Choosing the right Python framework makes a big difference: it can cut your development timeline in half or double your infrastructure costs.
While Python powers everything from Instagram's web platform to OpenAI's machine learning infrastructure, the framework landscape has fragmented into specialized tools optimized for distinct use cases.
This guide breaks down the most popular Python frameworks by category, with a focus on strategic trade-offs that matter for project planning and resource allocation.
What Are Python Frameworks?
Python frameworks are pre-built collections of modules, libraries, and tools that provide a structured foundation for building applications.
Rather than writing every component from scratch, frameworks give your development teams reusable architecture that accelerates time-to-market while maintaining code quality and consistency.
For technical leaders evaluating technology stacks, understanding the most popular Python frameworks is crucial for making informed decisions about project architecture, team productivity, and long-term maintenance costs.
The right framework choice can mean the difference between a product that ships on schedule and one that encounters repeated technical debt.
Web Development Frameworks: Building Customer-Facing Applications

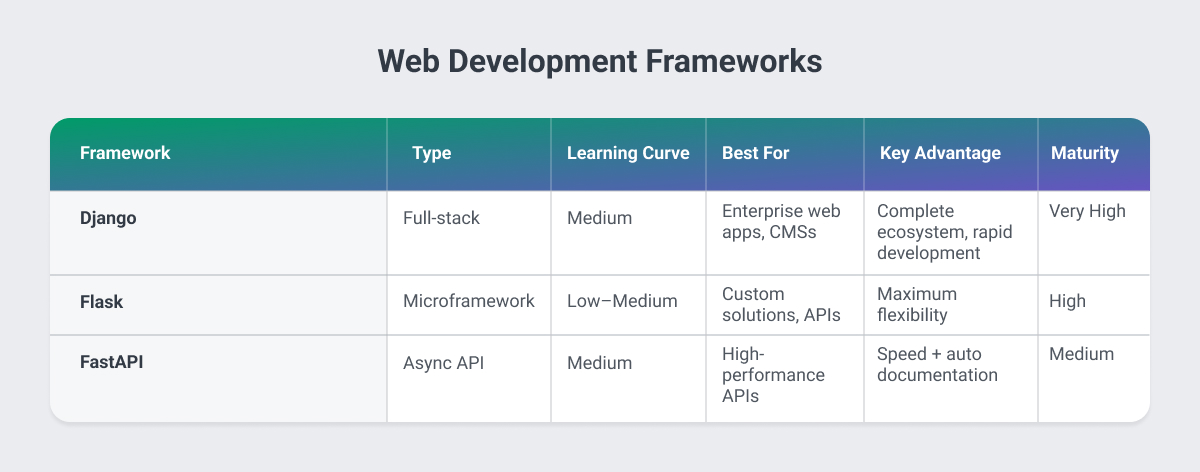
Django: Enterprise-Grade Full-Stack Development
Django remains one of the best Python frameworks for web development when your project requires robust, scalable infrastructure out of the box. This full-stack framework includes built-in admin panels, authentication systems, ORM (Object-Relational Mapping), and security features that would otherwise require months of custom development.
Business Value: Django's "batteries-included" philosophy means faster MVP development and reduced vendor lock-in. Major platforms like Instagram, Pinterest, and Mozilla rely on Django for handling millions of users, making it a proven choice for enterprises concerned about scalability.
Best For: Content management systems, e-commerce platforms, customer portals, and any application requiring rapid development without sacrificing enterprise security standards.
Flask: Flexible Microframework for Custom Solutions
Flask represents the opposite end of the spectrum among Python web development frameworks, as it's minimalist and unopinionated, giving your engineering team maximum flexibility. While Django prescribes architectural patterns, Flask allows teams to choose their own database layers, authentication methods, and project structure.
Business Value: Flask's lightweight nature reduces infrastructure costs and allows for highly customized solutions. It's particularly valuable when building API-first applications or when integrating with existing systems that don't fit standard patterns.
Best For: Custom internal tools, applications with unique requirements, projects where granular control over dependencies matters, and teams with strong architectural preferences.
FastAPI: Modern Async Performance
FastAPI has rapidly become one of the most used Python libraries for building high-performance APIs. Built on modern Python async capabilities, it delivers response times comparable to Node.js while maintaining Python's developer-friendly syntax.
