The financial technology sector continues to reshape how we interact with money and financial services. At the heart of this transformation lies fintech software development, AKA the process of creating innovative digital solutions that modernize financial services.
From mobile payment apps to AI-powered investment platforms, fintech software development combines financial expertise with cutting-edge technology to deliver more accessible, efficient, and secure financial products.
Whether you’re a startup founder entering the fintech space or a financial institution looking to modernize your offerings, this comprehensive guide will walk you through the essential aspects of building effective fintech solutions in 2026 and beyond.

Current Fintech Landscape
The Evolution of Financial Technology
Financial technology development has transformed how consumers interact with banking and payment services. What began as simple online banking portals has evolved into comprehensive ecosystems that handle everything from instantaneous payments to algorithmic trading.
The current landscape is characterized by rapid innovation, with new fintech applications continuously emerging to address specific pain points in the financial sector.
Traditional financial institutions are increasingly partnering with fintech developers to enhance their digital offerings. This collaboration represents a significant shift from the early days when fintech was viewed primarily as a disruptive threat.
Today, banks and fintech companies form strategic partnerships that leverage their respective strengths: established customer bases and regulatory expertise from banks, combined with technological agility and innovation from fintech developers.
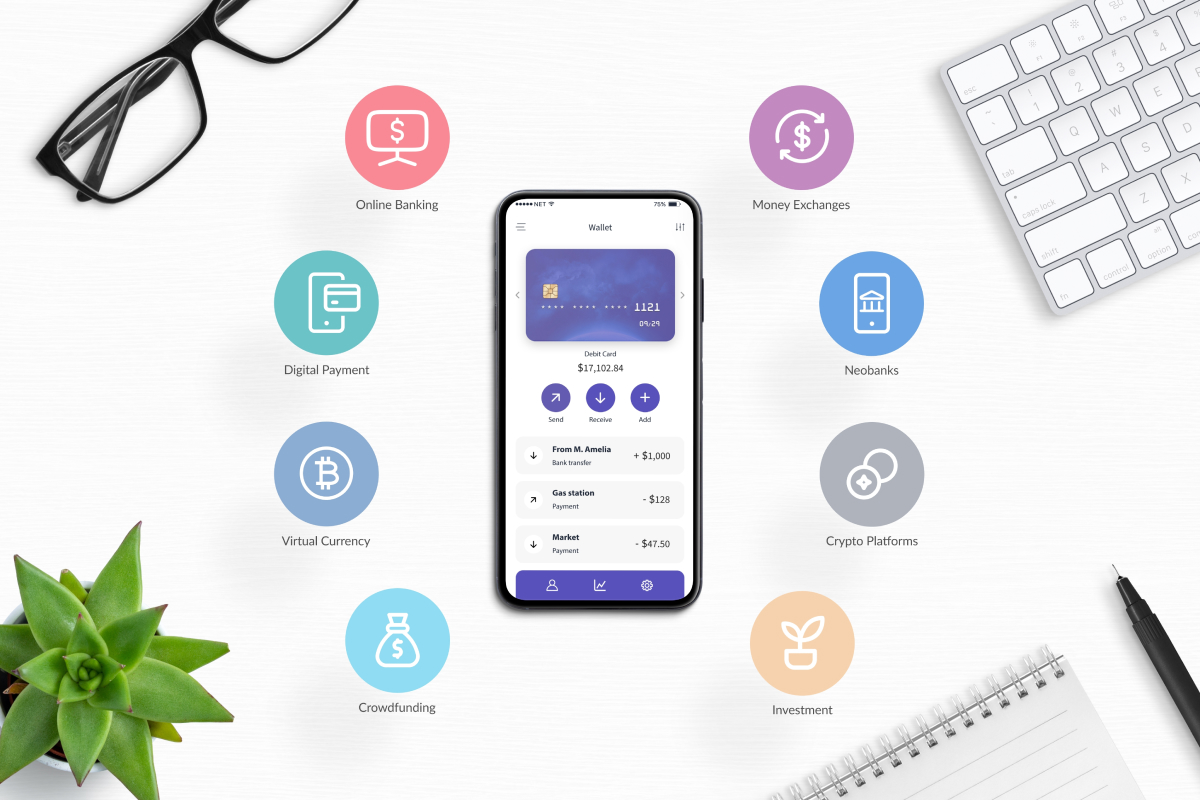
Popular Fintech Product Categories
Fintech is not a single product or service but a diverse ecosystem. Understanding the major categories helps align development efforts with market expectations and business models.
