New fintech apps are appearing on the market every single day. Investments in fintech are moving towards B2B, AI-driven automations, and a new focus on real-time infrastructure in 2026. With fintech investments totaling $95.6 billion globally in 2024 and the sector reaching record profitability in 2025, with 69% of publicly listed companies became profitable.
It's clear that banks and fintech companies are becoming direct competitors in the finance market. For customers, this competition offers interesting solutions to their problems and a wide range of innovative digital solutions to their problems.
We understand that developing a fintech app is not an easy process, and in this guide, we hope to share some of the insights we have gathered over nearly two decades of experience in the fintech industry.

A Brief Fintech Industry Overview
Understanding what fintech even is nowadays is not as easy as it once was. Today, it’s a term used to describe the companies that operate in the financial tech sector. Most of these companies are startups that develop innovative solutions for digital payments, big data, alternative finance, and financial management.
The global fintech market reached $340.10 billion in 2025 and is projected to grow to $394.88 billion in 2026, reaching $1,126.64 billion by 2032 at a CAGR of 16.2%. This explosive growth reflects fintech's evolution from a disruptive force to an essential component of the global financial system
The fintech market has grown so much in the past few years that 66.7% of bank executives believe that fintech will have a significant impact on mobile payments. We will see more than 65% of Americans using digital banking by the end of 2025.2

The Fintech Market
Since money is interconnected with everything we do, the market covers many different aspects of people's lives. Digital Payments remains the market's largest segment, with total transaction value reaching $24.07 trillion in 2025 and projected to grow to $36.09 trillion by 2030 at a CAGR of 8.44%. The number of users is expected to reach 3.81 billion by 2030, with digital wallets accounting for 49% of global e-commerce sales and mobile payments becoming the dominant method for in-store purchases in major markets.
Different markets for fintech applications:
- Payments and transactions
- Personal finance
- Neobanks
- Trading and Investing
- Insurance
- Lending
- Mortgage payments
- Crypto-based transactions
Successful Fintech Software Examples
When looking at the list of the most popular fintech apps, it’s clear that there’s a wide variety of success stories. However, some market players were able to get enough momentum to grow and start taking over revenue from traditional banks.

Venmo is a very popular payment app that helps users split the cost of anything from a dinner to a plane ticket. It started as a financial app for millennials because it is easy to use, works on iPhones and Android smartphones, and even has a chat feature for users.
Chime is a quickly growing, mobile-only bank in the US. The application allows users to manage their spending without hidden transaction fees and offers automatic saving options.
NuBank is a Brazil-based fintech company and the world's largest neobank by customer count. Founded in 2013, it became the first digital banking platform outside of Asia to surpass 100 million customers (May 2024), reaching 118.6 million customers by Q1 2025 across Brazil, Mexico, and Colombia. The application allows users to track spending, get real-time information about their cards, use Nubank rewards and points, plus access savings accounts, investments, crypto, personal loans, and insurance. NuBank's remarkable growth is powered by its customer-centric model, with approximately 80-90% of new customers acquired through word-of-mouth. In Q1 2025, NuBank generated $3.25 billion in quarterly revenue and $557 million in profit, making it the world's most profitable neobank with an industry-leading efficiency ratio of 24.7%
is a Brazil-based fintech application and one of the fastest-growing financial services on the market. The application is allowing users to track their spending, get real-time information about their cards, and even use Nubank rewards and points.
Revolut started as a London-based startup in 2015 offering prepaid debit cards, but has since evolved into a comprehensive financial super app. Today, it offers cryptocurrency exchange, the ability to send money in 36 currencies, stock trading, and P2P payments across 48 countries. As of late 2024, Revolut serves 52.5 million customers globally (growing to an estimated 65 million by 2025), with revenue of $4.0 billion in 2024, a 72% year-over-year increase. The company achieved a valuation of $75 billion in November 2025, demonstrating sustained momentum with 38% customer growth and profitability for four consecutive years.
Why Should You Make a Fintech Application?
Currently, users are already used to managing payments through their finance app on their smartphones. For that reason, fintech apps are a low-maintenance and user-friendly way to manage transactions and send and receive money with just a few clicks using a mobile banking app.