Business Value: FastAPI's automatic API documentation generation reduces documentation overhead, while its built-in data validation reduces bugs in production. Companies report 30-40% faster API response times compared to traditional synchronous frameworks, directly impacting user experience and infrastructure costs.
Best For: Microservices architectures, real-time applications, data-intensive APIs, and projects where performance directly impacts business metrics.
Backend Frameworks: Powering Business Logic

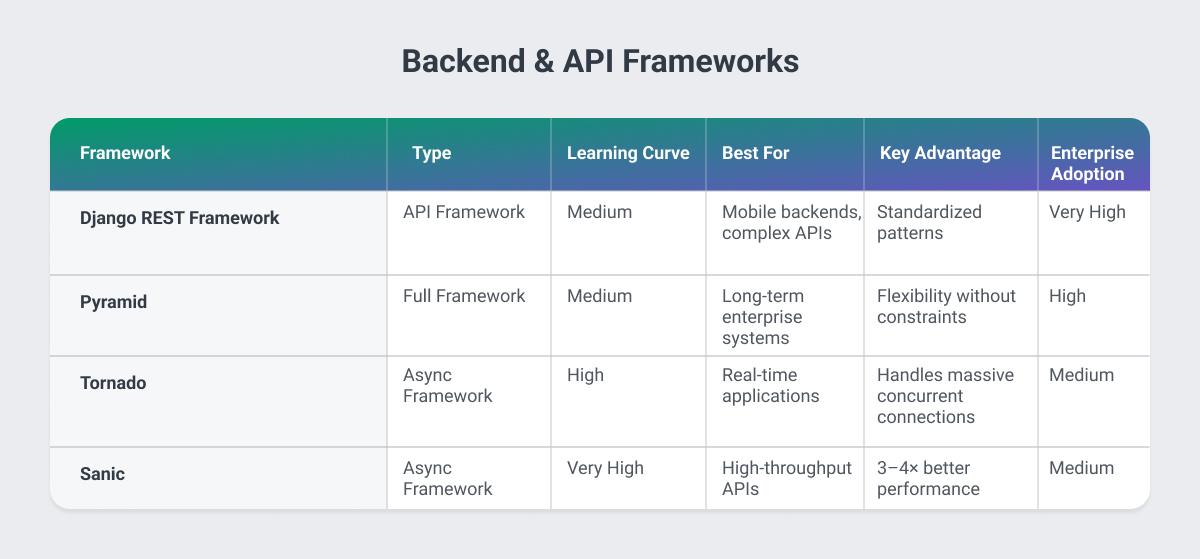
Django REST Framework: API Development at Scale
While Django excels at full-stack development, Django REST Framework (DRF) specializes in building robust backend APIs. It extends Django's reliability into the API space, providing serialization, authentication, and permission systems that enterprise applications demand.
Business Value: DRF's standardized approach to API development reduces onboarding time for new developers and creates consistent patterns across your API surface. Its mature ecosystem means fewer security vulnerabilities and faster resolution when issues arise.
Best For: Mobile app backends, partner API integrations, systems requiring complex permission structures, and organizations standardizing on Django across projects.
Pyramid: Flexibility for Complex Systems
Pyramid serves as a Python backend framework that scales from simple applications to complex enterprise systems. It's designed to avoid constraining architectural decisions, making it suitable for applications that will evolve significantly over time.
Business Value: Pyramid's flexibility prevents technical lock-in, allowing systems to grow organically without requiring rewrites. Organizations with long product lifecycles benefit from Pyramid's stability and non-prescriptive approach.
Best For: Long-term enterprise projects, applications with uncertain future requirements, systems requiring unique authentication or authorization patterns.
Python API Framework Options: Connecting Systems

Tornado: Real-Time at Scale
Tornado stands out among frameworks for python when real-time communication is critical. Originally developed at FriendFeed, it's designed for applications requiring long-lived network connections (think chat systems, live dashboards, or streaming data.)
Business Value: Tornado's non-blocking architecture allows single servers to handle tens of thousands of concurrent connections, dramatically reducing infrastructure costs for real-time applications.