- Payments & Transfers: This includes digital wallets, mobile P2P transfers, remittances, and merchant payment gateways. Apps like PayPal or Venmo prioritize transaction speed, security, and fraud detection.
- Lending & Credit: Platforms offering peer-to-peer lending, BNPL (Buy Now, Pay Later), or SME credit solutions require complex risk modeling, KYC integration, and regulatory compliance.
- Wealthtech & Personal Finance: Robo-advisors, budgeting tools, and automated savings apps focus on personalization and data visualization, often leveraging AI for portfolio recommendations.
- Insurtech: Digital-first insurance platforms use automation and data analytics for policy underwriting, claims processing, and customer service.
- Regtech: These solutions help financial institutions comply with evolving regulations via automated identity verification, transaction monitoring, and reporting tools.

Key Components of Modern Fintech Applications
Modern fintech applications typically incorporate several core components:
- Security Infrastructure
Implementing robust data security measures is non-negotiable in fintech software development. Financial applications handle highly sensitive information, making them prime targets for cyberattacks. Modern fintech security infrastructure includes advanced encryption, multi-factor authentication, and sophisticated fraud detection systems that leverage artificial intelligence to identify suspicious activities. - Process Automation
Automation represents one of the most significant advantages of fintech solutions. By automating routine processes like loan approvals, account verifications, and compliance checks, fintech applications can dramatically reduce operational costs while improving consistency and reducing human error. - User Experience (UX)
The most successful fintech applications prioritize intuitive interfaces and seamless user journeys. This focus on UX is not merely aesthetic, it directly impacts adoption rates and customer retention. Fintech solutions must deliver complex financial functionality while maintaining simplicity and accessibility for users with varying levels of financial literacy.
Case Study Snapshot: Building a Configurable Payments & Rewards Platform for Card Tent

Card Tent, a provider of corporate payments and global reward solutions, partnered with Softjourn to create a highly configurable payout platform with a seamless user experience. The solution required designing a proprietary eWallet interface that could integrate third-party APIs and support a range of payout options, including bank transfers, prepaid cards, and gift cards.
Through an API discovery phase, Softjourn mapped technical dependencies, aligned flows with user needs, and delivered Figma-based UI mockups along with clear business logic. The collaboration gave Card Tent a flexible architecture to scale integrations and a roadmap for future development – delivered on time and within budget.
Core Technologies Driving Fintech Innovation
The fintech software development landscape continues to evolve with emerging technologies and changing regulations. Three technologies, in particular, stand at the forefront of fintech innovation:
Implementing Blockchain in Fintech Applications
Implementing blockchain in fintech applications can enhance security and transparency in financial transactions. While cryptocurrencies represent the most well-known application of blockchain technology, its potential extends far beyond digital currencies. Fintech developers are implementing blockchain for secure identity verification, smart contracts that execute automatically when conditions are met, and creating immutable audit trails for regulatory compliance.
AI-Powered Innovation in Financial Services
Artificial intelligence has become a cornerstone of modern fintech development. AI algorithms power everything from chatbots that provide 24/7 customer service to sophisticated risk assessment models that evaluate creditworthiness using non-traditional data points. Machine learning models continuously improve by analyzing transaction patterns, enabling fintech applications to offer increasingly personalized experiences while strengthening security measures.
How Data Analytics Drives Modern Fintech Solutions
Modern fintech solutions leverage data analytics to identify patterns and predict customer behavior. The ability to process and analyze vast amounts of financial data enables fintech applications to offer personalized recommendations, detect fraudulent activities, and assess risk with unprecedented accuracy. Data analytics plays a vital role in risk assessment and fraud detection in fintech applications, allowing companies to make data-driven decisions that were impossible just a decade ago.
Case Study Snapshot: Optimizing Data Accuracy with a Custom Elasticsearch Upgrade
A fintech platform needed to upgrade from Elasticsearch 2.3.4 to 7.9 to support faster, more accurate data analytics and search performance. To ensure consistency in user results post-upgrade, Softjourn built a custom comparison tool that validated search outputs across both versions, processing over 500,000 queries with just a 0.02% result variance.
