Choosing the right programming language for your web development project is a business decision that will affect your time-to-market, development costs, ability to hire talent, and long-term scalability.
So which one is best to power your web development project?
This guide breaks down the best web development languages for business projects, organized by where they fit in your stack (frontend, backend, or full-stack), and provides clear guidance on which languages best suit different project types and business needs.

Frontend Languages: What Users See and Interact With
The frontend of your web app is like your digital storefront: it's what users interact with, what search engines crawl, and what determines whether visitors stay or leave.
While backend systems power functionality, frontend choices directly impact user experience, conversion rates, and your brand perception.
HTML/CSS: The Foundation
Every web project begins with HTML and CSS. These aren't programming languages in the traditional sense – they're markup and styling languages – but they're absolutely essential.
Business Considerations:
- Universal requirement: Every web developer knows these
- Low barrier to entry: Easy to find talent
- Cost-effective: Basic HTML/CSS skills are widely available
- Maintenance: Simple sites can be maintained by junior developers
When to emphasize: Content-heavy sites, marketing pages, blogs, and portfolios where visual design matters more than complex functionality.

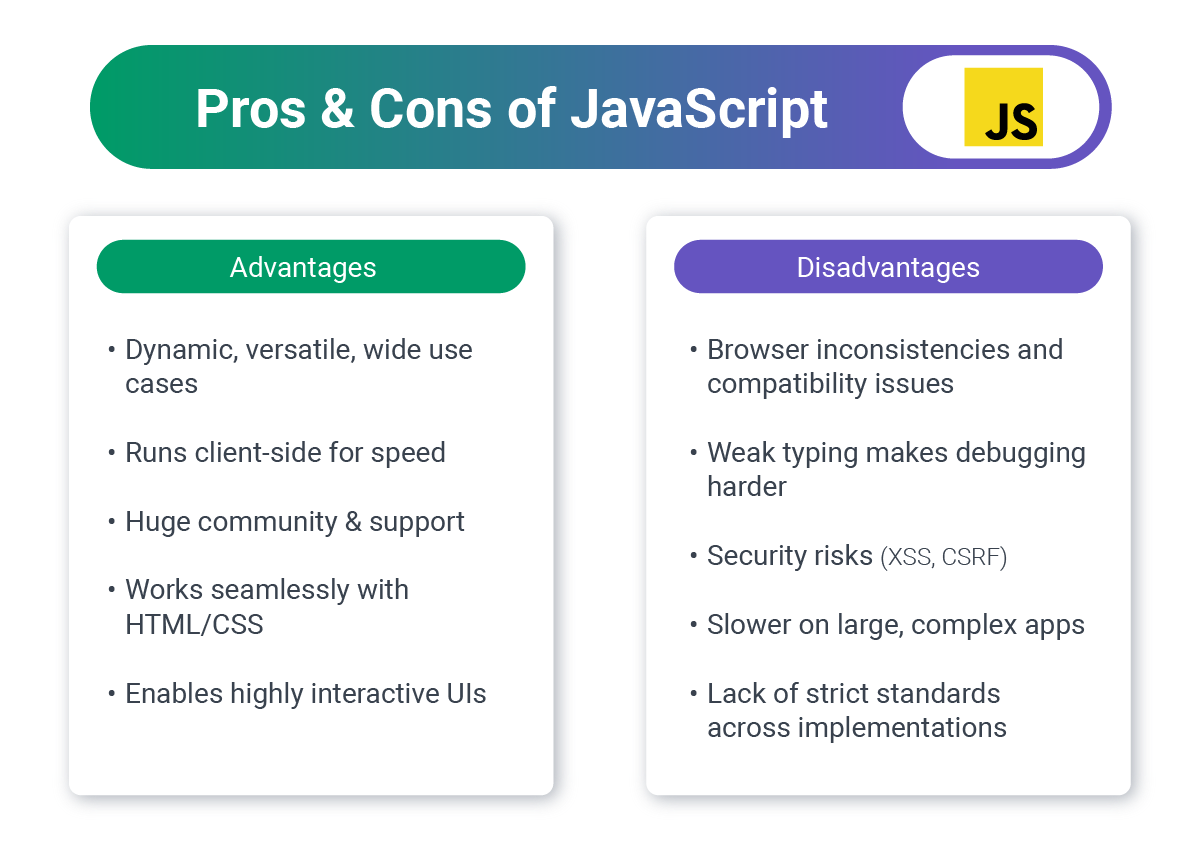
JavaScript: The Interactive Web
JavaScript powers the interactive elements of virtually every modern website. It's evolved from a simple scripting language to the backbone of sophisticated web applications.
Business Impact:
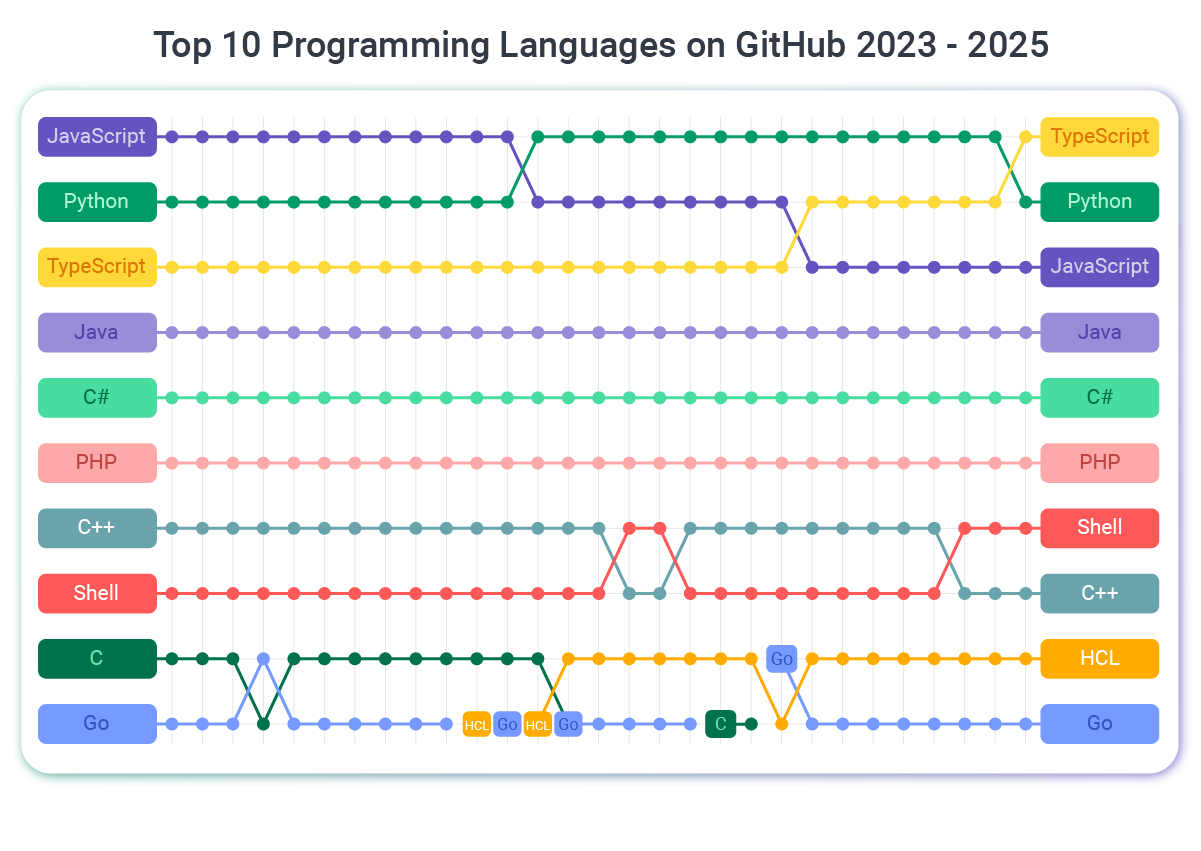
- Talent pool: Over 62% of developers worldwide use JavaScript
- Ecosystem: Massive library of packages via npm
- Versatility: Runs on both frontend and backend
- Community: The Largest developer community means abundant resources
Major Frameworks:
- Most popular frontend library
- Excellent for complex, interactive UIs
- Strong ecosystem with extensive third-party tools
- Used by: Facebook, Netflix, Airbnb, Uber
Business fit: Large applications requiring frequent updates and complex state management
- Progressive framework, easier learning curve than React
- Excellent documentation
- Flexible—can be incrementally adopted
Used by: Alibaba, GitLab, Nintendo
Business fit: Mid-size projects, teams wanting faster onboarding
- Full-featured framework with opinionated structure
- TypeScript-first approach
- Best for large enterprise applications
Used by: Google, Microsoft, Forbes
Business fit: Enterprise projects with large teams needing structure
Svelte
- Emerging framework with excellent performance
- Compiles to vanilla JavaScript (smaller bundle sizes)
- Simpler syntax, less boilerplate
Used by: Apple, The New York Times, IKEA
Business fit: Performance-critical applications, modern greenfield projects
TypeScript: JavaScript with Safety
TypeScript is a superset of JavaScript that adds static typing, catching errors before they reach production.
