Java frameworks form the backbone of modern enterprise software development, providing the structured foundation that enables organizations to build scalable, maintainable, and secure applications.
As businesses increasingly rely on digital solutions to drive growth and efficiency, understanding what frameworks are and how to leverage the right Java framework is critical for technical leadership and project success.
What is a Framework in Programming?
A framework in programming serves as a pre-built foundation of code that provides structure, common functionality, and established patterns for application development.
Think of frameworks as sophisticated blueprints that handle the complex underlying infrastructure, allowing development teams to focus on building business-specific features rather than reinventing fundamental components.
What Are Frameworks and Why Do They Matter?
Frameworks solve several critical business challenges:
Accelerated Time-to-Market: By providing pre-built components for common tasks like database connectivity, security, and user interface management, frameworks significantly reduce development time. What might take months to build from scratch can often be accomplished in weeks with the right framework.
Reduced Development Costs: The reusable nature of framework components means less custom code to write, test, and maintain. This translates directly to lower development costs and more predictable project budgets.
Enhanced Security: Established frameworks incorporate security best practices and receive regular security updates from their communities, providing a more secure foundation than custom-built solutions.
Improved Code Quality: Frameworks enforce consistent coding patterns and architectural decisions, leading to more maintainable and scalable applications.
What is a Framework in Java?
Java frameworks are specialized collections of pre-written code, libraries, and tools designed specifically for the Java ecosystem. These frameworks leverage Java's platform independence and robust ecosystem to provide comprehensive solutions for enterprise development needs.
Understanding Java's Framework Ecosystem
The Java framework landscape encompasses several categories:
- Backend Java Frameworks: Handle server-side logic, database interactions, and API development
- Java UI Frameworks: Manage user interface components and client-side interactions
- Java Web Development Frameworks: Provide complete solutions for web application development
- Java Enterprise Frameworks: Offer comprehensive tools for large-scale enterprise applications
Popular Java Frameworks: Strategic Analysis for Business Leaders
Spring Framework: The Enterprise Standard
Spring has established itself as the dominant force in Java enterprise development, and for compelling business reasons. With the highest adoption rate among Java frameworks and extensive enterprise usage, Spring offers unmatched ecosystem maturity and community support.
Business Value Proposition:
- Risk Mitigation: Largest talent pool and most comprehensive documentation reduce project risks
- Future-Proofing: Continuous innovation and strong roadmap ensure long-term viability
- Integration Capabilities: Seamless integration with cloud platforms and enterprise systems
- Microservices Ready: Spring Boot and Spring Cloud enable modern architectural patterns
When to Choose Spring: For most enterprise projects, especially those requiring scalability, cloud deployment, or integration with existing enterprise systems.
Hibernate: Data Layer Excellence
While technically an ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) tool rather than a full framework, Hibernate's impact on enterprise Java development cannot be overstated. It abstracts database complexity and provides a robust foundation for data management.
Strategic Benefits:
- Database Agnosticism: Reduces vendor lock-in by supporting multiple database platforms
- Performance Optimization: Advanced caching and query optimization features
- Developer Productivity: Eliminates boilerplate database code
Java Server Faces (JSF): Standards-Based UI Development
JSF represents Oracle's official approach to Java web UI development and remains relevant for organizations prioritizing standards compliance and long-term support.
Business Considerations:
- Standards Compliance: Part of Jakarta EE specifications, ensuring long-term support
- Component Ecosystem: Rich third-party component libraries available
- Legacy Integration: Excellent choice for extending existing Java EE applications
Struts: Proven MVC Architecture
Apache Struts pioneered many MVC patterns still used today and continues to serve enterprises with specific architectural requirements.
Strategic Value:
- Architectural Clarity: Clear separation of concerns simplifies maintenance
- Enterprise Integration: Strong integration capabilities with enterprise systems
- Mature Ecosystem: Extensive plugin architecture and community resources
Google Web Toolkit (GWT): Java-First Frontend Development
GWT enables teams to leverage Java expertise for frontend development, translating Java code to optimized JavaScript.
