When digital transformation drives competitive advantage, selecting the right programming language can make or break your technology strategy.
Python has emerged as one of the most strategic choices for enterprises seeking rapid development, cost-effective solutions, and future-proof technology stacks.
Over the last 30 years, Python has evolved from an academic language to a cornerstone of modern enterprise technology. Today, it powers everything from Netflix to NASA, making it a language that technology leaders can't afford to ignore.
This guide explains Python’s business impact – speed to market, total cost, talent availability, and cloud alignment – plus limits you should plan for.

What is Python Programming: The History and Business Impact
Python is a high-level, interpreted programming language known for its simplicity, readability, and versatility.
Created by Guido van Rossum in 1991, Python was designed with a philosophy that emphasizes code readability and developer productivity; principles that translate directly into business value through faster development cycles and reduced maintenance costs.
The Business Revolution Python Enabled
Python didn't just introduce a new programming language; it fundamentally changed how businesses approach software development. The language's "batteries included" philosophy means that most common programming tasks can be accomplished with built-in libraries, dramatically reducing development time and costs.
The rise of data science, artificial intelligence, and machine learning has positioned Python as the de facto standard for these transformative technologies.
When companies like Google, Facebook, and Amazon needed to build AI systems that would define the next decade of technology, they chose Python.
This strategic positioning has created a virtuous cycle: as more enterprises adopt Python for critical systems, the ecosystem grows stronger, attracting more talent and investment.
For technology leaders, this means choosing Python isn't just about immediate project needs but about aligning with the future direction of enterprise technology.
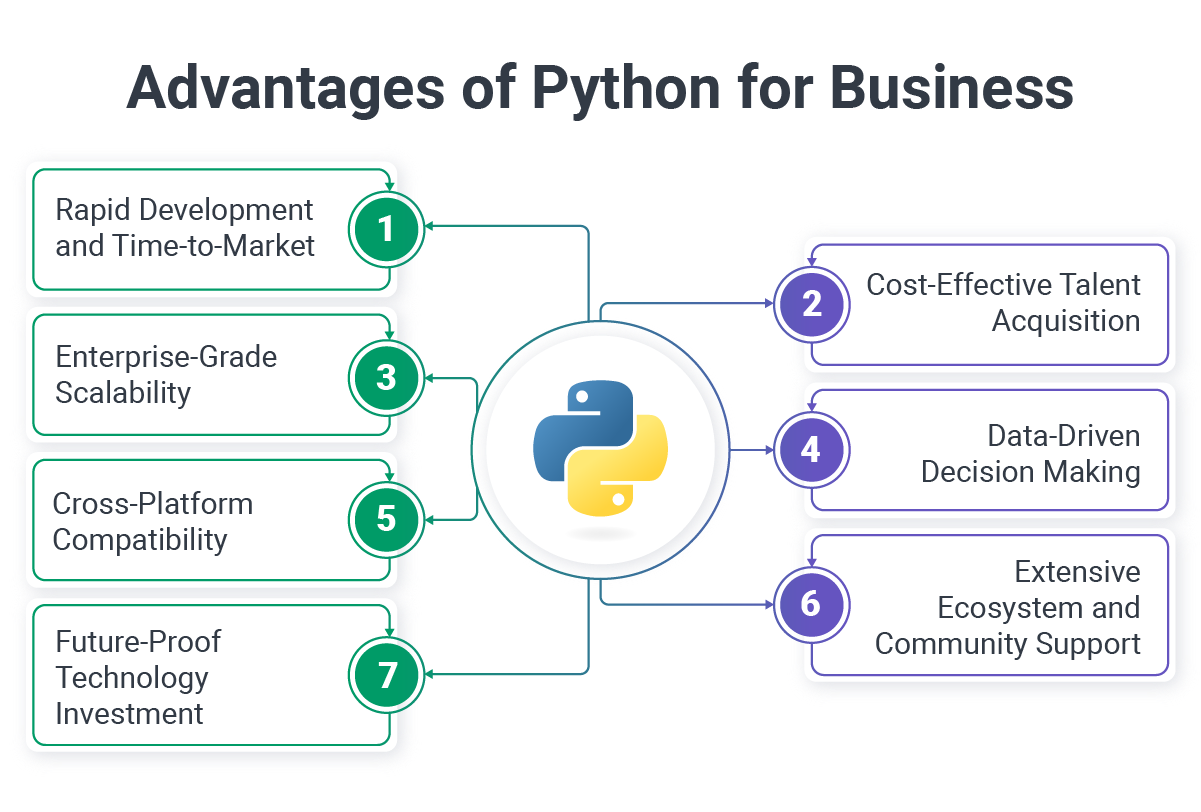
Advantages of Python for Businesses
The advantages of Python programming extend far beyond technical capabilities, offering tangible business benefits that impact your bottom line, development velocity, and competitive positioning.