With more than 5 billion people worldwide owning smartphones, apps are becoming an easy way to manage many aspects of modern life. Instead of going to a bank, users can send and receive money instantly, and when they need help, smart chatbots are there to provide answers. Additionally, since the COVID-19 pandemic, factors like restrictions, safety, and convenience influenced many people to be less inclined to go in-person to a bank.
Another reason why banks and financial institutions should develop fintech apps is to promote financial education. A report by the Financial Regulatory Authority uncovered that financial literacy among Americans has decreased, more people than ever have some kind of debt, and half of all Americans feel like their personal finances are a source of stress.
Fintech applications could be key to helping people manage their money and debts. Apps can help people better understand their spending habits and overall finances and even provide them with useful advice on how to save money.
Choose Your Sub-Industry of Fintech
Fintech has developed into a market giant in the past few years. With more than 1.7 billion unbanked people worldwide, it has become clear that banking apps are the catalyst to help people get access to funds, remittances, and other services.
With an abundance of trends and sub-niches they can cover, newcomers to the fintech product development are slowly focusing on providing specific solutions to address different user needs. While some fintech apps focus solely on offering gift cards, remittance payments, and BNPL services, others are creating a multitude of services as part of one ‘super-app’.
If you are planning to develop a new fintech app or add a digital wallet or payments element to your existing platform, one of the first things you should consider is what niche or sub-industry you are interested in targeting, so you can focus on solving a specific problem for a group of users.
Trying to solve everything and offering as many services as possible puts you in a tough position, as you will be competing with big companies. Instead, we advise our clients to find a particular problem of the industry to target.
Types of Fintech Apps
Building software that responds to users’ needs requires a deep understanding of the industry and a unique perspective. There are many different paths a startup can take, and over the years, Softjourn has provided unique solutions to clients working on various fintech apps. Below, we have included the most common app types we have helped build and provided solutions for.

Mobile Banking App Development
Mobile banking is usually the most popular type of app for managing accounts, paying bills, and transferring funds. Most digital banking apps can be separated into two categories: digital-only and digital banking apps connected to brick-and-mortar banks. Both types of apps allow users to have 24/7 access to their money and include other banking services, such as:
- Fast money transfers
- Customer service
- Access to account balances and spending trackers
- QR payments
- Biometric authentication
- Bill Splitting
- A savings manager
- Integrations with Google Pay and Apple pay
Mobile Payments Processors
Digital payments is the largest category of applications in the fintech sector. Payment processing apps provide a quick way to manage payment transactions and make payments more accessible. Reputable payment processors are a key tool for any successful business since they enable instant transfers of funds from buyers to sellers as well as multiple payment options for customers.
Here are key features that are typically found in payment processors:
-
Ease of Use and Security: User-friendly interfaces are essential. Simple navigation, quick setup, and intuitive design enable both merchants and customers to use the service without extensive training.
- Multiple Payment Options: The ability to process various payment methods, including credit/debit cards, bank transfers, mobile wallets, and even cryptocurrencies, is vital to cater to a wide range of customers.
-
Mobile Point of Sale (mPOS) Capabilities: Processors often include mPOS functionality, allowing merchants to use mobile devices as point-of-sale terminals.
-
Fast Processing Speed: Quick processing of transactions is critical in providing a smooth customer experience and improving business efficiency.
-
Real-Time Analytics and Reporting: Access to real-time data on sales, customer behaviors, and other transaction metrics helps businesses make informed decisions.
-
Integration with Other Systems and Customizability: The ability to integrate with existing business systems, like accounting software, CRM systems, and inventory management tools, is important for seamless business operations.
-
Global Currency and Language Support: For businesses operating internationally, supporting multiple currencies and languages is essential.
-
Contactless Payments: With the growing trend of contactless transactions, payment processors need to support NFC (Near Field Communication) or QR code-based payments.
-
Customer Support: Reliable customer support is crucial, including assistance with setup, troubleshooting, and resolving transaction issues.
-
Recurring Billing and Subscription and Invoicing Management: For businesses that operate on a subscription model, features to manage recurring billing and subscriptions are important.