Business Case:
- Unified Skill Set: Java teams can handle both frontend and backend development
- Performance: Generates highly optimized JavaScript code
- Type Safety: Compile-time error checking reduces runtime issues
Play Framework: Modern Reactive Architecture
Play Framework brings reactive programming principles to Java web development, making it ideal for high-concurrency applications.
Strategic Advantages:
- Scalability: Designed for high-concurrency, real-time applications
- Developer Experience: Hot reloading and modern development practices
- Reactive Patterns: Built-in support for asynchronous, non-blocking operations
Vaadin: Rapid Enterprise UI Development
Vaadin excels in internal business application development where rapid UI creation takes precedence over extensive customization.
Business Benefits:
- Rapid Prototyping: Accelerated development for internal business applications
- Java-Only Development: No need for separate frontend expertise
- Enterprise Components: Rich set of business-oriented UI components
Grails: Convention-Driven Development
Built on Groovy but fully Java-compatible, Grails emphasizes convention over configuration for rapid application development.
Value Proposition:
- Rapid Development: Convention-driven approach accelerates development cycles
- Java Compatibility: Leverages existing Java libraries and expertise
- Full-Stack Solution: Complete framework for end-to-end application development
Dropwizard: Microservices Excellence
Dropwizard packages the Java ecosystem's best libraries into a cohesive microservices framework.
Strategic Benefits:
- Microservices Architecture: Purpose-built for modern distributed systems
- Operational Excellence: Built-in metrics, health checks, and monitoring
- Lightweight: Minimal overhead and fast startup times
Quarkus: Cloud-Native Innovation
Red Hat'sQuarkus represents the cutting edge of cloud-native Java development, specifically designed for Kubernetes and containerized environments.
Strategic Advantages:
- Container-First Design: Optimized for Docker and Kubernetes deployments
- Startup Performance: Sub-second startup times and low memory footprint
- Native Compilation: GraalVM integration for native executable generation
- Developer Experience: Live coding capabilities and extensive extension ecosystem
Apache Wicket: Component-Based Web Development
Apache Wicket offers a component-oriented approach to web application development, focusing on reusable UI components and object-oriented design principles.