Best For: Live notification systems, real-time analytics dashboards, chat applications, streaming data platforms.
Sanic: Async Speed Without Compromise
Sanic brings async/await syntax to web frameworks, positioning itself as the best Python web framework for high-throughput scenarios. It's designed specifically for applications where response time directly impacts revenue.
Business Value: In benchmark testing, Sanic handles 3-4x more requests per second than traditional synchronous frameworks, allowing businesses to serve more customers with less infrastructure.
Best For: High-traffic APIs, applications with strict latency SLAs, and cost-sensitive projects where infrastructure expenses are significant.
Data Science Frameworks: Turning Data Into Insights

Pandas: Industry Standard for Data Analysis
Pandas has become synonymous with data manipulation in Python, serving as the backbone for most Python frameworks for data science. Its DataFrame structure provides an intuitive way to clean, transform, and analyze structured data.
Business Value: Pandas' widespread adoption means your data teams can hire from a large talent pool and leverage extensive community resources. Its integration with visualization libraries enables rapid prototyping of data products.
Best For: Data pipeline development, business intelligence applications, data cleaning and preparation, and exploratory data analysis for product decisions.
Dash: Interactive Data Visualization
Built on Flask, Dash transforms Python data analysis into interactive web applications without requiring frontend development expertise. It bridges the gap between data science and business users, making insights accessible to non-technical stakeholders.
Business Value: Dash eliminates the need for separate frontend development teams when building internal analytics tools, reducing time-to-insight and project costs. Executives can interact with data models directly rather than waiting for static reports.
Best For: Executive dashboards, internal analytics tools, client-facing data products, proof-of-concept demonstrations for stakeholders.
NumPy & SciPy: Mathematical Foundation
While technically libraries rather than full frameworks, NumPy and SciPy form the computational backbone of the most used Python libraries in data science. They provide optimized numerical operations that make Python competitive with compiled languages for mathematical workloads.
Business Value: These libraries enable complex financial modeling, scientific computing, and algorithmic work without requiring teams to drop down to lower-level languages, maintaining productivity while achieving performance.
Best For: Financial modeling, scientific research applications, algorithmic trading systems, simulation, and optimization problems.
Machine Learning Frameworks: AI-Powered Products

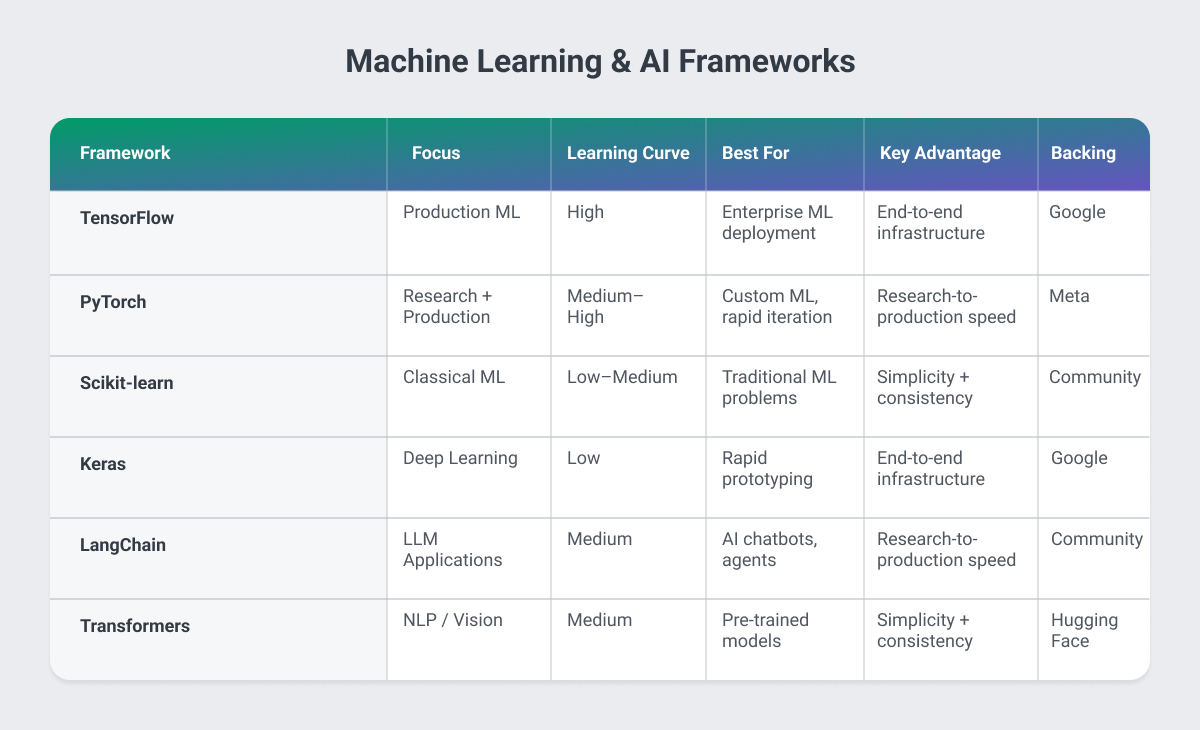
TensorFlow: Enterprise Machine Learning Infrastructure
TensorFlow ranks among the most popular Python frameworks for machine learning, backed by Google's engineering resources. It provides end-to-end infrastructure for building, training, and deploying ML models at scale.