The platform is now hosted on AWS, delivering enhanced speed, scalability, and security. The client retains the tool for future upgrades, ensuring continued data accuracy with minimal disruption.
Technology Stack for Fintech Development
Specialized software development for fintech requires expertise in both financial systems and modern technology stacks. The technology stack for fintech applications must balance innovation with security, scalability with compliance, and performance with reliability.
When evaluating software development for fintech, consider both technical capabilities and domain knowledge.
Infrastructure Layer
The foundation of any fintech application is its infrastructure layer. Most modern fintech solutions leverage cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud for their scalability, reliability, and security features. Cloud infrastructure allows fintech applications to handle fluctuating transaction volumes efficiently while maintaining performance during peak usage periods.
Key considerations for the infrastructure layer include:
- Scalability: The ability to handle growing user bases and transaction volumes
- Reliability: Ensuring consistent uptime and performance
- Disaster Recovery: Robust backup and recovery systems to prevent data loss
- Geographic Distribution: Deploying across multiple regions to reduce latency and ensure compliance with data localization requirements
Case Study Snapshot: Future-Proofing UPC’s Open Banking Platform with a Secure AWS Migration

Ukrainian Processing Center (UPC) partnered with Softjourn to migrate its Open Banking platform from on-premise infrastructure to AWS, ensuring PCI DSS compliance and aligning with new banking regulations. Softjourn led a phased, serverless migration using infrastructure-as-code and centralized environment management.
The result: A scalable, secure, and cost-efficient cloud environment that improved performance, enhanced compliance, and positioned UPC for long-term innovation in financial services.
Database Management
Fintech applications manage vast amounts of sensitive financial data, making database selection and configuration critical decisions in the development process. The database layer must ensure data integrity, security, and performance while complying with relevant regulations.
Common database solutions in fintech include:
- Relational Databases
Traditional relational databases like PostgreSQL and MySQL remain popular choices for fintech applications that require ACID compliance (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability). These databases excel at handling structured financial data and complex transactions. - NoSQL Solutions
For applications that deal with unstructured or semi-structured data, NoSQL databases like MongoDB offer greater flexibility. These databases can be particularly useful for applications that analyze diverse data sources or need to scale horizontally across multiple servers. - Time-Series Databases
Specialized time-series databases optimize the storage and retrieval of time-stamped data, making them ideal for applications that track market movements, transaction histories, or user behavior over time.
Case Study Snapshot: Boosting Performance with a Zero-Downtime Database Migration for Versapay

Versapay, a leading AR automation fintech, partnered with Softjourn to improve performance and scalability by migrating their data-heavy platform to AWS Aurora. Faced with growing volumes of historical data and increasingly complex queries, the team needed a more efficient solution, with zero disruption to live operations.
Softjourn used AWS DMS and schema transformation techniques to migrate the database with minimal downtime, delivering improved query performance, cost-optimized test runs, and future-ready scalability - backed by complete documentation for ongoing maintenance.
Programming Languages and Frameworks
The best software development for fintech balances innovation with strict security and compliance requirements. Several programming languages have established themselves as standards in the fintech industry:
- Python
Python’s simplicity, readability, and extensive libraries for data analysis and machine learning make it a favorite for fintech development. It’s particularly well-suited for applications involving complex financial calculations, risk modeling, or algorithmic trading. - Java
Java’s robustness, security features, and platform independence have made it a staple in enterprise financial applications. Many established financial institutions build their core systems using Java. - JavaScript and TypeScript
For front-end development, JavaScript frameworks like React and Angular enable responsive, interactive user interfaces. TypeScript adds static typing to JavaScript, reducing errors in complex fintech applications.

Architecture Best Practices for Fintech
The architecture of a fintech application must support performance, scalability, compliance, and change-resilience. Here are key architectural considerations:
- Microservices vs. Monolith: A microservices architecture allows teams to build, test, and deploy services independently—ideal for fintechs with fast iteration cycles. However, this adds complexity in orchestration and monitoring.
- Event-Driven Architecture: Leveraging tools like Kafka, fintech apps can decouple services and build robust workflows based on asynchronous events (e.g., “transaction completed” or “KYC approved”).