Rapid Development and Time-to-Market
Python's simple syntax and extensive libraries enable significantly faster development cycles compared to traditional languages like Java or C#. This translates directly into competitive advantage: your products reach market faster, your MVP cycles are shorter, and your ability to respond to market changes improves dramatically.
For CTOs managing tight budgets and aggressive timelines, Python's development speed represents a significant cost advantage. Many development teams report substantially reduced project timelines when using Python, without sacrificing quality or scalability.
Cost-Effective Talent Acquisition
One of Python's greatest business advantages is the extensive talent pool. As of late 2025, the global number of Python developers has reached approximately 8.2 million, surpassing the estimated 7.6 million Java developers worldwide. Python is taught in universities worldwide and is often the first language developers learn. This widespread adoption means:
- Lower hiring costs: More candidates are available, reducing recruitment time and salary premiums
- Faster onboarding: New team members can become productive quickly due to Python's readable syntax
- Reduced training costs: Existing developers can learn Python faster than most other languages
Enterprise-Grade Scalability
Contrary to common misconceptions, Python scales effectively for enterprise applications when properly architected. Companies like Instagram handle billions of users with Python-based systems, proving that performance concerns are often overblown for most business applications.
Python's scalability advantages include:
- Horizontal scaling: Python applications scale well across multiple servers
- Microservices architecture: Excellent support for modern distributed systems
- Cloud-native development: Superior integration with AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure services
Data-Driven Decision Making
Python's dominance in data science and analytics provides unprecedented business intelligence capabilities.
With Python, your development team can build applications that not only serve users but also generate actionable insights about user behavior, system performance, and business metrics.
This integration eliminates the traditional barrier between application development and data analysis, enabling faster iteration and more informed product decisions.
Cross-Platform Compatibility
Python applications run consistently across Windows, macOS, and Linux environments. This cross-platform compatibility reduces infrastructure costs and provides flexibility in deployment strategies. For enterprises managing diverse technology environments, Python simplifies standardization efforts.
Additionally, Python’s ability to be embedded within other programming languages allows developers to integrate its code into applications built with languages like C++ and Java. This makes it possible to incorporate Python’s functionality seamlessly into existing systems.
Extensive Ecosystem and Community Support
Python's massive ecosystem means that most business requirements can be met with existing libraries and frameworks. This "build vs. buy" advantage significantly reduces development costs and risks:
- Proven solutions: Thousands of tested libraries for common business needs
- Community support: Large, active community providing free support and resources
- Enterprise backing: Major corporations like Google, Microsoft, and Facebook actively contribute to Python's development
One of Softjourn's Python software engineers, Volodymyr Miroshnychenko, said that a major advantage of Python is its community. There are tons of very useful third-party libraries that you can use in your projects," he stated.
Future-Proof Technology Investment
Python's central role in emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data science makes it a strategic technology investment. Organizations building Python capabilities today position themselves to leverage these transformative technologies tomorrow.