Business Value: TensorFlow's production-readiness reduces the gap between data science experimentation and deployed products. Its model serving infrastructure (TensorFlow Serving) allows seamless deployment of ML models as APIs, reducing DevOps complexity.
Best For: Computer vision applications, natural language processing systems, recommendation engines, or any project requiring production ML deployment.
PyTorch: Research to Production
PyTorch has become the framework of choice for research teams and increasingly for production systems. Its intuitive API accelerates experimentation while its TorchServe component handles production deployment.
Business Value: PyTorch's popularity in research means access to cutting-edge pre-trained models that can dramatically reduce development time. Companies report faster iteration cycles compared to earlier-generation ML frameworks.
Best For: AI product development, projects leveraging the latest research, custom ML model development, and organizations prioritizing research-to-production speed.
Scikit-learn: Traditional Machine Learning
Scikit-learn excels at classical machine learning algorithms – regression, classification, and clustering – making it one of the best Python frameworks for projects that don't require deep learning. Its consistent API design reduces the learning curve for business analysts transitioning into ML.
Business Value: Many business problems are better solved with classical ML than deep learning, and scikit-learn provides these solutions with minimal infrastructure requirements. Projects ship faster with lower cloud computing costs.
Best For: Predictive analytics, customer segmentation, fraud detection, demand forecasting, recommendation systems for structured data.
Keras: Simplified Deep Learning
Keras serves as a high-level API for TensorFlow, dramatically simplifying deep learning model development. It's designed for fast experimentation, allowing data science teams to test hypotheses quickly.
Business Value: Keras reduces the time from idea to prototype, allowing businesses to validate ML concepts before committing significant engineering resources. Its simplicity also enables a broader range of team members to contribute to ML projects.
Best For: Rapid ML prototyping, projects with tight timelines, organizations building ML capabilities with smaller teams.
AI Frameworks: Beyond Traditional ML
LangChain: Large Language Model Applications
LangChain has emerged as a leading framework for building applications powered by large language models like GPT-4 or Claude. It provides abstractions for prompt management, memory, and agent behaviors.
Business Value: LangChain accelerates the development of AI-powered features compared to building directly against LLM APIs. It handles complex orchestration that would otherwise require significant custom development.
Best For: AI chatbots, document analysis systems, AI-powered customer service, and automated content generation tools.
Hugging Face Transformers: State-of-the-Art NLP
The Transformers library provides access to thousands of pre-trained models for natural language processing, computer vision, and audio processing. It's become essential infrastructure for AI frameworks in Python.
Business Value: Pre-trained models eliminate the need for expensive model training, reducing project costs while maintaining competitive performance. Time-to-market for AI features drops from months to weeks.
Best For: Text analysis, sentiment detection, document classification, translation services, and any NLP application.