Business Value:
- Reduced bugs: TypeScript has been shown to reduce bugs by 15% or more on average
- Better tooling: Enhanced IDE support and autocomplete
- Easier refactoring: Safe code changes in large codebases
- Team scaling: Makes collaboration easier on large teams
- Adoption: TypeScript was used by 38.5% of developers worldwide in 2024
When to choose: Any medium-to-large JavaScript project, enterprise applications, or projects with multiple developers. The upfront investment in typing pays off in reduced debugging time and fewer production issues.
Backend Languages: The Engine Behind Your Web App
The backend is where your business logic lives: it powers data handling, processing transactions, managing users, and serving content to the frontend.
1. JavaScript/Node.js: Full-Stack Simplicity
Node.js allows JavaScript to run on the server, enabling full-stack JavaScript development.
Business Advantages:
- Single language: Frontend and backend developers can share code
- Fast development: Rapid prototyping and quick iterations
- Real-time capabilities: Excellent for chat, notifications, live updates
- Hiring efficiency: Leverage existing JavaScript developers
- Performance: Non-blocking I/O handles concurrent requests well
Popular Frameworks:
- Express.js: Minimalist, flexible, most widely used
- NestJS: Enterprise-grade, TypeScript-first, Angular-inspired architecture
- Fastify: High-performance alternative to Express
Ideal for:
- Real-time applications (chat, collaboration tools)
- API backends for mobile/web apps
- Microservices architectures
- Startups wanting rapid development
- Teams with strong JavaScript expertise
Challenges:
- Callback complexity (though modern async/await helps)
- Less suitable for CPU-intensive operations
- Relatively younger ecosystem compared to Java/Python for backend
Used by: Netflix, PayPal, LinkedIn, Uber, NASA
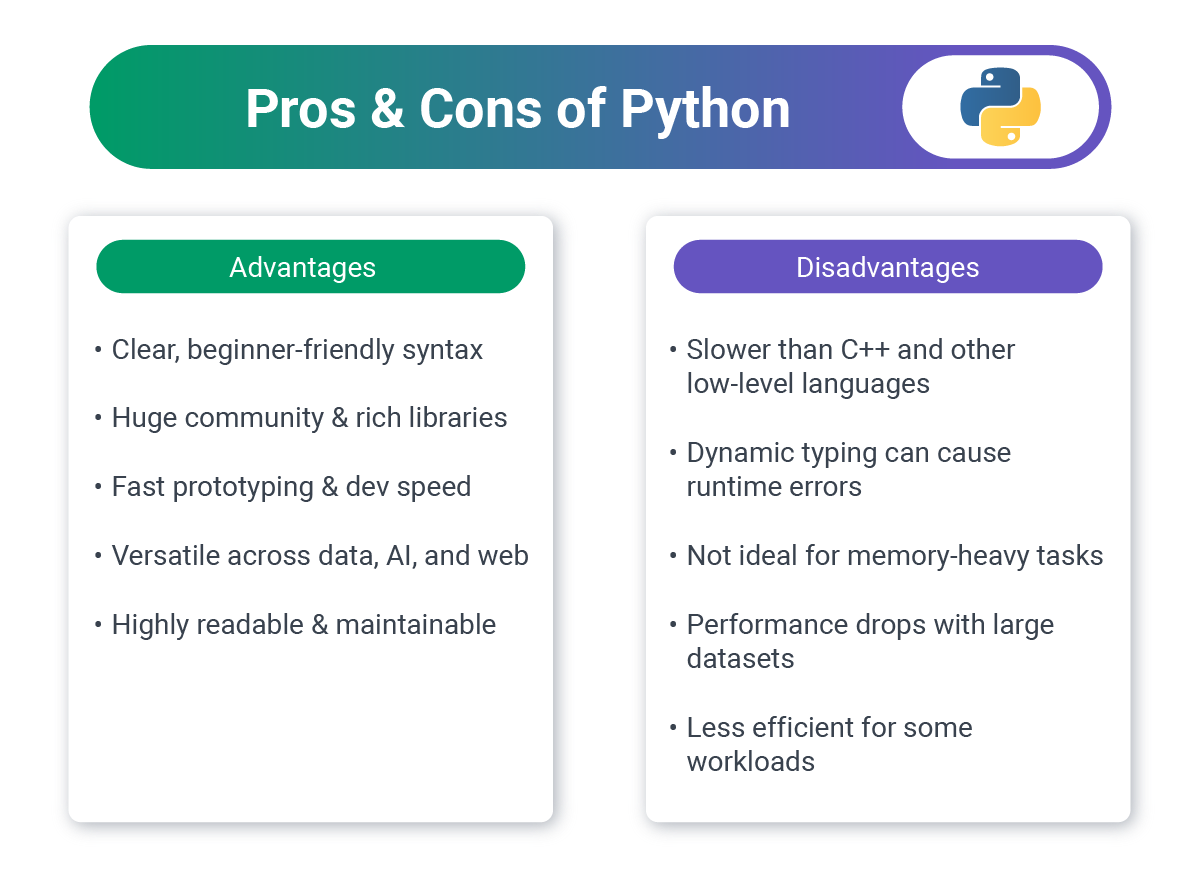
2. Python: Developer Productivity and AI Integration
Python combines readable syntax with powerful capabilities, making it a favorite for web applications and data-driven projects.