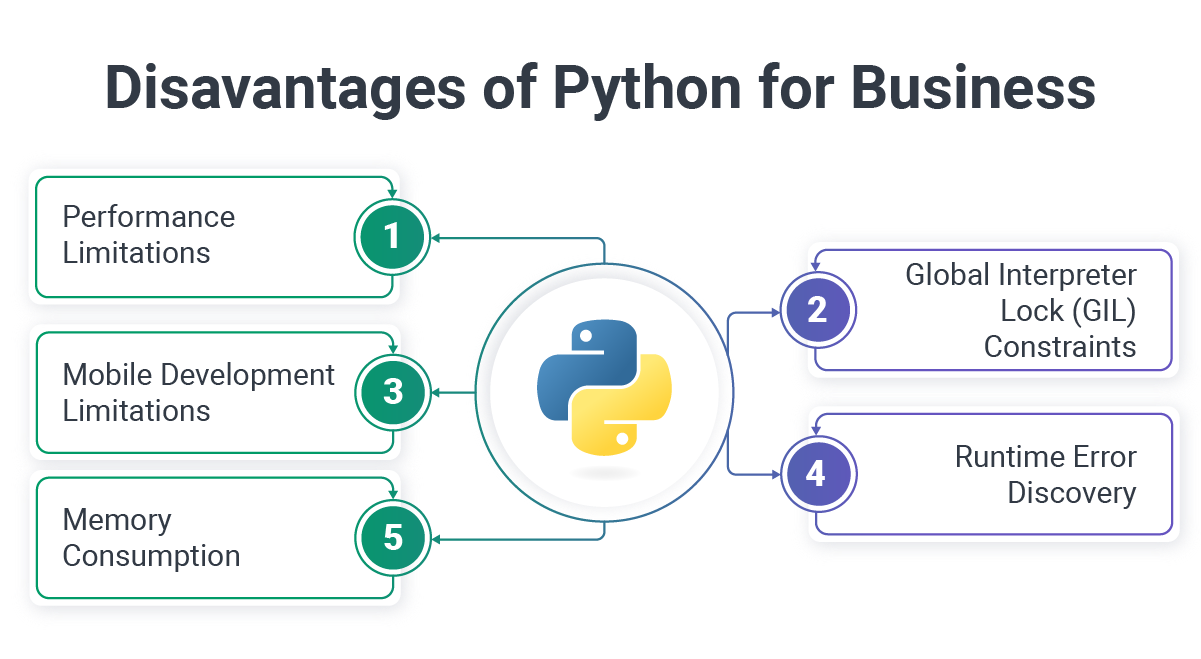
Disadvantages of Python for Businesses
While Python offers significant advantages, technology leaders must understand its limitations to make informed decisions and plan appropriate mitigation strategies.
Performance Limitations
Python's interpreted nature results in slower execution compared to compiled languages like C++ or Go. For latency-sensitive applications like high-frequency trading or real-time AI inference, Python may require additional infrastructure optimization or hybrid architectures.
However, this limitation affects fewer business applications than commonly believed. Most web applications, APIs, and business systems perform adequately with Python, especially when combined with performance optimization techniques.
Global Interpreter Lock (GIL) Constraints
Python's Global Interpreter Lock prevents true multi-threading for CPU-intensive tasks. While this limitation is often overstated, it can impact applications that require intensive parallel processing on a single machine.
Python’s concurrency model limits true parallel execution in some scenarios, but workarounds like multiprocessing and cloud scaling mitigate most enterprise use cases.
Mobile Development Limitations
Python is not the primary choice for native mobile application development. While frameworks like Kivy and BeeWare exist, they don't match the ecosystem maturity of native iOS/Android or cross-platform solutions like React Native or Flutter.
For enterprises requiring mobile applications, Python typically serves as the backend technology while other languages handle mobile interfaces.
Runtime Error Discovery
Python’s dynamic typing can introduce unexpected runtime errors, but strong testing strategies and enterprise-ready frameworks reduce risks.
Memory Consumption
Python applications can consume more memory than lower-level languages, which may affect infrastructure costs when working with massive datasets or high-scale environments.
However, Python's development speed advantages often offset increased infrastructure costs, especially when considering the total cost of ownership.

Best Applications for Python: What is Python Good For?
Python's versatility makes it suitable for a wide range of business applications, from startup MVPs to enterprise-scale systems.
Web Development and APIs
Python excels at building web applications and APIs that power modern businesses. Frameworks like Django and Flask enable rapid development of secure, scalable web services that integrate seamlessly with frontend technologies and mobile applications.
Business Benefits:
- Rapid prototype development for validating business concepts
- Easy integration with third-party services and APIs
- Strong security features built into popular frameworks
- Excellent support for modern architecture patterns like microservices
Data Science and Business Intelligence
Python's dominance in data science translates into powerful business intelligence capabilities. Organizations can build custom analytics platforms, predictive models, and automated reporting systems that provide competitive advantages.
Applications:
- Customer behavior analysis and personalization
- Financial modeling and risk assessment
- Supply chain optimization
- Predictive maintenance for manufacturing
- Marketing attribution and ROI analysis
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Python's AI and ML ecosystem is unmatched, providing access to cutting-edge technologies that can transform business operations. From chatbots to recommendation systems, Python enables practical AI implementation.