Testing Frameworks: Ensuring Quality

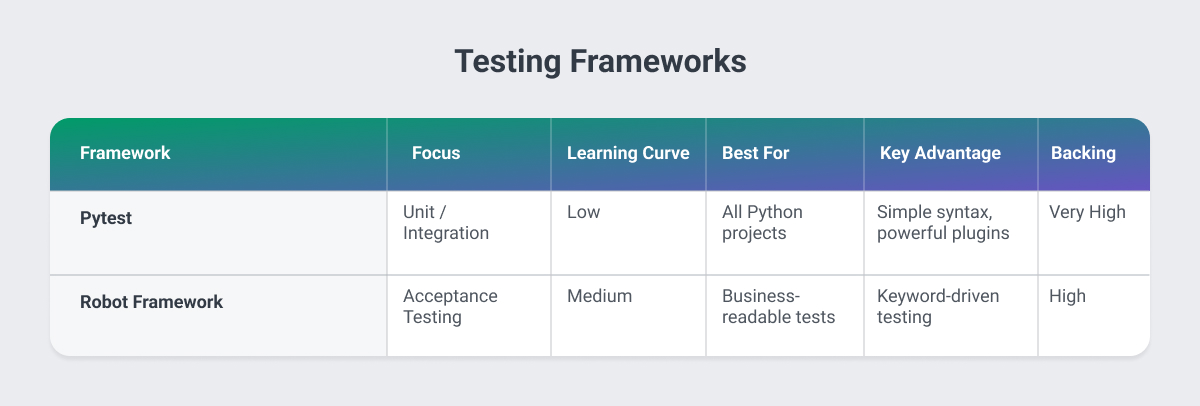
Pytest: Modern Testing Infrastructure
Pytest has become the de facto standard for testing Python applications. Its simple syntax and powerful plugin ecosystem make it easier to maintain comprehensive test coverage.
Business Value: High test coverage correlates directly with reduced production incidents. Pytest's ease of use encourages developers to write tests, reducing long-term maintenance costs and improving system reliability.
Best For: All Python projects benefit from Pytest, but it's particularly valuable for mission-critical systems where downtime carries significant business costs.
Robot Framework: Acceptance Testing
Robot Framework enables keyword-driven testing that non-technical stakeholders can understand and even write. This bridges the gap between business requirements and technical validation.
Business Value: When product managers and QA teams can directly write test cases, miscommunication between business requirements and technical implementation decreases significantly.
Best For: Projects with complex business logic, systems requiring regulatory compliance documentation, and products with extensive acceptance criteria.
Making the Right Framework Choice
Selecting from the most popular Python frameworks requires balancing several factors:
Project Timeline: Full-stack frameworks like Django accelerate initial development but may introduce complexity later. Microframeworks like Flask offer flexibility but require more upfront architectural decisions.
Team Expertise: Leverage your team's existing knowledge when possible. The productivity gains from familiar tools often outweigh the theoretical advantages of alternatives.
Scalability Requirements: Consider both technical scalability (handling growth) and organizational scalability (team growth, feature expansion). Some frameworks are easier to scale technically, others organizationally.
Ecosystem Maturity: Established frameworks have better documentation, more third-party packages, and larger talent pools. Newer frameworks might offer technical advantages but come with a higher risk.
Integration Needs: Evaluate how the framework fits into your existing technology stack. Some framework Python options integrate more naturally with specific databases, frontend frameworks, or cloud platforms.
Maintenance Horizon: Projects with 5-10 year lifespans benefit from conservative framework choices with proven longevity. Shorter-term projects can take more risks on emerging technologies.