Business Benefits:
- Developer productivity: Clean syntax means faster development
- Talent availability: Python is rated as one of the most popular programming languages, and adoption has accelerated significantly – it saw a 7 percentage point increase from 2024 to 2025.
- AI/ML integration: Best-in-class for adding intelligence to your app
- Data processing: Excellent for analytics, reporting, data pipelines
- Versatility: Use the same language for web, data science, automation
Leading Frameworks:
Django - "The web framework for perfectionists with deadlines"
- Batteries-included: Authentication, admin panel, ORM out-of-the-box
- Rapid development for complex applications
- Strong security defaults
- Excellent documentation
- Best for: Complex business applications, content management, internal tools
Flask - Lightweight and flexible
- Minimal, unopinionated framework
- Easy to learn and extend
- Great for APIs and smaller services
- Best for: APIs, microservices, simple web apps, prototypes
FastAPI - Modern, fast, and API-focused
- Automatic API documentation
- Built-in data validation
- Async support for better performance
- Best for: Modern APIs, microservices, data science applications
Ideal for:
- Content-heavy platforms
- Projects requiring AI/ML features
- Data-driven applications
- Scientific or academic web tools
- Rapid MVP development
Used by: Instagram, Reddit, Spotify, NASA, Mozilla
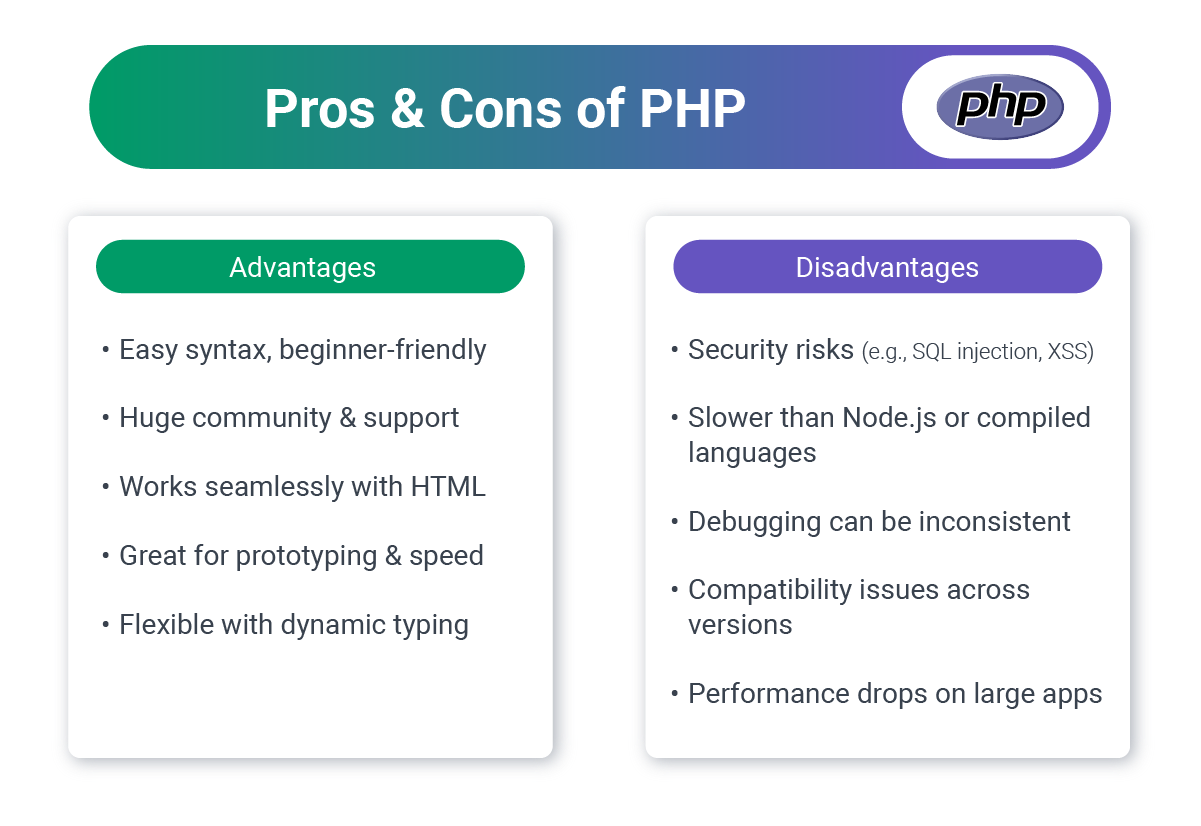
3. PHP: Proven, Scalable, Cost-Effective
Despite skeptics, PHP powers a substantial portion of the web and has evolved significantly with modern versions (7.x and 8.x).
Business Case:
- Market share: PHP is used by 73.4% of all websites.
- Affordable hosting: Widely supported, cheap to deploy
- Abundant developers: Large talent pool at competitive rates
- Mature ecosystem: Solutions exist for virtually any need
- E-commerce strength: Powers major platforms
Modern PHP Frameworks:
Laravel - Elegant PHP framework
- Beautiful syntax, developer-friendly
- Comprehensive ecosystem (authentication, queues, caching)
- Active community and extensive packages
- Best for: Modern PHP applications, SaaS platforms, e-commerce
Symfony - Enterprise-grade components
- Reusable PHP components
- Highly flexible and modular
- Used as foundation for other frameworks (including Laravel)
- Best for: Complex enterprise applications, long-term projects
Ideal for:
- E-commerce platforms
- Content management
- Web applications requiring affordable scaling
- Projects with limited budgets
- Companies with existing PHP infrastructure
Challenges:
- Legacy perception (though modern PHP is excellent)
- Inconsistent function naming in core language
- Async capabilitiesare limited compared to Node.js
Used by: Facebook (started with PHP), WordPress, Slack, Etsy, Mailchimp
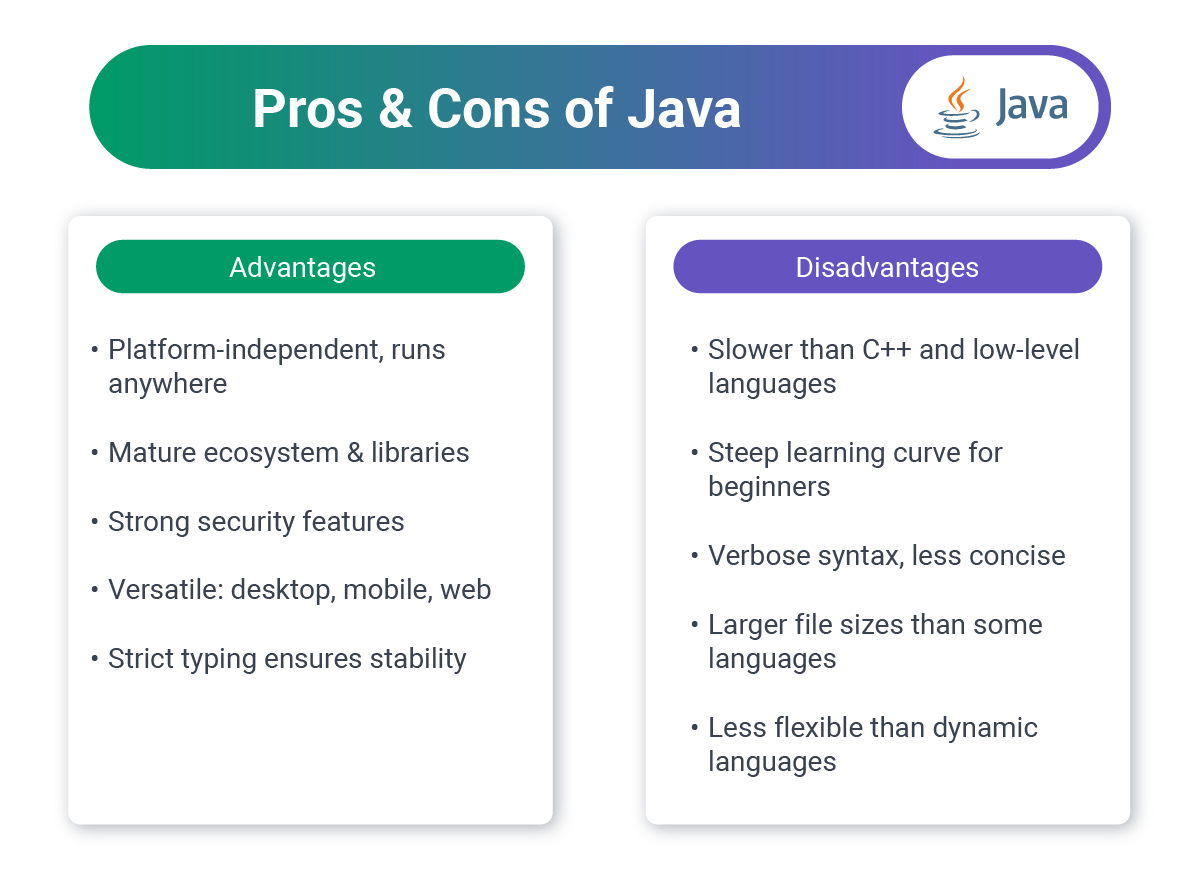
4. Java: Enterprise Reliability
Java remains a cornerstone of enterprise web development, known for stability, performance, and extensive tooling.