Business Use Cases:
- Automated customer service and support systems
- Fraud detection and prevention
- Intelligent document processing
- Personalized product recommendations
- Automated quality control and inspection
DevOps and Automation
Python excels at automation tasks that improve operational efficiency and reduce manual work. IT teams use Python for infrastructure management, deployment automation, and system monitoring.
Operational Benefits:
- Reduced manual errors through automation
- Faster deployment cycles
- Improved system reliability and monitoring
- Cost reduction through operational efficiency
Financial Technology
Python's combination of rapid development, extensive libraries, and strong security features makes it ideal for fintech applications. Many financial institutions use Python for trading systems, risk management, and regulatory compliance.
Scientific and Research Applications
Python's role in scientific computing makes it valuable for research-driven organizations and companies working with complex data analysis requirements.

Why do Businesses Choose Python for their Software Development Projects?
We asked our Python software engineer about the use cases he most often sees for clients who decide to use Python for their projects.
He described the three most common reasons:
For Cloud
"Nowadays, businesses try to use a serverless approach for their products. In the projects I work on, we use AWS services, specifically AWS Lambda. Since we need our app to start separately on each request, interpreted languages, like Python, are perfect here."
Easy Adaptability
"If you already have ML engineers and data analytics that use Python, it is relatively easy to assign them as Python web developers. Even engineers who use other programming languages can pretty quickly learn Python and start using it. This means Python works great when businesses need to pivot or scale quickly."
Python is Just Popular
"Since Python is such a popular language, there are so many more engineers in the market searching for work with this technology, in comparison to other languages. Plus, Python can be used anywhere from web development to ML to data analytics and beyond, so if your project might become complex, you have a language that covers your bases."

Real-World Examples: Companies that Use Python
Python powers technology infrastructure at some of the world's most successful companies, demonstrating its enterprise readiness and scalability.
Technology Platforms
Netflix uses Python for its recommendation engine, content delivery optimization, and data analytics platform. Python enables Netflix to process billions of viewing decisions and deliver personalized experiences to over 200 million subscribers worldwide.
Meta apps, including Instagram, use Python/Django for their backend as well as AI and ML pipelines, and automation scripts, proving that Python can scale to support over 1 billion users with billions of photos and interactions daily.
Reddit leverages Python for its backend web services and APIs, relying on its frameworks and scalability to support the platform’s rapid user growth.
Financial Services
JPMorgan Chase uses Python for risk management, trading systems, and regulatory reporting. The bank's adoption of Python for critical financial systems demonstrates the language's reliability and security for enterprise applications.
Goldman Sachs leverages Python for quantitative analysis, algorithmic trading, and client portfolio management systems.
Bank of America uses Python extensively, especially within its internal global markets platform called Quartz, which centralizes data and runs major enterprise and regulatory programs for the investment bank.
Enterprise Software
Spotify uses Python for backend services, data analysis, and recommendation algorithms that power music discovery for over 400 million users.
Uber relies on Python for pricing algorithms, driver matching, and data analytics that optimize their global transportation network.
Airbnb uses Python for their booking platform, pricing optimization, and fraud detection systems that process millions of transactions annually.
Our Clients Who Use Python
UPC uses Python as part of its backend infrastructure to power its Open Banking platform and payment processing systems. Working with Softjourn, UPC migrated from on-premise infrastructure to a secure, serverless AWS environment, improving scalability, maintaining PCI DSS compliance, and enabling seamless integration of APIs across multiple banking partners.
Tribal Credit uses Python as part of its fintech platform to support multi-currency payments, AI-driven credit approvals, and database optimization. Partnering with Softjourn, Tribal Credit transitioned from its 1.0 system to a faster, more scalable 2.0 platform while maintaining backend stability, improving performance, and accelerating product launches.
A Leading Expense Management Platform uses Python to automate manual approval workflows, streamline integrations, and accelerate reimbursements. Working with Softjourn, the client implemented custom automation scripts and direct-pay features, improving operational efficiency, reducing human errors, and saving users significant time across thousands of expense reports.
Will Python Remain Relevant in 2026 and Beyond?
Python's future relevance is secured by several strategic factors that make it a safe long-term technology investment.