Business Considerations:
- Component Reusability: Facilitates development of consistent UI libraries
- Type Safety: Compile-time checking reduces runtime errors
- Stateful Components: Simplifies complex UI state management
- Markup Separation: Clean separation between Java logic and HTML presentation
Java Web Development: Framework Selection Strategy
Choosing the Best Java Framework for Web Development
The selection of Java web frameworks should align with specific business objectives and technical requirements:
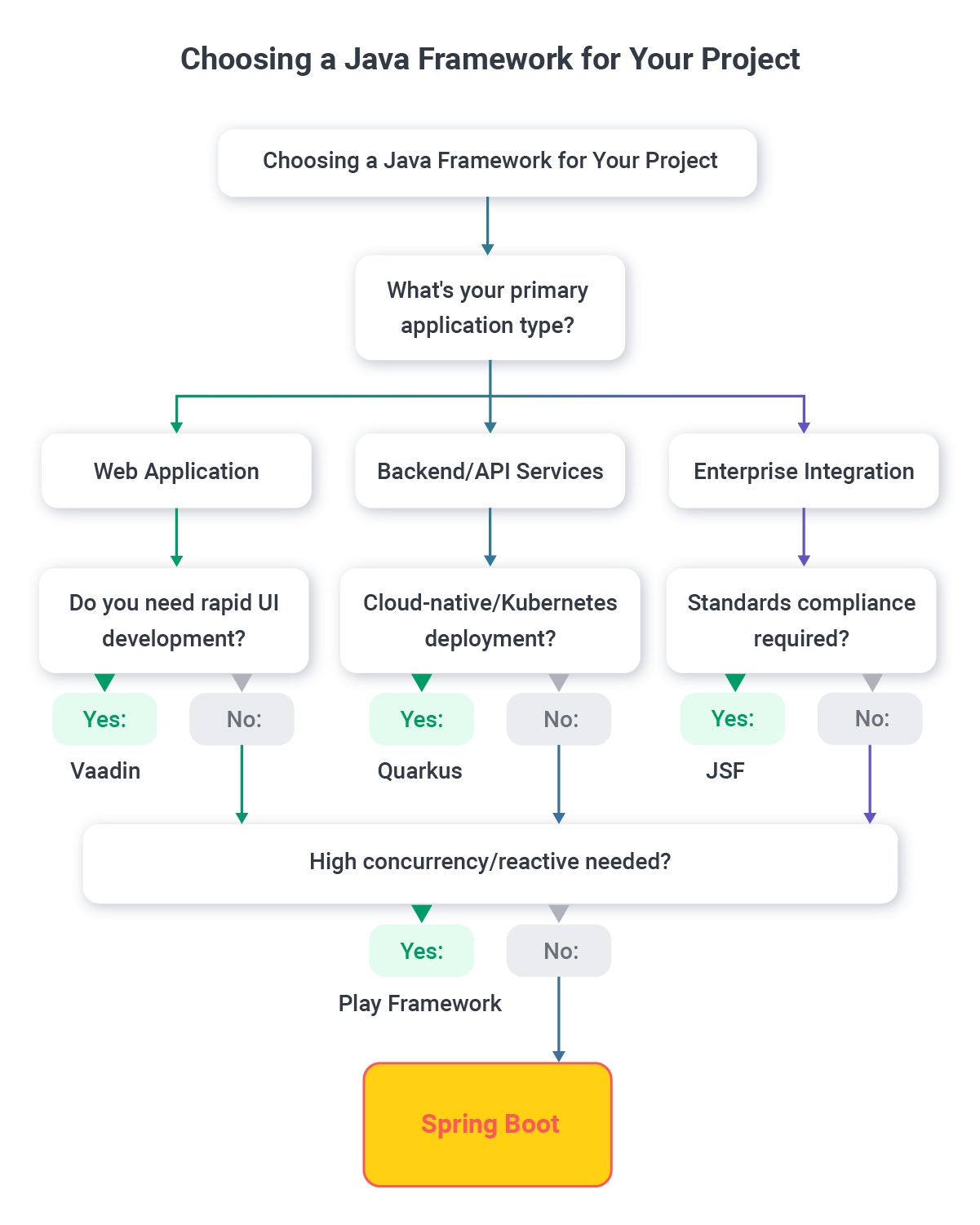
For Large Enterprise Applications: Spring Boot provides the most comprehensive ecosystem and enterprise features. Its extensive cloud-native capabilities make it ideal for organizations pursuing digital transformation initiatives.
For Standards-Driven Organizations: JSF offers the security of following official Java standards, making it suitable for regulated industries or government projects.
For High-Performance Requirements: Play Framework's reactive architecture excels in scenarios requiring high concurrency and real-time capabilities.
For Rapid Internal Development: Vaadin enables quick development of business applications with minimal frontend complexity.
Java Backend Development Considerations
Java backend frameworks must address several critical enterprise requirements:
Scalability Requirements: Modern applications must handle varying loads efficiently. Spring's cloud-native features and Play's reactive architecture both excel in this area.
Integration Capabilities: Enterprise applications rarely exist in isolation. Spring's extensive integration options make it the preferred choice for complex enterprise environments.
Security Compliance: With increasing regulatory requirements, frameworks with robust security features and regular updates become essential. Spring Security and JSF both offer comprehensive security frameworks.
Maintenance and Support: Long-term maintenance costs often exceed initial development costs. Choosing frameworks with active communities and commercial support options mitigates future risks.
Java REST API Framework Selection
For organizations building API-first architectures, framework selection becomes particularly critical:
Spring Boot dominates the Java REST API framework landscape due to its comprehensive feature set, excellent documentation, and extensive ecosystem. Its auto-configuration capabilities and embedded server support make it ideal for containerized deployments.