- Zero Trust Architecture: With increasing cyber threats, Zero Trust models treat all internal and external requests as untrusted by default, requiring authentication and validation at every step.
- Domain-Driven Design (DDD): DDD helps fintech developers model the software based on real-world financial domains, aligning the codebase with business logic and compliance requirements.
Third-Party Integrations and Fintech Ecosystems
Fintech applications rarely operate in isolation. They need to integrate with a wide array of third-party services to deliver core functionality and meet compliance requirements.
- Banking APIs and Open Banking: Services like Plaid, Tink, and Yodlee allow apps to connect with users’ bank accounts for real-time data access. In regions where Open Banking is regulated, APIs must comply with PSD2 and similar standards.
- Identity Verification and AML Tools: Tools like Onfido, Jumio, and Alloy help fintech apps meet KYC/AML requirements by verifying identities through biometric data, document scanning, and watchlist screening.
- Card Networks and Payment Processors: Visa, Mastercard, Stripe, and Adyen offer APIs for card issuance, payments, and fraud prevention. Building around these APIs requires careful handling of tokenization and PCI DSS compliance.
- Core Banking Integrations: For fintechs partnering with banks or using Banking-as-a-Service platforms, reliable integration with core systems is essential for services like ledgering, deposits, and credit checks.

Case Study Snapshot: Integrating Complex Financial Services to Future-Proof an Expense Management Platform
A global expense management leader partnered with Softjourn to integrate services from US Bank, Wise, and Finicity. Their legacy architecture was over a decade old and required restructuring to support modern APIs, data validation, and multi-currency transactions.
Softjourn handled end-to-end integration: mapping architecture, enhancing internal systems, and executing secure API calls. The result? A seamless user experience and new capabilities delivered on time and within budget. This positioned the client to scale and stay competitive in the evolving fintech ecosystem.
Data Security Challenges in Fintech Software Development
Data security concerns remain one of the biggest challenges in fintech software development. Security cannot be an afterthought, it must be integrated into every layer of the technology stack from the beginning of the development process.
Key security components include:
- Encryption
All sensitive data should be encrypted both at rest and in transit. This includes implementing TLS/SSL for all communications and using strong encryption algorithms for stored data. - Authentication and Authorization
Robust authentication systems, including multi-factor authentication, biometric verification, and risk-based authentication, help ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive financial information. - Secure API Design
As fintech applications increasingly rely on APIs to connect with other services, securing these interfaces becomes critical. This includes implementing proper authentication, rate limiting, and input validation. - Security Monitoring
Continuous monitoring for suspicious activities, combined with automated alerts and response systems, helps detect and mitigate security threats before they cause significant damage.
Case Study Snapshot: Fortifying Security & PCI Compliance for an Expense Management Platform
PEX, a leader in corporate expense management, partnered with Softjourn to proactively enhance their data security and streamline PCI compliance. With evolving threats and growing platform complexity, they sought improvements in vulnerability management, remote access, and log monitoring.
Softjourn overhauled their Azure infrastructure, introduced a new SIEM system for real-time insights, and transitioned the platform toward Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA). The result: a stronger security posture, smoother compliance processes, and a scalable foundation for future growth.

Development Methodologies and Processes
Agile Development Methodologies for Fintech Projects
Agile development methodologies allow fintech teams to adapt quickly to regulatory changes and market demands. The financial sector’s dynamic regulatory environment and rapidly evolving customer expectations make traditional waterfall development approaches insufficient for most fintech projects.
Benefits of Agile in Fintech
Many successful fintech projects rely on agile development practices to deliver value incrementally. The benefits of agile methodologies in fintech development include:
- Adaptability to Regulatory Changes
When new regulations emerge, agile teams can quickly pivot and adjust their development priorities to ensure compliance. - Faster Time to Market
By delivering working software in short iterations, fintech companies can release features incrementally rather than waiting for a complete product. - Reduced Risk
Regular testing and stakeholder feedback throughout the development process help identify issues early when they’re less costly to fix. - Better Alignment with Business Goals
Frequent communication between development teams and business stakeholders ensures that the technical implementation aligns with business objectives.