Business Strengths:
- Enterprise trust: Decades of proven reliability, and it is considered to be one of the most popular programming languages.
- Performance: Excellent for high-traffic applications
- Type safety: Strong typing catches errors early
- Scalability: Handles growth from startup to enterprise
- Security: Robust security features built-in
- Long-term support: Stable, backward-compatible
Spring Boot Framework:
- Industry standard for Java web development
- Comprehensive feature set
- Microservices-ready
- Excellent integration with enterprise tools
- Large ecosystem of extensions
Ideal for:
- Enterprise web applications
- Financial services platforms
- High-security requirements
- Applications requiring complex business logic
- Long-lived projects (10+ year horizon)
- Large development teams
Challenges:
- Verbose syntax (more code to write)
- Slower initial development compared to Python/Node.js
- Higher infrastructure requirements
Used by: LinkedIn, Amazon, eBay, Airbnb (backend), Netflix (backend)
5. Go (Golang): Performance and Simplicity
Go, created by Google, is gaining traction for backend services requiring high performance and concurrency.
Business Value:
- Performance: Near C/C++ speed, faster than Node.js/Python
- Concurrency: Built-in support for handling many simultaneous operations
- Simple deployment: Single binary, no dependencies
- Fast compilation: Quick build times
- Growing adoption: Go is among the top three fastest-growing programming languages in 2025.
Ideal for:
- Microservices architectures
- API gateways and middleware
- Cloud-native applications
- High-performance backends
- DevOps tools and infrastructure
Challenges:
- Smaller talent pool than JavaScript/Python
- Fewer libraries than more established languages
- Less suitable for rapid prototyping
- Simpler language means more code for complex features
Used by: Google, Uber, Twitch, Dropbox, Docker, Kubernetes
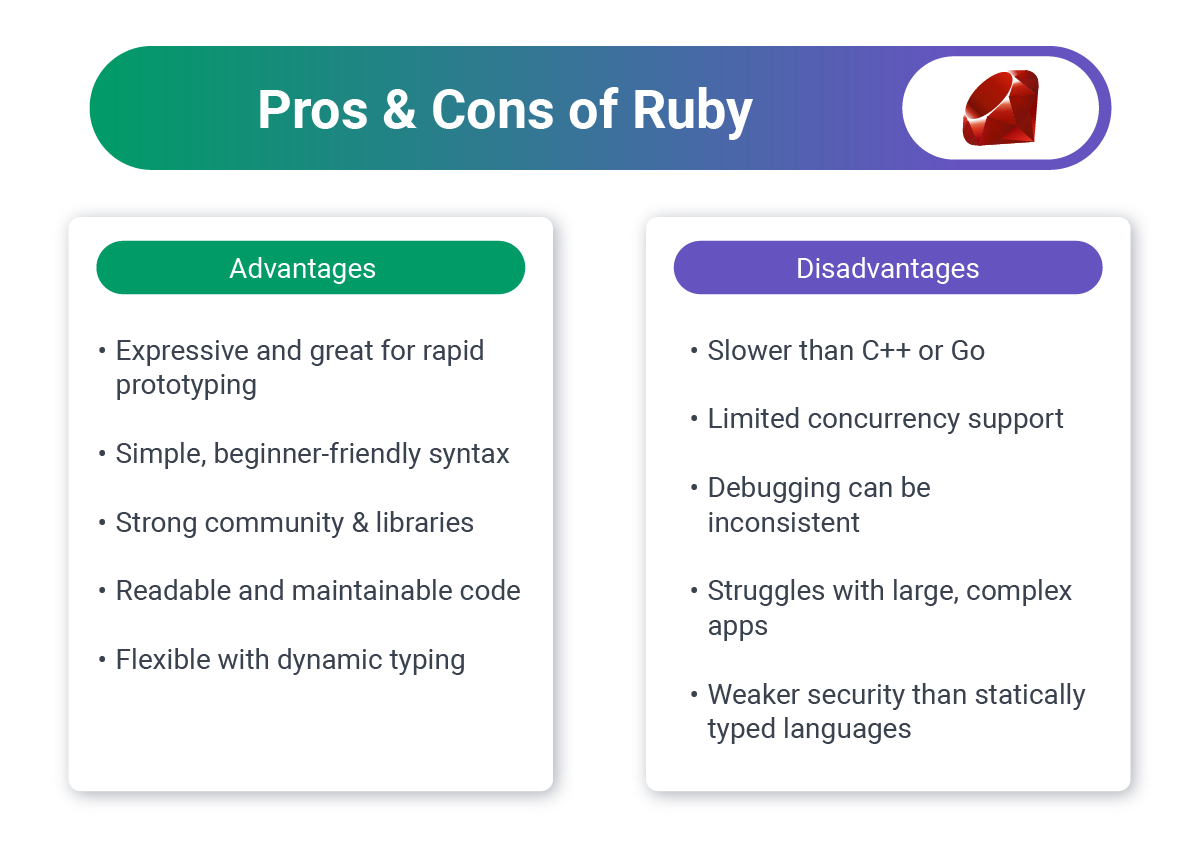
6. Ruby: Developer Happiness
Ruby, particularly with the Rails framework, pioneered many modern web development practices.