Dropwizard offers a more opinionated approach specifically designed for REST services, with built-in operational tools that reduce the complexity of service monitoring and management.
Play Framework provides excellent REST capabilities with its reactive foundation, making it suitable for APIs requiring high throughput and low latency.
Framework Implementation: Business Risk Mitigation
Managing Technical Debt
Framework selection significantly impacts long-term technical debt:
Community Vitality: Frameworks with active communities receive regular updates, security patches, and feature enhancements. Spring, with its massive community and commercial backing, represents the lowest risk option.
Migration Complexity: Consider the complexity of future migrations. Well-established frameworks typically provide clearer upgrade paths and migration tools.
Vendor Lock-in: While Java frameworks generally avoid vendor lock-in due to Java's open nature, some frameworks tie more closely to specific platforms or vendors.
Team Skill Development
Framework selection should align with organizational skill development goals:
Market Demand: Spring skills command premium salaries and broad market demand, making it easier to recruit and retain talent.
Learning Curve: Consider the time investment required for team members to become productive with new frameworks.
Cross-Training Opportunities: Some frameworks, like GWT, enable Java developers to work across the full stack, potentially reducing team size requirements.
Java Frameworks List: Strategic Assessment
When evaluating frameworks for Java development, consider this prioritized assessment:
Tier 1: Enterprise Standard
- Spring/Spring Boot: Default choice for most enterprise applications
- Hibernate: Standard for data layer management
Tier 2: Specialized Excellence
- Play Framework: Reactive and high-performance applications
- JSF: Standards-compliant enterprise applications
- Vaadin: Rapid internal business application development
Tier 3: Specific Use Cases
- Grails: Rapid prototyping and convention-driven development
- Struts: Legacy system integration and specific architectural requirements
- GWT: Java-first frontend development
- Dropwizard: Microservices and REST API development
Implementation Roadmap and Best Practices
Phase 1: Assessment and Planning (Weeks 1-2)
- Evaluate current technical landscape and integration requirements
- Assess team skills and training needs
- Define architectural requirements and constraints
- Create framework evaluation criteria specific to business objectives
Phase 2: Proof of Concept (Weeks 3-6)
- Develop small-scale prototypes with top framework candidates
- Evaluate development velocity and team productivity
- Test integration capabilities with existing systems
- Assess operational requirements and deployment complexity
Phase 3: Pilot Implementation (Weeks 7-12)
- Implement a production-ready pilot project
- Establish development workflows and best practices
- Create documentation and training materials
- Validate performance and scalability assumptions
Phase 4: Full-Scale Adoption (Month 4+)
- Roll out framework adoption across development teams
- Implement monitoring and operational procedures
- Establish ongoing training and skill development programs
- Create governance processes for framework updates and evolution

Java Frameworks in 2026: Looking Forward
The Java framework ecosystem continues evolving to address modern development challenges:
Cloud-Native Development: Frameworks increasingly provide first-class support for containerization, microservices, and cloud platforms. Spring's continued investment in cloud-native features positions it well for future enterprise needs.
Reactive Programming: As applications require higher concurrency and responsiveness, frameworks like Play that embrace reactive principles become increasingly valuable.
Developer Experience: Modern frameworks prioritize developer productivity through features like hot reloading, comprehensive tooling, and simplified configuration.
Security Integration: With cybersecurity threats increasing, frameworks that integrate security as a foundational element rather than an add-on become essential for enterprise applications.
AI/ML Integration: Java frameworks are increasingly incorporating AI and machine learning capabilities. Spring AI provides integration with major AI platforms, while specialized frameworks like DL4J enable native Java machine learning development.
Making the Most Strategic Framework Decision
The choice of Java framework represents a strategic decision that impacts development velocity, operational costs, security posture, and long-term maintainability. While Spring Boot has emerged as the de facto standard for most enterprise Java development, specific business requirements may justify alternative approaches.