-
Compatibility with Multiple Devices: The system should work seamlessly across various devices, including smartphones, tablets, and desktop computers.
-
Offline Functionality: The ability to process payments even when offline and sync them once the connection is restored can be crucial for businesses in areas with unstable internet connections.
Payment processors can range from card swiping technologies that pair with apps, such as Square, or online payment platforms that allow for international transfers of different currencies. PayPal is currently one of the biggest processors in the world, and it offers some of the fastest cross-border transactions.

Neobanks (Digital-Only Banks)
Digital-only banks, also known as neobanks, are changing the banking landscape by removing physical branches from banking operations. Instead, all services are conducted via desktop or mobile application.
There are two types of digital banks: front-end neobanks and full-stack neobanks.
While full-stack neobanks have banking licenses and the ability to cooperate independently, front-end neobanks need to partner with brick-and-mortar banks to provide their services to a variety of customers.
Expense Management Systems
Centralizing all expenses in one system is important for any type of business. Whether it is used for a small company or a large corporation, financial information is crucial for decision-making processes.
Expense management applications are already finding their way to users since they enable companies to keep track of every dollar to visualize where money is going and how it can be better spent.
Digital Wallets
Digital wallets are one of the most used online payment tools. A digital wallet securely stores virtual versions of debit and credit cards as well as vaccine QR codes and other handy items. Different fintech apps use different types of wallets, but most of them fall within one of these three groups: open, semi-closed, or closed.
Open wallets allow for fast online transactions, purchases, in-store payments, and cashback, while semi-closed and closed work only with specific retailers.
Crypto wallets are emerging as a new type of digital wallet, as they store cryptocurrency passwords in one place. Unlike standard digital wallets, crypto wallets don’t hold any currency, but only codes to access crypto.
Investment Fintech Apps
Investment apps are a great way for people to get into the stock market. They provide helpful analytics and financial data to ensure users have all the right tools for their personal investment management.
Investment apps usually work like financial advisors and include an easy-to-use interface that allows users to follow different stocks. Furthermore, they often come with integrations for smartwatches and a variety of alerts to notify users of any changes within the market.
Remittance Fintech Apps
Every day the demand for money transferring services grows. Remittance apps, also as money transferring, enable users from all over the world to move money with multi-bank and multi-currency options, with few restrictions. They also give users the ability to manage different types of transfers and follow the exchanged money, and they even support multiple currencies and languages to make foreign exchange easy and affordable.
Insurance App
The insurance industry is ripe for technological disruption. Insurtech apps provide customized insurance policies based on unique risk profiles, integrating with wearables and IoT devices for real-time data analytics. Features include instant quotes, AI-powered policy management, automated claims processing, and predictive risk alerts. This B2C approach modernizes legacy insurance practices to be transparent, affordable, and hassle-free—covering life, health, home, auto, and disability insurance.
Legal Requirements
Legal requirements vary greatly depending on the country, state, and even regions within a country. This is why it is so important to research the requirements needed before creating a fintech application. As previously mentioned, while some countries have a specific regulatory body for fintech companies, others regulate it on a case-to-case basis.
Since governments still haven’t reached a consensus on how to deal with fintech companies on a global level, companies need to work with experts to navigate through all the complexities of financial standards, regulations, and laws per country.
These regulations are designed to protect consumers, ensure fair and competitive markets, and prevent financial crimes. Here's an introduction to some key laws and regulations in fintech application development:
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR):
- Region: European Union
- Description: GDPR is a regulation on data protection and privacy in the EU and the European Economic Area. It also addresses the transfer of personal data outside these areas. It gives individuals control over their personal data and simplifies the regulatory environment for international business.
- Read more: General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) – Official Legal Text
Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act:
- Region: United States
- Description: Enacted in response to the 2008 financial crisis, this comprehensive set of financial regulations includes measures to prevent excessive risk-taking and deceptive practices in financial markets. It also established several new government agencies, including the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB).
- Read more: Dodd-Frank Act | CFTC
Payment Services Directive 2 (PSD2):
- Region: European Union
- Description: PSD2 is an EU Directive that regulates payment services and payment service providers. It aims to increase competition and participation in the payments industry, including from non-banks, and to provide a more secure and efficient payment environment.