AI and Machine Learning Dominance
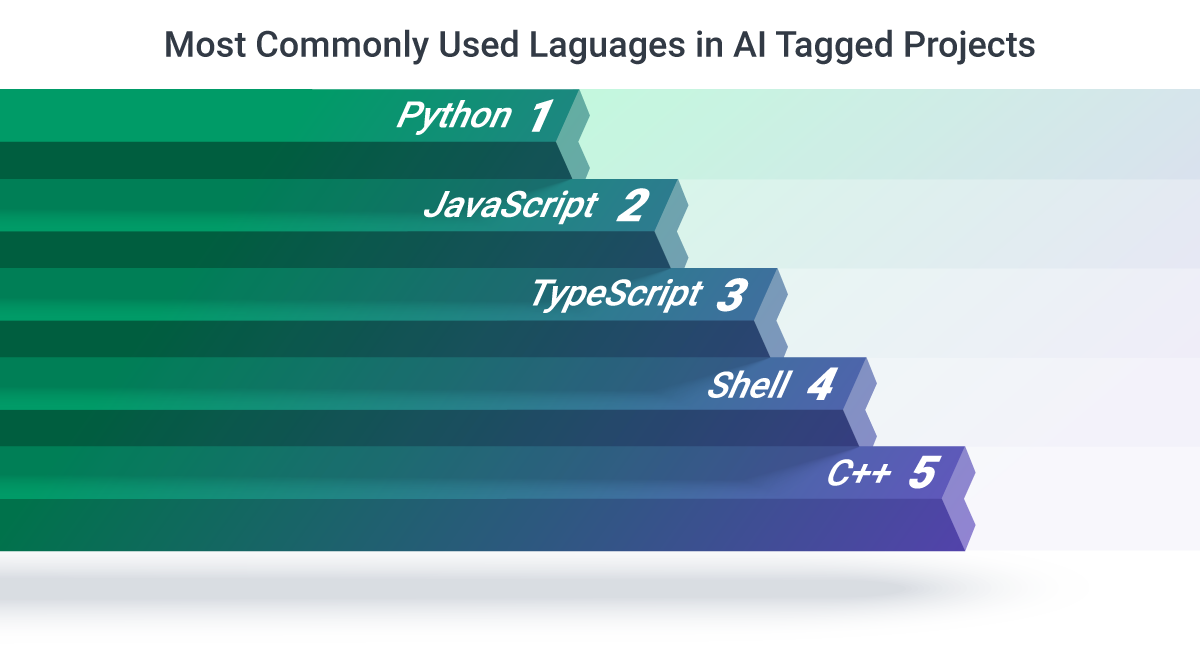
As artificial intelligence becomes central to business strategy, Python's dominant position in AI/ML ensures continued relevance. Major AI breakthroughs from OpenAI, Google, and other leaders consistently emerge from Python-based research, creating a self-reinforcing cycle of innovation and adoption. Interestingly, the most in-demand skill in AI-related job postings in the US is Python, with 152,201 postings citing it, far outpacing other technical skills.
Enterprise Adoption Momentum
Large enterprises are increasingly standardizing on Python for data science, automation, and web development. This enterprise momentum creates substantial switching costs and ensures long-term demand for Python skills and systems.
Cloud Platform Integration
Major cloud providers (AWS, Google Cloud, Azure) offer extensive Python support and services. This deep integration with cloud infrastructure makes Python a natural choice for modern, cloud-native applications.
Community and Corporate Investment
Python receives significant investment from major technology companies who depend on it for core business functions. This corporate backing ensures continued development, security updates, and performance improvements.
Educational Foundation
Python's role as a primary teaching language in computer science programs ensures a continuous pipeline of skilled developers, supporting long-term talent availability and cost-effectiveness. In fact, Python is now the most popular introductory teaching language at top U.S. universities.

Final Word
Python offers enterprises strategic advantages: faster innovation, lower development costs, and access to an extensive global talent pool. Its versatility across web, AI, data, and automation – making it one of the most future-ready investments in modern technology stacks.
That said, Python isn’t ideal for every business scenario. At Softjourn, we help financial institutions, technology providers, and enterprises evaluate the right technology mix and implement Python-powered solutions designed for scalability, compliance, and long-term ROI.
Our team of expert solution architects can help you assess whether Python is the optimal choice for your specific project through custom technology consulting.
If Python is the right fit, our experienced development teams have deep expertise in enterprise-scale Python applications, data science implementations, and AI/ML solutions to execute your vision successfully.





