The key to successful framework adoption lies not just in making the right initial choice, but in establishing processes for ongoing evaluation, team development, and strategic evolution as business needs change and technology advances.
At Softjourn, our Java expertise spans the full framework ecosystem – whether you need strategic consultation on framework selection, team augmentation with specialized Java developers, or guidance on modernizing existing applications, our experienced practitioners can help you navigate these critical technology decisions and accelerate your development initiatives. Contact us to learn more and get started.
The framework landscape will continue evolving, but the fundamental principles of choosing mature, well-supported frameworks with active communities remain constant.
FAQ About Java Frameworks
What is a framework in programming?
A framework in programming is a pre-built foundation that provides structure, libraries, and tools for developing applications. Frameworks establish architectural patterns and provide reusable components that handle common functionality, allowing developers to focus on business-specific features rather than building everything from scratch.
What are frameworks and why are they important for businesses?
Frameworks are essential for modern software development because they accelerate development timelines, reduce costs, improve code quality, and enhance security. For businesses, frameworks represent a strategic investment that reduces technical risk, speeds time-to-market, and ensures applications can scale with business growth.
What is the most popular Java framework?
Spring Framework, particularly Spring Boot, is currently the most popular Java framework. It dominates enterprise Java development due to its comprehensive ecosystem, extensive community support, cloud-native capabilities, and proven track record in large-scale applications.
What are the best Java web frameworks for enterprise development?
The top Java web frameworks for enterprise development include Spring Boot for comprehensive full-stack development, JSF for standards-compliant applications, Play Framework for high-performance reactive applications, and Vaadin for rapid internal business application development.
Which Java backend frameworks should I consider in 2026?
The leading Java backend frameworks for 2026 include Spring Boot for most enterprise applications, Quarkus for cloud-native microservices, Dropwizard for lightweight REST services, and Play Framework for reactive systems requiring high concurrency.
What is the difference between Java frontend frameworks and backend frameworks?
Java backend frameworks handle server-side operations like database interactions, business logic, and API development. Java frontend frameworks (like GWT or Vaadin) manage user interface components and client-side interactions, though many modern architectures separate frontend and backend completely.
How do I choose the best Java framework for my project?
Choose a Java framework based on your project requirements (scalability, performance, security), team expertise, integration needs, and long-term maintenance considerations. Spring Boot is the safest choice for most enterprise projects, while specialized requirements may justify frameworks like Play (reactive), Quarkus (cloud-native), or Vaadin (rapid UI development).
What is Spring Framework in Java and why is it so popular?
Spring Framework is a comprehensive programming model for Java that provides dependency injection, aspect-oriented programming, and extensive integration capabilities. It's popular because it simplifies enterprise Java development, offers excellent cloud-native support, has the largest community, and provides solutions for virtually every enterprise development challenge.
Are Java frameworks still relevant for web development?
Java frameworks remain highly relevant for web development, especially in enterprise environments. They provide the reliability, security, and scalability that large organizations require. Modern Java frameworks like Spring Boot and Quarkus continue evolving to support cloud-native architectures and microservices.
What are the top web frameworks that support Java?
The top web frameworks supporting Java include Spring Boot for comprehensive web development, Play Framework for reactive applications, JSF for component-based development, Struts for MVC architecture, and GWT for Java-to-JavaScript compilation.
Which Java frameworks are best for REST API development?
For Java REST API development, Spring Boot leads with comprehensive REST support and ecosystem integration. Dropwizard excels for dedicated microservices, Play Framework offers excellent performance for high-throughput APIs, and Quarkus provides superior cloud-native capabilities with fast startup times.
What Java application frameworks should enterprise developers know?
Enterprise Java developers should prioritize Spring Framework (including Spring Boot, Spring Security, Spring Data), Hibernate for data persistence, and understand JSF for standards-based development. Knowledge of emerging frameworks like Quarkus for cloud-native development is increasingly valuable.






