- Read more: DIRECTIVE (EU) 2015/2366 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL
Payment Services Directive 3 (PSD3):
- Region: European Union
- Description: Payment Services Directive 3 (PSD3) is an updated version of Payment Services Directive 2 (PSD2) and provides rules on the efficiency and security of electronic/digital payments and financial services in the EU. It aims to improve competition and innovation in the financial industry.
Read more:
Anti-Money Laundering Directives (AML):
- Region: International, with regional variations
- Description: AML regulations are designed to prevent money laundering and terrorist financing. They require financial institutions to monitor their clients' transactions and report suspicious activities. The specifics can vary by country but generally include requirements for customer due diligence and record-keeping.
- Read more: Directive - 2015/849 - EN - Fourth Anti-Money Laundering Directive - EUR-Lex
Bank Secrecy Act (BSA):
- Region: United States
- Description: The BSA requires financial institutions in the U.S. to assist government agencies in detecting and preventing money laundering. It includes requirements for record-keeping and reporting by private individuals, banks, and other financial institutions.
- Read more: The Bank Secrecy Act | FinCEN.gov
Electronic Fund Transfer Act (EFTA):
- Region: United States
- Description: EFTA provides protection to consumers engaging in electronic fund transfers. It offers rights and liabilities for transactions made through ATMs, debit cards, and other electronic payment systems.
- Read more: Electronic Fund Transfer Act
Know Your Customer (KYC) Regulations:
- Region: International, with regional variations
- Description: KYC is a standard practice in the investment industry that ensures investment advisors know detailed information about their clients' risk tolerance, investment knowledge, and financial position. KYC regulations are crucial for combating fraud and money laundering.
- Read more: Understanding the "Know Your Customer" (KYC) Process | Dow Jones
Markets in Financial Instruments Directive II (MiFID II):
- Region: European Union
- Description: MiFID II is a legislative framework instituted by the EU to regulate financial markets in the region and improve protections for investors. It aims to increase transparency across the EU's financial markets and standardize the regulatory disclosures required for particular markets.
- Read more:
Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX):
- Region: United States
- Description: Enacted in response to high-profile financial scandals, SOX aims to protect investors from fraudulent accounting activities by corporations. It mandates strict reforms to improve financial disclosures from corporations and prevent accounting fraud.
Consumer Financial Protection Act (CFPA):
- Region: United States
- Description: Part of the Dodd-Frank Act, the CFPA created the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) and established significant consumer protections against unfair, deceptive, or abusive practices in financial products and services.
- Read more: Consumer Financial Protection Act
These regulations illustrate the complex and varied landscape of fintech regulation, reflecting the need to balance innovation with consumer protection, market integrity, and financial stability.
Choosing the Right Tech Stack for a Fintech Application
Selecting the best tech stack for fintech app development is not always a simple decision. Some services you’d like to offer will require unique approaches, especially if your goal is to outperform competitors in the market.
Some apps are very particular and require specific technologies to ensure their success. Other times, a fresh twist on a popular app may allow you to select a simpler tech stack. It is crucial to consider what you are trying to build, weigh the pros and cons, and make a well-informed decision with the advice of a trusted expert.

MVP Development of a Fintech App
A minimum viable product (MVP) is important for any fintech app because it is used to test the application before it is launched. Usually, the MVP is a version of the app with key functionality and which only includes basic features.
Getting feedback from users is important, seeing as they will be the ones who you will try to market the app to. They should be able to provide suggestions for improvements and possible features to be included for ease of use. The most essential features of any fintech application are security, notifications, QR codes and scanning, and API integration.
We recommend following the steps below to develop a successful app:
- Design wireframes
- Create an MVP
- Test the MVP with users and gather feedback
- Produce the UI/UX of the app
- Construct an app prototype using the UI
- Verify the prototype and gather feedback
- Make the app open for public
Must-Have Features for Users

When you build a fintech app, it is essential for it to have user-friendly features, so it will be well-received on the market. Make sure your app has the following features if you want it to succeed against the competition:
Security & Data Privacy. To satisfy both user safety needs and legal requirements, fintech apps must demonstrate strong security in protecting users’ data and financial information. To achieve this, a fintech developer can implement blockchain, encryption, biometric and two-factor authentication, data obfuscation, and other security measures.