Business Benefits:
- Rapid development: Convention over configuration speeds up building
- Developer productivity: Optimized for programmer happiness
- Startup favorite: Quick MVP to market
- Mature ecosystem: Gem libraries for almost everything
Ruby on Rails:
- Full-stack framework with everything included
- Strong conventions reduce decision fatigue
- Excellent for CRUD applications
- Active community and regular updates
Ideal for:
- Startup MVPs
- SaaS applications
- Content platforms
- Projects prioritizing speed to market
Challenges:
- Performance limitations at extreme scale
- The talent pool of experienced and senior Rails developers is shrinking and highly competitive
- 3rd highest paying technology (which means a likely paying a higher salary to access development talent)
- Less prevalent in enterprise environments
Used by: Airbnb, GitHub, Shopify, Basecamp, Twitch
7. C# / .NET: Microsoft's Web Powerhouse
C# with .NET (now .NET Core) offers a modern, performant platform especially strong in Windows environments.
Business Advantages:
- Microsoft integration: Seamless with Microsoft stack (Azure, SQL Server)
- Performance: Excellent speed and efficiency
- Type safety: Strong typing prevents errors
- Enterprise features: Built for large-scale applications
- Cross-platform: .NET Core runs on Linux/Mac/Windows
ASP.NET Core:
- Modern, high-performance web framework
- Excellent tooling (Visual Studio)
- Strong security features
- Good documentation
Ideal for:
- Enterprises using Microsoft infrastructure
- Windows-based environments
- Large-scale applications
- Projects requiring .NET libraries/integrations
Challenges:
- Historically Windows-focused (less so with .NET Core)
- Smaller open-source ecosystem than JavaScript/Python
- There’s a shortage of truly skilled .NET professionals, with intense competition driving up salaries
Used by: Microsoft, Stack Overflow, GE Aviation, UPS
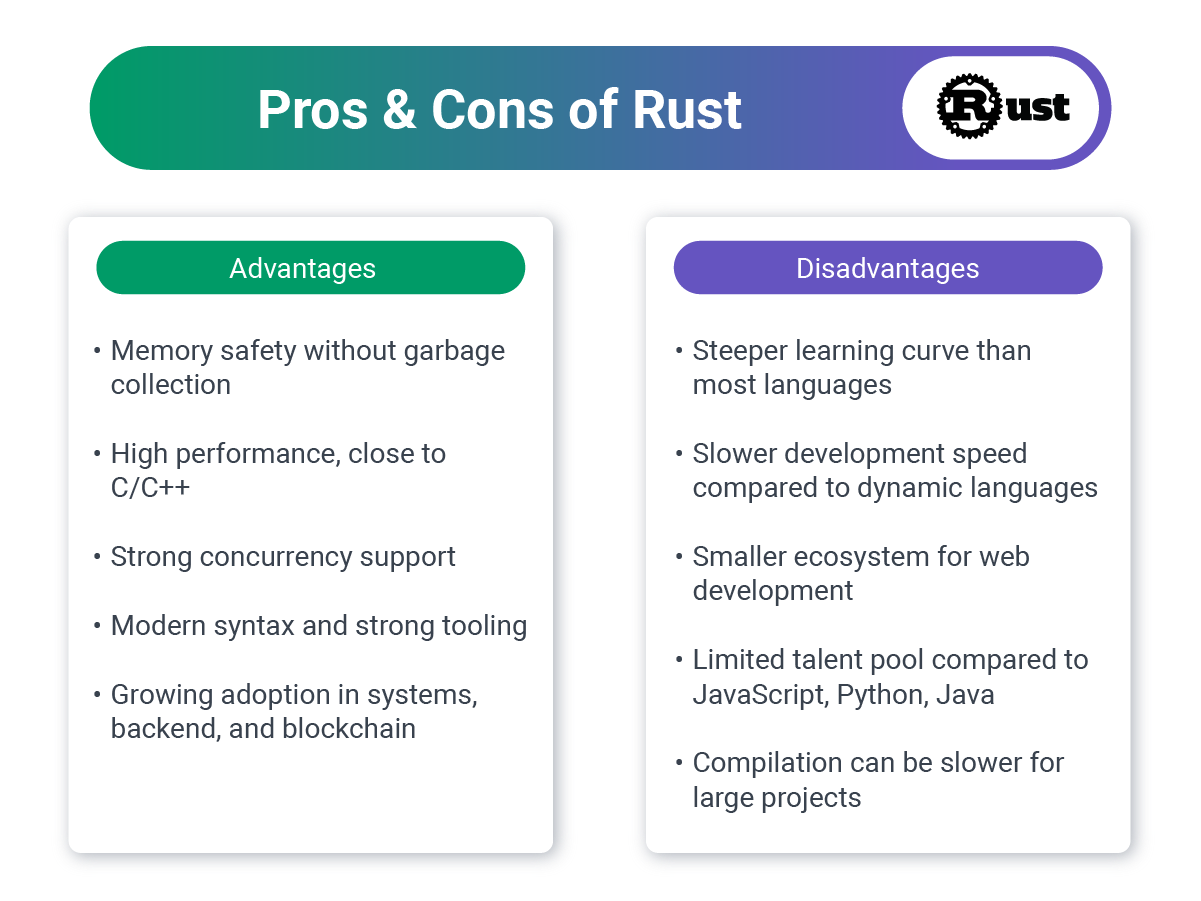
8. Rust: Safety Meets Speed
Rust is gaining momentum for high-performance backends and WebAssembly (Wasm) applications. Its memory safety guarantees and concurrency model make it attractive for mission-critical systems.
Business Value:
- Performance: Comparable to C/C++ with safer memory management.
- Reliability: No garbage collector, fewer runtime crashes.
- Growing ecosystem: Frameworks like Actix and Rocket for web development.
Ideal for:
- Performance-critical web services, fintech backends requiring maximum reliability, and apps leveraging WebAssembly.
Challenges:
- Steeper learning curve: Memory safety and ownership rules make it harder for teams without systems-level experience.
- Smaller talent pool: Far fewer Rust web developers compared to JavaScript or Python.
- Slower development speed: Productivity can lag in early phases compared to rapid frameworks like Django or Rails.
