, that open access to certain prizes depending on their location.
If you want to customize your event based on fan suggestions, you can send a pre-event questionnaire where fans can share their preferences. Alternatively, if fans are interested in connecting with other participants, an event app can allow attendees to collect each other’s e-business cards.
2. Use Data to Make Real-Time Adjustments
Real-time data collection allows event organizers to monitor participant engagement levels during an event. If analytics indicate attendee disengagement, organizers can trigger notifications, engaging calls to action, or suggest alternative event activities to improve the experience.
There are two basic data-collection approaches: active and passive, which can affect the quality of the raw data collected. Gathering active data focuses more on attendees’ activities within an event application, while the passive approach collects data as the participant moves through the event.
You can use wearables to keep an eye on the most popular areas at a venue to see where people like to spend their time. Event managers can use the data to offer more activities in those places and arrange spaces efficiently for varying group sizes and activity-type.
3. Resolve Crowd Flow Issues
New technology allows event organizers to understand crowd density so that the venue design, entrance and exit flow, and management procedures are optimized for best performance. Long lines at the entrance are usually a signal that something isn’t working, and with that data, organizers can set up additional check-in spots.
Attendees who wander around misguidedly may need better signage at the event or a map inside the event app to direct them. Tracking seating trends is also helpful in understanding if there are gaps, oversaturated spots, and any other seating problems.
4. Using Data for Dynamic Ticket Pricing
In ticketing, dynamic pricing is a successful selling strategy that adjusts ticket prices based on demand, timing, and customer segments. The price varies intentionally to optimize overall profit and influence purchase timing. Modern dynamic pricing systems use automated algorithms that offer the same ticket at different price points to different customers based on their purchase history, browsing behavior, and other factors.
Traditionally, prices in retail were set based on static rules using limited data inputs, which left potential revenue opportunities untapped. In today's fast-paced environment, data-driven dynamic pricing strategies leverage comprehensive consumer analytics to optimize pricing decisions. The proliferation of big data has unlocked significant new revenue opportunities through intelligent, responsive pricing solutions.
Examples of Data-Driven Decision Making Across Industries
New technologies and data analytics capabilities are disrupting traditional business models across industries. In every sector, DDDM is transforming operational practices, and organizations face a critical choice: adapt to data-driven methodologies or risk market obsolescence.
Big entertainment platforms are growing at an exponential rate, and big data has an immense impact on advertising and entertainment since it influences: viewer behavior predictions, ad targeting, video ratings, retention analyses, and stream schedule.
Netflix: Using DDDM to Understand Users and Plan New Content
Developing new and exciting content is not a walk in the park, even for a media giant like Netflix. The entertainment industry is developing faster than ever, and staying relevant requires using all tools at your disposal, including DDDM, to move in the right direction. The data Netflix collects is vast, for example, it remembers which shows users watched and at what time, content abandonment rates, scrolling behavior, and searches.
Netflix utilizes data to run predictive analysis to learn what their viewers like to watch the most, how receptive they are to content, and where their interests lie. By analyzing millions of subscriber ratings and searches, they’ve made well-researched conclusions about the type of content they need to produce.
In addition, Netflix uses data collected from users to predict what would be the next best show for a particular user to watch and offers recommendations based on previous behavior on the platform.
Uber: Understanding Data Leads to Better Services
Everyone in the world knows what Uber is. However, the road to success and notoriety wasn’t as easy as it may seem, and it was working with data that helped them get to the point they are today.
After implementing predictive analytics tools and DDDM, Uber is able to analyze historical data and various metrics surrounding the clients’ requests to understand which areas have supply issues and at what times of the day. They use this information preemptively to inform drivers to go to certain parts of the city and respond to any sudden increase in demand.
Shopify: Advanced Analytics Leads to Growth
Since 2004, Shopify has slowly grown to become one of the biggest e-commerce platforms in the world. The key to their success is using data and AI to support their merchants. On Shopify’s tech blog, they shared a playbook they created to scale machine learning to show how valuable data is for optimization.
Another way Shopify uses data is by providing their best merchants with business loans. The team analyzes more than 70 million data points on sales history and overall performance, then they calculate the correct loan amount and send an offer.
The model Shopify is using surpasses any bias and focuses only on business performance and future potential. When Shopify made funding more accessible, it created a big change for merchants and validated the immense impact data has on their business.
How Can Your Company Adopt Data-Driven Decision Making?
An organization's data can reveal critical insights about productivity, operational efficiency, and growth opportunities. By analyzing this information, leaders can determine optimal strategic directions based on current performance metrics, future projections, and consumer analytics.
Businesses should establish transparent data management practices that enhance performance across all organizational levels. This approach fosters better decision making throughout the company while building employee trust and engagement.
We recommend that companies in ticketing and FinTech should have efficient ticketing information systems in order to take advantage of collecting and analyzing all data possible.
What your company can do:
- Make AI-based DDDM the base of customer experience
- Centralize all data
- Embrace real-time decision environments
- Enhance data management
Advantages of AI-Driven Decision Making
Thanks to artificial intelligence (AI), particularly machine learning (ML), advanced business information systems now support decision making by analyzing both historical patterns and predictive trends. These AI-powered systems can:
- Process massive datasets beyond human analytical capacity
- Identify subtle patterns and correlations that traditional analysis might miss
- Generate predictive models that anticipate customer needs and market shifts
- Automate routine decisions while flagging complex issues for human review
- Continuously improve through feedback loops and model retraining
![Advantages of AI-Driven Decision-Making [Infographics]](../../../media/images/Articles/Data-driven-decision-making/Advantages_of_AI_Driven_Decision_Making.png)
Let's summarize
Data-driven decision-making offers a multitude of benefits across various sectors and industries. Here are a few key benefits of data-driven decision-making:
- Improved Accuracy: Making data-based decisions helps eliminate bias and guesswork, leading to more accurate and reliable outcomes.
- Increased Efficiency: Data can reveal patterns, trends, and insights that can streamline processes, optimize resources, and improve efficiency.
- Risk Management: Data can help identify potential risks and challenges, allowing for proactive strategies and contingency planning.
- Competitive Advantage: Leveraging data effectively can provide insights into market trends, customer behavior, and competitive landscape, giving businesses a competitive edge.
- Predictive Capability: Advanced data analytics can forecast future trends and outcomes, enabling businesses to plan and strategize effectively.
- Personalization: Data can help understand individual customer preferences and behaviors, enabling businesses to offer personalized services and enhance customer satisfaction.
- Profitability: Through operational efficiency, risk management, and improved customer experience, data-driven decision-making can significantly boost profitability.
Remember, the key to reaping these benefits is not just having data but being able to analyze and interpret it effectively to inform strategic decisions.
Understanding Data-Driven Decision Making
Data is crucial for the overall performance of every organization. Because data is at the foundation of all processes, it makes sense that data-driven decision making is a powerful tool for companies to know what is working well and what is not.
When organizations have the ability to systematically analyze historical and real-time data, they can generate valuable predictive insights. This empowers leadership to implement evidence-based policies and strategies that drive organizational growth while enhancing operational transparency and accountability.
In the Ticketing and FinTech industries, among many others, data is not going anywhere; in fact, most systems make it easier than ever to collect and analyze data and predict industry trends.
If you want your business to maintain a competitive advantage in today's marketplace, implementing data-driven management practices is no longer optional—it's essential for survival and growth. Organizations that master data analytics will continue to outperform those that rely on intuition and experience alone.