Security, fraud detection, and prevention are critical aspects of successful fintech app development, as they directly impact both the trustworthiness and the long-term viability of the app. Here are some detailed insights and strategies for enhancing security and preventing fraud in fintech apps:
-
Advanced Encryption Technologies: Utilize strong encryption protocols for data at rest and in transit. This includes implementing the latest standards like AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and TLS (Transport Layer Security) to safeguard sensitive financial information.
-
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA to add an extra layer of security. This could involve a combination of something the user knows (like a password), something the user has (like a smartphone), and something the user is (like a fingerprint or facial recognition).
-
Continuous Monitoring and Real-Time Alerts: Establish systems for continuous monitoring of transactions to detect unusual patterns or suspicious activities. Real-time alerts to users and administrators can facilitate immediate action to prevent potential fraud.
-
Behavioral Analytics and Machine Learning: Employ machine learning algorithms to analyze user behavior patterns. These systems can identify anomalies that may indicate fraudulent activities, such as unusual login times or locations, and strange transaction patterns.
-
Regular Security Audits and Compliance Checks: Conduct regular security audits to assess the vulnerability of the app. This should be complemented with compliance checks to ensure adherence to the latest regulatory standards in financial services.
-
Biometric Authentication: Incorporate biometric authentication methods like fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, or voice recognition. These methods provide a high level of security and are difficult for fraudsters to replicate.
-
Secure APIs: When integrating with third-party services through APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), ensure that these APIs are secure. This includes using authenticated APIs and regularly updating them to patch any security vulnerabilities.
-
User Education and Awareness: Educate users about security best practices. This could include information on creating strong passwords, recognizing phishing attempts, and understanding the importance of securing personal devices.
-
Fraud Detection Infrastructure: Invest in building a robust fraud detection infrastructure. This includes setting up rules and parameters that trigger automatic responses or alerts when certain suspicious activities are detected.
-
Incident Response Plan: Develop a comprehensive incident response plan. In the event of a security breach or fraud detection, having a clear plan can minimize damage and restore normal operations more quickly.
-
Data Privacy Compliance in Mobile App Development: Ensure that the app complies with data privacy laws relevant to the regions it operates in, such as GDPR in Europe or CCPA in California. This involves secure handling, storage, and processing of personal data.
-
Tokenization of Sensitive Data: Use tokenization to protect sensitive data like credit card numbers. This involves replacing the data with unique identification symbols (tokens) that retain all the essential information without compromising its security.
-
Regular Software Updates and Patch Management: Keep all software components of the app updated, including the operating system, libraries, frameworks, and even app store descriptions. Regular updates and patches help to close security vulnerabilities.
By focusing on these areas, fintech apps can greatly enhance their security and fraud prevention measures, which are vital for maintaining users' trust and confidence.
Biometric Authentication. Not long ago, many users hesitated to use biometric authentication, but as it has become a more commonplace way to log in and make payments, many users are feeling more comfortable with this technology. A Visa survey from 2021 found that 72% of U.S. consumers are interested in verifying their identity using fingerprint authentication, and 67% would like to use their fingerprint to make payments.
Payment Gateway Integration. Most apps need payment functionality. Common services like Stripe, PayPal, Zelle, or bank APIs can be integrated to make payment convenient for users.
User-friendly UI/UX. An easy-to-use and attractive interface creates a smooth and intuitive experience for users. A simple UI/UX should feature a visual dashboard that offers users a high level of flexibility.