Used by: Dropbox and Cloudflare
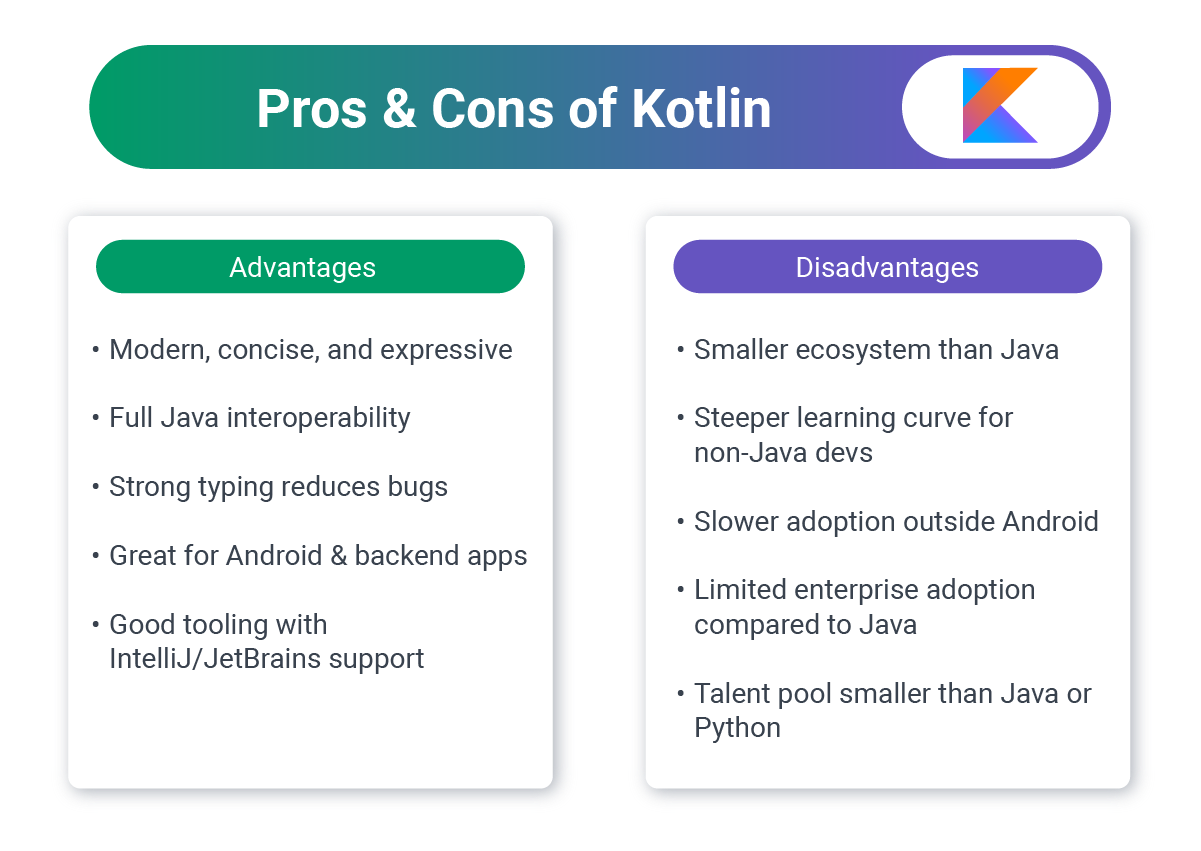
9. Kotlin: Java-Compatible and Versatile
Kotlin, officially supported by Google for Android, is also making its way into web backends through frameworks like Ktor and Spring Boot (interoperable with Java).
Business Value:
- Java interoperability: Works seamlessly with Java codebases.
- Modern syntax: Reduces boilerplate compared to Java.
- Scalability: Strong option for enterprise backends and APIs.
Best For:
- Teams with Java experience looking for more concise, modern code while maintaining enterprise-grade scalability.
Challenges
- Hiring costs: Senior Kotlin developers are often in high demand for Android, which can drive up rates.
- Ecosystem maturity: While Ktor and Spring support Kotlin, the broader web tooling isn’t as deep as Java’s.
- Learning curve for teams moving from Java: Syntax is cleaner, but teams need time to adopt new idioms.
Used by: N26, ING, American Express, and Kakao Pay
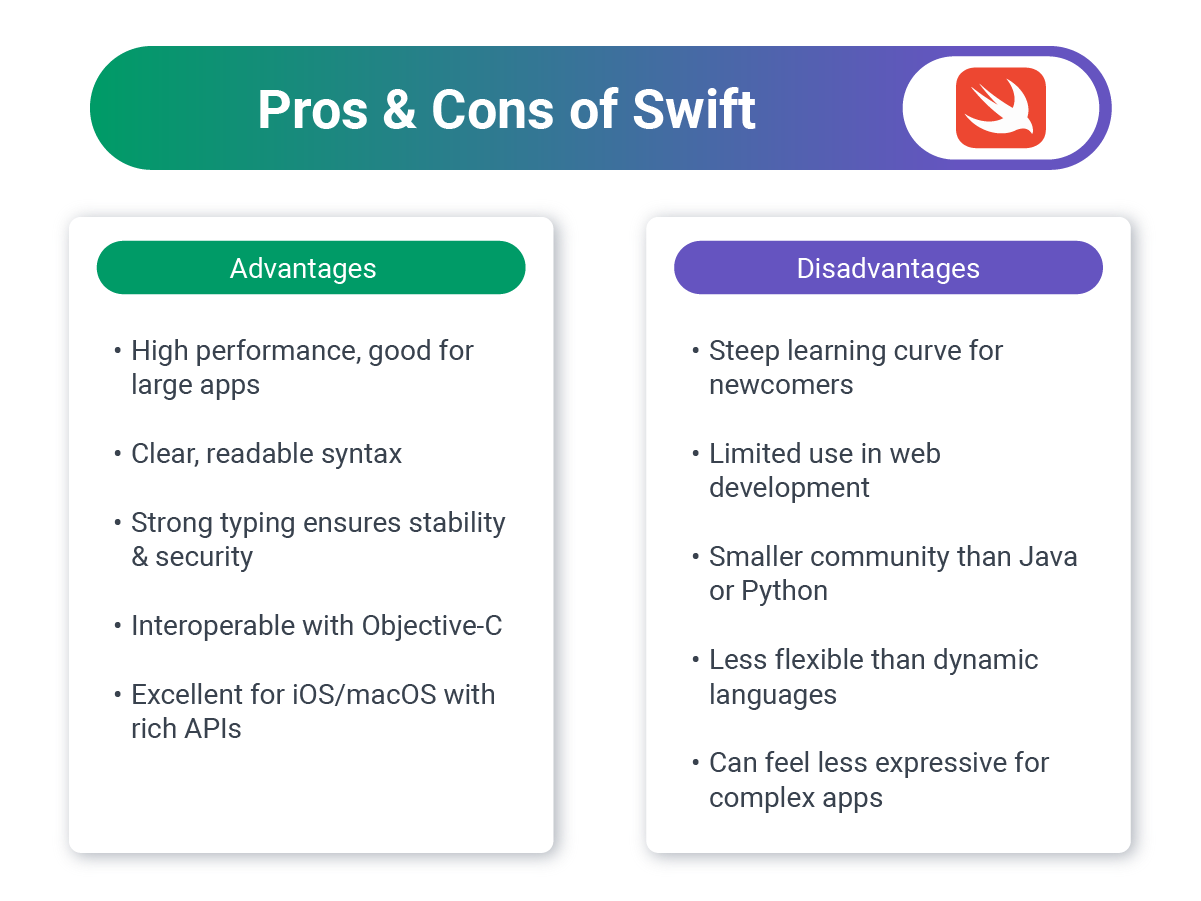
Swift: Apple’s Modern Contender
Swift is Apple’s modern, high-performance language designed to eventually replace Objective-C. While primarily known for iOS/macOS development, Swift is increasingly used for server-side web development via frameworks like Vapor and Kitura.
Business Value:
- Ecosystem strength: Ideal if your web app integrates deeply with iOS/macOS products.
- Performance: Compiled language with strong memory safety and speed.
- Talent pool: Smaller than JavaScript or Python, but growing thanks to iOS developer crossover.