Development Cycle Management
Implementing agile development in fintech projects helps balance innovation with compliance requirements. A typical fintech development cycle includes the following stages:
- Planning and Requirement Analysis
This phase involves gathering requirements from stakeholders, understanding regulatory constraints, and defining the scope of the project. For fintech applications, this stage must include a thorough analysis of applicable regulations and security requirements. - Design and Architecture
During this phase, developers create the technical architecture for the application, considering factors like scalability, security, and integration with existing systems. In fintech, particular attention must be paid to data protection, audit trails, and compliance features. - Development and Testing
The actual coding and testing of the application occur in iterative cycles, with continuous integration ensuring that new code integrates smoothly with the existing codebase. Automated testing is particularly important in fintech to catch potential security vulnerabilities and compliance issues. - Deployment and Monitoring
After thorough testing, the application is deployed to production environments. Continuous monitoring helps identify performance issues, security threats, or unusual patterns that might indicate fraud.
Quality Assurance in Fintech
Quality assurance for fintech applications goes beyond functional testing to include:
- Security Testing
This includes penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and code reviews specifically focused on identifying security weaknesses. - Compliance Testing
Verifying that the application meets all relevant regulatory requirements, including proper handling of personal financial information and adequate audit trails. - Performance Testing
Ensuring that the application can handle expected transaction volumes, especially during peak periods, without degradation in performance. - User Acceptance Testing
Involving actual users to verify that the application meets their needs and provides an intuitive, accessible experience.
Case Study Snapshot: Automating Testing to Accelerate Fintech Platform Transition
Tribal Credit, a fintech innovator, turned to Softjourn to implement robust manual and automated testing processes while transitioning from their legacy 1.0 platform to a new 2.0 system. Softjourn designed a comprehensive QA strategy, built regression checklists, launched automation using PyTest, and fully integrated CI/CD tools.
We helped them with a seamless system migration, faster test cycles, improved team coordination, and a sustainable QA structure that Tribal Credit continues to rely on for quality assurance and platform stability.
Building the Right Fintech Development Team
Fintech development success depends not just on code quality but also on team structure and domain knowledge. A high-performing fintech team typically includes:
- Product Manager (with fintech experience): Bridges business needs, compliance, and technical execution.
- Tech Lead / Solution Architect: Designs a scalable and secure system architecture tailored to fintech needs.
- Security Engineer or DevOps: Embeds security practices throughout the CI/CD pipeline.
- Compliance or Regulatory Expert: Especially for projects operating across multiple regions or regulated sectors.
- QA Specialist: Ensures regulatory, performance, and usability testing are all prioritized.
Many fintech companies also work with external partners or consultants to supplement missing expertise, such as cloud architecture or embedded finance integrations.
Navigating Regulatory Compliance in Fintech Development
The Regulatory Landscape
Navigating regulatory compliance in fintech development requires specialized knowledge and ongoing vigilance. Fintech applications operate in one of the most heavily regulated sectors, with requirements varying significantly across different jurisdictions. Successful fintech applications build regulatory compliance into their development process from day one.
Key regulatory considerations include:
- Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML)
Fintech applications that handle money transfers or account openings must implement robust KYC procedures to verify customer identities and monitor for suspicious activities. - Data Protection Regulations
Regulations like GDPR in Europe, CCPA in California, and similar laws worldwide impose strict requirements on how financial data can be collected, stored, and processed. - Payment Processing Regulations
Applications that process payments must comply with standards like PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) to protect cardholder data. - Banking Regulations
Fintech applications that offer banking-like services may need to comply with banking regulations or partner with licensed financial institutions.
Case Study Snapshot: Meeting CBI Regulatory Requirements with a Secure AWS Migration
Bullet, an Irish accounting software provider, partnered with Softjourn to meet Central Bank of Ireland (CBI) regulatory requirements by modernizing their infrastructure. To achieve this, Softjourn led a seamless migration from a legacy monolithic system to a scalable, AWS-based architecture.
The new setup enabled high availability, observability, and regulatory-grade redundancy, including disaster recovery, zero-downtime deployment, and secure data management across zones. Today, Bullet is one of the few CBI-licensed AWS resellers and is trusted by SMEs, enterprises, and financial institutions alike.