Framework Comparison at a Glance
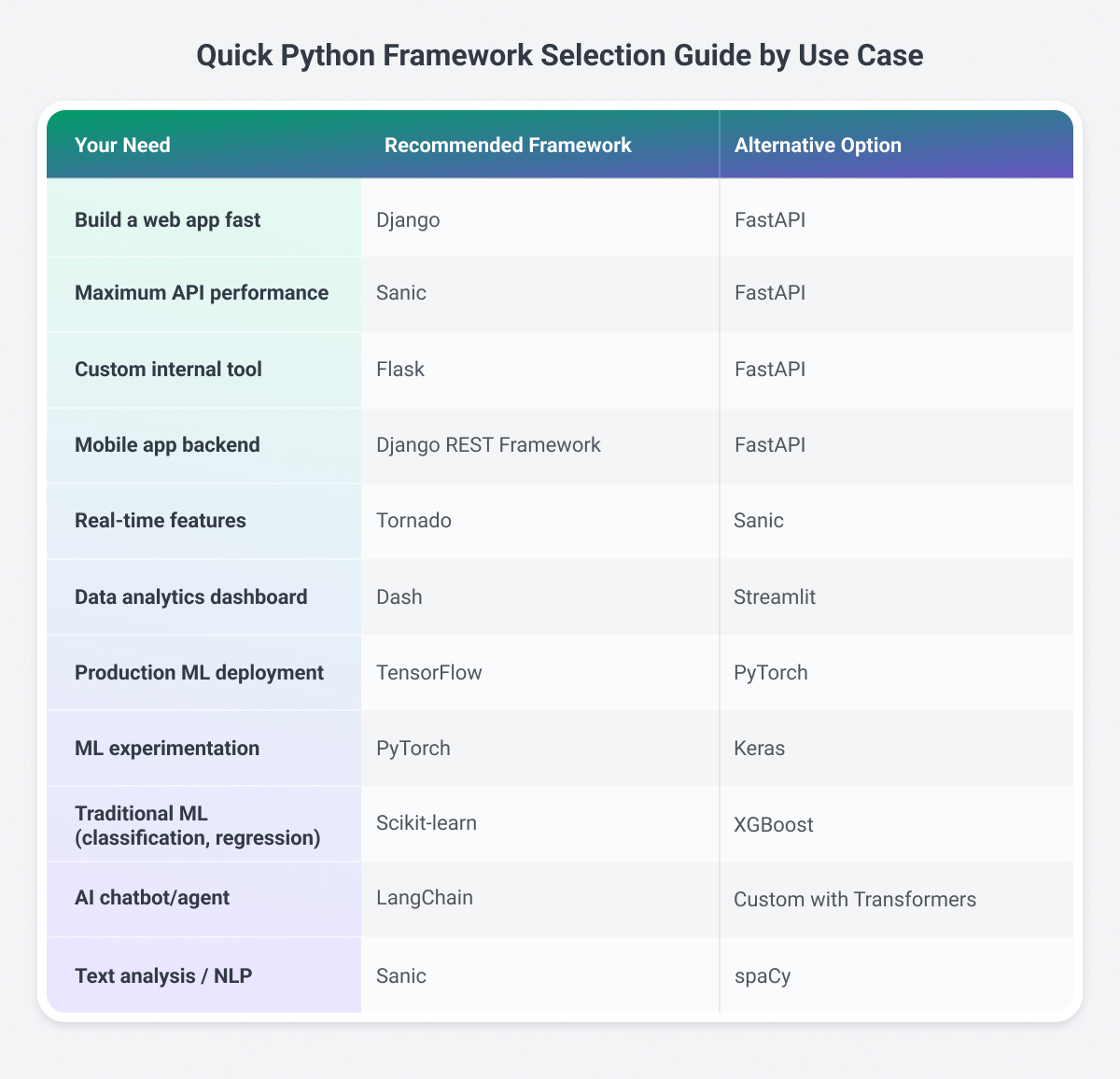
Strategic Considerations for Technical Leadership
When evaluating Python frameworks for web development, backend systems, or AI/ML applications, consider these strategic factors:
Total Cost of Ownership: Initial development speed is only one factor. Consider ongoing maintenance, infrastructure costs, and the availability of developers who know the framework.
Vendor Independence: Some frameworks tie you more tightly to specific cloud providers or databases. Maintaining optionality has strategic value.
Community and Support: Active communities mean faster problem resolution and more innovation. Frameworks backed by major companies offer different risk profiles than community-maintained projects.
Hiring and Retention: Popular frameworks make hiring easier but create more competition for talent. Specialized frameworks might build unique capabilities but increase hiring challenges.
Final Word
The Python framework landscape offers solutions for virtually every use case – the key to choosing the right one is matching technical capabilities to your business objectives.
By understanding the strengths and trade-offs of each framework Python developers use, technical leaders can make informed decisions that align technology choices with business strategy, ensuring projects deliver value efficiently and sustainably.
Not sure which framework is right for your project? Our expert Python developers and consultants can help you evaluate options, architect solutions, and build high-performance applications tailored to your business needs.