Challenges:
- Limited backend adoption: Still seen primarily as a mobile language; fewer developers use Swift for server-side projects.
- Smaller ecosystem: Fewer mature libraries/frameworks compared to Node.js, Java, or Python.
- Talent availability: While many iOS developers know Swift, fewer have real backend experience.
Best For:
- Fintech or SaaS platforms targeting Apple-centric users, or when building backend services aligned with iOS apps.
Used by: Apple, Lyft, IBM (Vapor projects).
Full-Stack Approaches: Unified Development
Full-stack development using a single language across frontend and backend can significantly accelerate development, reduce hiring complexity, and enable better code sharing.
While not every project needs this approach, the efficiency gains often outweigh the trade-offs for startups and mid-sized teams.
JavaScript Everywhere
Using JavaScript for both frontend and backend offers unique advantages:
Benefits:
- Code sharing: Reuse validation, utilities, types between client/server
- Team efficiency: Developers can work across the entire stack
- Faster hiring: One skill set to look for
- Consistent tooling: Same build tools, testing frameworks
Popular Stacks:
MERN Stack (MongoDB, Express, React, Node.js)
- Most popular full-stack JavaScript combination
- NoSQL database for flexibility
- React for modern frontend
MEAN Stack (MongoDB, Express, Angular, Node.js)
- Angular provides more structure than React
- Better for enterprise projects needing conventions
Modern Meta-Frameworks:
Next.js (React-based)
- Server-side rendering for better SEO and performance
- API routes for backend functionality
- Deployment optimization
Best for: Marketing sites, e-commerce, SaaS applications
Nuxt.js (Vue-based)
- Similar benefits to Next.js, but for Vue developers
Best for: Teams preferring Vue's approach
SvelteKit (Svelte-based)
- Newer but gaining traction
- Excellent performance
Best for: Modern projects prioritizing speed
Python Full-Stack
While less common than JavaScript full-stack, Python can power complete applications:
- Django for both frontend (templates) and backend
- Django REST Framework + React/Vue for API-driven apps
- FastAPI backend + modern JavaScript frontend
Best for: Data-heavy applications, scientific web tools, internal business applications

Business Considerations: Beyond the Code
Technical capabilities matter, but business factors often determine project success. Understanding talent availability, development costs, scaling expenses, security requirements, and deployment options helps you make decisions that serve both your immediate needs and long-term business goals.
Talent Pool & Hiring
Developer Availability:
- Most abundant: JavaScript, Python, Java
- Growing: TypeScript, Go
- Specialized: Ruby, C#, PHP (modern frameworks)
Salary Considerations:
- Average Salaries according to Glassdoor and Indeed: Python $130,000, Java $115,000, .NET $109,000, C++ $108,000, Go $105,000, Rust $102,000, JavaScript $100,000, Swift $98,000, TypeScript $96,000, Kotlin $94,000, Ruby $92,000, PHP $81,000
- Generally lower costs: PHP, JavaScript
- Higher costs: Go, Java (experienced), Python, .NET, and other specialized skills (such as DevOps engineers and Solution Architects)
Geographic factors: Consider remote hiring—talent availability varies by region.

Development Speed & Time-to-Market
Fastest to MVP:
- Ruby on Rails (convention over configuration)
- Python/Django (batteries included)
- JavaScript/Next.js (modern full-stack)
- PHP/Laravel (rapid development tools)
Slower but more structured:
- Java/Spring Boot (enterprise features take time)
- C# / .NET (comprehensive but heavier)
Timeline impact: Choosing a rapid-development framework can cut initial development time compared to lower-level approaches.
Long-Term Costs: Maintenance & Scaling
Maintenance Considerations:
- Easiest to maintain: TypeScript, Java, C# (strong typing catches errors)
- Requires discipline: JavaScript, Python, Ruby (dynamic typing needs good testing)
- Documentation: Java, C# have excellent tooling for large codebases
Scaling Costs:
- Most efficient at scale: Go, Java, C#
- Good performance: Node.js, modern PHP
- Requires more resources: Ruby, Python (but often worth the developer productivity)
Security & Compliance
Security-first languages:
- Java: Extensive security libraries, proven in finance
- C#: Strong security features, Microsoft's security focus
- Python/Django: Security best practices built-in
All languages can be secure, but some have:
- Better security defaults (Django, Rails, Spring)
- Larger security communities finding vulnerabilities
- More security-focused libraries and tools
Compliance considerations: For HIPAA, PCI-DSS, SOC 2, choose mature ecosystems with proven security track records (Java, C#, Python, Node.js with proper frameworks).

Cloud & Deployment
Deployment ease:
- Containerization-friendly: All modern languages work well with Docker
- Serverless options: JavaScript (AWS Lambda, Vercel), Python (AWS Lambda), Go
- Platform-as-a-Service:
- Heroku: Ruby, Node.js, Python, PHP, Java
- Vercel/Netlify: JavaScript (Next.js, etc.)
- Azure: C# / .NET (native support)
Multi-cloud strategy: JavaScript, Python, and Go offer the most flexibility across AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
Third-Party Integration & APIs
Ecosystem strength:
- JavaScript (npm): Over 3.1 million packages
- Python (PyPI): Over 680,000 packages.
- Java (Maven): Mature, extensive enterprise libraries with over 17 million indexed packages.
- PHP (Composer): Strong for CMS and e-commerce integrations, with over 450,000 packages.
API integrations: All languages have good HTTP/REST libraries, but JavaScript and Python often have the most up-to-date SDK support for modern SaaS tools.

Project-Type Recommendations
Different types of web projects have distinctly different requirements: what works perfectly for e-commerce may be overkill for a content site, while a startup MVP needs different priorities than an enterprise application. Here's how to match languages to your specific project type for optimal results.