Compliance by Design
The complexity of regulatory compliance in fintech varies significantly across different global markets. Rather than treating compliance as a checkbox exercise, successful fintech developers integrate compliance considerations throughout the development process:
- Regulatory Research
Before development begins, thoroughly research applicable regulations in all target markets. - Compliance Architecture
Design the application architecture with compliance in mind, including features like audit trails, data retention policies, and user consent management. - Regular Compliance Reviews
Schedule regular reviews to ensure ongoing compliance, especially when entering new markets or when regulations change. - Documentation
Maintain comprehensive documentation of compliance measures to demonstrate due diligence to regulators if required.
Case Study Snapshot: Enabling Audit-Ready Architecture for a Regulated Financial Institution

A U.S.-based financial institution partnered with Softjourn to prepare for stringent regulatory audits, including FDIC and PCI-DSS requirements. The engagement focused on designing secure, audit-ready architecture; implementing structured development and QA processes; and producing the documentation needed to pass compliance reviews with confidence.
The institution successfully passed its FDIC audit – earning praise for its technical maturity – and is now well-positioned for future PCI-DSS certification. Many of the secure practices and documentation standards introduced by Softjourn remain in use today as internal best practices.

Mobile Banking: The Core of Modern Fintech Applications
The Mobile-First Approach
Mobile banking features have become essential components of any comprehensive fintech solution. The shift toward mobile-first development reflects changing consumer preferences, with many users now managing their finances primarily through smartphones.
Key considerations for mobile banking development include:
- Cross-Platform Compatibility
Ensuring the application works seamlessly across different mobile operating systems and device types. - Offline Functionality
Providing basic functionality even when users have limited or no internet connectivity. - Biometric Authentication
Implementing fingerprint, facial recognition, or other biometric authentication methods for enhanced security and convenience. - Push Notifications
Using push notifications to alert users about important account activities, potential fraud, or upcoming payments.
The demand for secure and intuitive mobile banking applications continues to drive innovation in fintech. As smartphone capabilities advance, mobile banking applications increasingly leverage features like augmented reality for visualizing spending patterns, voice commands for hands-free banking, and near-field communication (NFC) for contactless payments.
Case Study Snapshot: Expanding Mobile App Payments with a New Integration
A long-time Softjourn client, Tacit, sought to expand the reach of its mobile ordering platform by integrating a new payment method popular among debit-first consumers. Softjourn developed the first-ever in-app integration to support a domestic debit card network via a major mobile wallet, helping Tacit remove adoption barriers and improve accessibility.
They gained a broader user base, smoother user experience, and strengthened relationships with payment service providers, all without compromising security or performance.

Future Trends in Fintech Software Development
The State of Fintech in 2026
The fintech landscape in 2026 is defined by rapid digital transformation, increased regulation, and growing demand for inclusive and sustainable financial services. Key trends include:
- Global fintech adoption continues to rise, with countries in Latin America, Africa, and Southeast Asia leapfrogging traditional infrastructure.
- BigTech firms like Apple and Google are deepening their financial offerings, blurring lines between tech and finance.
- Venture funding has shifted from hypergrowth to sustainable models, with a focus on profitability, compliance, and niche verticals.
As fintech matures, development priorities are shifting from speed-to-market to long-term scalability, risk mitigation, and ecosystem integration.
Emerging Technologies
The future of financial technology development lies in creating more personalized and accessible financial services. Several emerging technologies are poised to reshape fintech software development in the coming years:
- Embedded Finance
Financial services are increasingly being integrated into non-financial platforms, allowing users to access banking services, payments, and credit within the apps they already use daily. - Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Blockchain-based financial services that operate without traditional intermediaries are gaining traction, offering new models for lending, borrowing, and investing. - Voice Banking
As voice assistants become more sophisticated, voice-activated banking services are emerging as a convenient alternative to traditional mobile banking interfaces. - Quantum Computing
While still in its early stages, quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize areas like cryptography, risk modeling, and fraud detection in fintech.
Fintech Solutions for Financial Institutions
Traditional financial institutions are increasingly partnering with fintech developers to enhance their digital offerings. This collaboration represents a significant evolution in the relationship between banks and fintech companies:
- Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS)
Banks are opening their infrastructure through APIs, allowing fintech companies to build new services on top of regulated banking platforms. - Digital Transformation
Established financial institutions are investing heavily in modernizing their legacy systems, often partnering with fintech developers to accelerate this process. - Hybrid Models
The line between traditional banks and fintech companies is blurring, with many institutions adopting hybrid models that combine the regulatory expertise of banks with the technological agility of fintech.
Sustainability and Inclusion
Two important trends are shaping the future direction of fintech development:
- Green Fintech
Financial applications that help users track and reduce their carbon footprint, invest in sustainable projects, or access green financing options are gaining popularity. - Financial Inclusion
Fintech developers are creating solutions specifically designed to serve underbanked populations, using alternative data sources for credit scoring and designing interfaces accessible to users with limited financial or technological literacy.

Final Word
Fintech software development stands at the intersection of financial expertise and technological innovation. As we’ve explored throughout this guide, creating successful fintech applications requires a multifaceted approach that balances cutting-edge technology with stringent security and compliance requirements.
The future of fintech software development promises even greater integration of financial services into our daily lives, with more personalized, accessible, and secure solutions.
If you're planning your next fintech solution and want a trusted technology partner to support you, let’s talk.
Frequently Asked Questions
What skills are most important for fintech software developers?
Successful fintech developers need a combination of technical skills (programming, security, cloud infrastructure) and domain knowledge (financial regulations, banking processes). They should also understand data privacy requirements and have experience with secure coding practices.
How long does it typically take to develop a fintech application?
Development timelines vary widely depending on the complexity of the application and regulatory requirements. Simple applications might be developed in 3-6 months, while more complex platforms involving multiple financial services could take 12-18 months or longer to reach full production.
What are the biggest challenges in fintech software development?
The most significant challenges include navigating complex regulatory requirements, ensuring robust security while maintaining usability, integrating with legacy financial systems, and keeping pace with rapidly evolving technologies and customer expectations.
How can fintech applications ensure compliance across different countries?
Developing a compliance strategy that accounts for regional variations is essential. This often involves creating a modular architecture that can adapt to different regulatory requirements, partnering with local experts in each market, and implementing configurable compliance features that can be adjusted for different jurisdictions.
What’s the best way to test security in fintech applications?
Security testing for fintech should include a combination of automated vulnerability scanning, manual penetration testing by security experts, regular code reviews focused on security, and simulated phishing attacks to test employee awareness. Many fintech companies also implement bug bounty programs to incentivize ethical hackers to identify vulnerabilities.
How do I choose the right tech stack for a fintech project?
The best tech stack balances your business goals with compliance, scalability, and speed to market. Consider factors like existing team expertise, required integrations (e.g., banking APIs), target platforms (web, mobile), and long-term maintainability. Working with a tech partner familiar with financial services can help you avoid pitfalls and select tools that align with industry standards.
What are the best practices for designing a fintech application?
Fintech UX should be intuitive, accessible, and built on trust. Key practices include simplifying complex flows (e.g., KYC, transfers), prioritizing clarity in data presentation, implementing strong error handling, and building mobile-first. Accessibility, personalization, and user education are increasingly important for adoption.
How much does it cost to develop a fintech application?
Costs vary based on scope, complexity, and compliance needs. A simple MVP can start around $50K–$100K, while enterprise-grade platforms may exceed $500K. Costs are often impacted by the need for integrations, certifications (e.g., PCI DSS), and whether you build in-house or with a specialized fintech development partner.
What compliance certifications should I consider for a fintech product?
Depending on your service, geography, and partners, you may need to comply with standards such as:
- PCI DSS for handling payment data
- SOC 2 for data security controls
- GDPR/CCPA for data privacy
- ISO/IEC 27001 for information security
Consult with legal and technical experts early to plan for these from day one.
When should I bring in a fintech development partner?
Bringing in a partner early, such as in the discovery or planning phase, can accelerate time-to-market and help avoid costly missteps. Experienced fintech partners bring insights from other platforms, reduce development risks, and help you plan for security, compliance, and scalability from the ground up.
How can I future-proof my fintech platform?
Futureproofing starts with modular architecture, API-first design, and strong DevOps practices. Choose cloud-native infrastructure, automate testing and deployment, and stay up to date with industry trends (e.g., embedded finance, digital ID, AI/ML). Continuous refactoring and regular audits can help your platform evolve without major rewrites.


