E-commerce Platforms
Best choices:
- PHP (Laravel, Magento, WooCommerce):
- Proven ecosystem
- Payment gateway integrations
- Affordable developers
- JavaScript (Next.js + Shopify/Stripe):
- Modern, fast frontends
- Headless commerce capabilities
- Great user experience
- Python (Django + DRF):
- Custom business logic
- Complex inventory management
- AI-powered recommendations
Key factors: Payment processing support, inventory systems, security compliance
SaaS Applications
Best choices:
- JavaScript/TypeScript (Next.js, NestJS):
- Rapid feature development
- Real-time capabilities
- Modern UX expectations
- Python (Django, FastAPI):
- Complex business rules
- Data analytics features
- AI/ML integration
- Ruby (Rails):
- Fast MVP to market
- Mature SaaS patterns
- Subscription management gems
Key factors: Multi-tenancy, subscription billing, API integrations, scalability

Content-Heavy Sites (CMS, Blogs, News)
Best choices:
- PHP (WordPress, Drupal):
- Massive plugin ecosystems
- Non-technical content management
- SEO-optimized out of box
- JavaScript (Next.js, Gatsby):
- Static site generation
- Excellent performance
- Modern authoring experience
- Python (Django CMS, Wagtail):
- Custom content workflows
- Editorial tools
- Strong admin interface
Key factors: SEO, content workflows, media management, performance
Real-Time Applications (Chat, Collaboration)
Best choices:
- JavaScript/Node.js (Socket.io, WebSockets):
- Built for real-time
- Event-driven architecture
- Bi-directional communication
- Go:
- High concurrency
- Low latency
- Efficient resource usage
- Python (Django Channels, FastAPI WebSockets):
- Real-time + traditional web features
- Good for hybrid applications
Key factors: WebSocket support, concurrent connections, latency
Enterprise Web Applications
Best choices:
- Java (Spring Boot):
- Battle-tested reliability
- Complex business logic
- Long-term support
- C# / .NET:
- Microsoft ecosystem integration
- Strong typing and tooling
- Enterprise features built-in
- Python (Django):
- Rapid development
- Data processing
- Integration flexibility
Key factors: Maintainability, security, compliance, team size, long-term support
Startups & MVPs
Best choices:
- JavaScript/TypeScript (Next.js, T3 Stack):
- Fastest to market with modern UX
- Large talent pool
- Easy to pivot
- Python (Django, FastAPI + React):
- Rapid backend development
- Easy prototyping
- Flexibility to scale
- Ruby (Rails):
- Convention over configuration
- Startup-proven
- Quick iterations
Key factors: Time to market, iteration speed, hiring flexibility, cost

Ticketing & Event Management Platforms
Best choices:
- Python (Django, FastAPI):
- Complex booking logic and inventory management
- Real-time seat selection
- Integration with payment processors
- Fraud detection and analytics
- JavaScript/Node.js (Next.js, NestJS):
- Real-time availability updates
- Interactive seat maps
- WebSocket support for live events
- Mobile-responsive interfaces
- Java (Spring Boot):
- High-volume transaction handling
- Enterprise ticketing systems
- Complex pricing rules
- Strong consistency guarantees
Key factors: Real-time inventory, payment security, scalability for sale surges, mobile optimization, third-party integrations (payment gateways, email services, calendar apps)

Fintech Applications
Best choices:
- Java (Spring Boot):
- Banking-grade security
- Proven in financial sector
- Strong transaction handling
- Regulatory compliance features
- Extensive audit trails
- Python (Django, FastAPI):
- Complex financial calculations
- Machine learning for fraud detection
- Data analysis and reporting
- Rapid feature development
- Strong libraries for finance (pandas, NumPy)
- C# / .NET:
- Enterprise-grade security
- Windows integration for legacy systems
- Strong typing prevents calculation errors
- Excellent performance for high-frequency operations
- Go:
- High-performance trading systems
- Low-latency requirements
- Microservices for payment processing
- Excellent concurrency for real-time data
Key factors: PCI-DSS compliance, encryption standards, audit logging, transaction reliability, regulatory requirements (KYC, AML), third-party financial APIs, data integrity, uptime guarantees

Language Comparison Matrix

Final Word
Selecting the right programming language for your web development project is a strategic business decision that extends far beyond technical preferences. The language you choose affects your ability to hire talent, your time-to-market, your operational costs, and your capacity to scale.
Remember to validate your choice with small prototypes, consult with experienced developers, and remain focused on delivering value to your users. The best programming language is ultimately the one that helps you build the right product for your business and customers.
Looking to build your next web project? Consider consulting with experienced development teams who can help you navigate these choices based on your specific business needs and technical requirements.
Key Takeaways:
- There is no universal "best" language - The optimal choice depends on your specific project requirements, business constraints, and team capabilities.
- JavaScript/TypeScript dominates the modern web development landscape, offering versatility across the full stack with the largest talent pool and ecosystem.
- Project type matters most - E-commerce, SaaS, content platforms, and enterprise applications each have different optimal technology choices.
- Consider the total cost - Factor in development speed, developer salaries, hosting costs, and long-term maintenance, not just initial development.
- Don't neglect talent availability - The most technically perfect language won't help if you can't hire skilled developers within your budget and timeline.
- Proven technologies reduce risk - While emerging languages like Go offer compelling benefits, established languages like Python, Java, and JavaScript provide safer bets for mission-critical projects.
- Flexibility is valuable - Choose technologies that allow you to pivot and scale as your business evolves.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which language is best for web development?
There's no single "best" language for all web development projects. JavaScript/TypeScript is the most versatile choice for full-stack development, Python excels for rapid development and AI integration, Java leads for enterprise applications, and PHP remains strong for e-commerce and budget-conscious projects. The best choice depends on your specific project requirements, team skills, and business constraints.
Which programming language is best for backend web development?
For backend development, top choices include:
- Node.js for JavaScript full-stack projects and real-time applications
- Python (Django/FastAPI) for rapid development and data-driven apps
- Java (Spring Boot) for enterprise-grade applications
- Go for high-performance microservices
- PHP (Laravel) for cost-effective, proven solutions
The "best" depends on your performance needs, team expertise, and specific use case.
What language is best for frontend web development?
JavaScript (or TypeScript) is essential for modern frontend development. Choose frameworks based on project needs:
- React for complex, interactive applications
- Vue.js for balanced simplicity and power
- Angular for enterprise projects needing structure
- Svelte for performance-critical applications
All of these require JavaScript/TypeScript as the base language.
Which is the best programming language for full-stack web development?
JavaScript/TypeScript offers the most seamless full-stack experience, allowing you to use one language across frontend and backend. Modern frameworks like Next.js, Nuxt.js, and SvelteKit enable complete full-stack applications with JavaScript. Python can also serve full-stack needs, though typically with a JavaScript frontend.
What is the best language to learn for web development in 2026?
For business projects in 2026, prioritize:
- JavaScript/TypeScript - Most versatile, largest ecosystem
- Python - Best for AI integration and rapid development
- Go - Growing for performance-critical backends
If hiring developers, focus on the first two as they have the largest talent pools.
Which backend language is best for web development performance?
For maximum performance:
- Go - Fastest for concurrent operations
- Java - Excellent sustained performance at scale
- C#/.NET - Very fast, especially for Windows environments
- Node.js - Good performance for I/O-heavy applications
However, remember that proper architecture often matters more than raw language speed.
What is the best programming language for web development for beginners?
While this guide focuses on business projects, if you're building an internal team: JavaScript or Python are the best starting points due to:
- Gentle learning curves
- Extensive learning resources
- Large supportive communities
- Immediate practical applications
- Career versatility
Which language is most cost-effective for web development?
PHP and JavaScript typically offer the best cost-effectiveness due to:
- Large, competitive talent pools
- Lower average developer salaries
- Affordable hosting options
- Extensive free resources and frameworks
- Quick development times
Python also offers good value for complex projects requiring rapid development.
What are the best web development languages for e-commerce?
For e-commerce projects:
- PHP - Powers WooCommerce, Magento, extensive e-commerce ecosystem
- JavaScript - Modern headless commerce solutions (Shopify + Next.js)
- Python - Custom platforms with complex business logic
PHP remains dominant due to mature payment integrations and shopping cart solutions.
Which programming language is commonly used for web development?
The most commonly used languages are:
- JavaScript - Powers the client side of most websites and is also widely used on the server side with Node.js.
- PHP – Still used by the majority of websites on the server side, especially content-driven and CMS platforms (like WordPress).
- Python – Rapidly growing for modern web apps, APIs, and data-driven services.
- Java – Dominant in enterprise-level web applications and large-scale systems.
JavaScript and PHP together power the majority of the web.