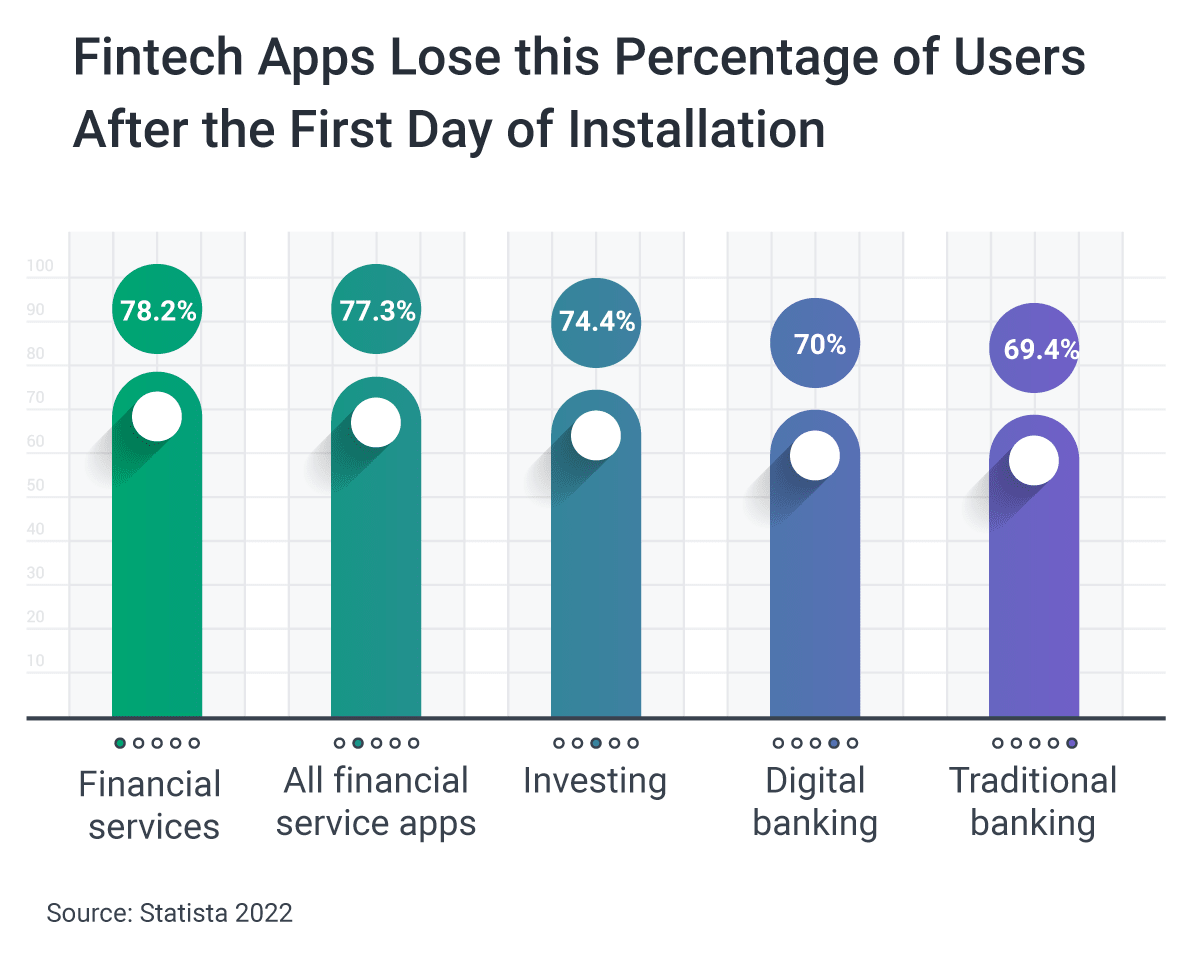
Streamlined Onboarding. Difficult onboarding processes are a top reason FinTech apps lose users so quickly after installation. According to MessageGears, after just the first day of installation, all financial service apps lose 77% of users. It is key to make sure your app’s onboarding process is simple and runs smoothly.
Data Analytics Integration. One of the main reasons why users download and use apps is to analyze their financial data. With the right analytics plug-ins, users are sent customized reports of their financial transactions and the state of their finances. Most well-known apps already take advantage of these integrations, so adopting data analytics will keep your app competitive.
Reward Programs. Reward campaigns are popular ways fintechs employ users as their biggest promoters. Robinhood used a simple email referral campaign to bring over one million users before their app launched. Referral bonuses, sign-up freebies, and gamification are all excellent ways to draw in users to your app.
Multi-Tier Functionality. The ability to multi-tier functions allows your app to work seamlessly while running different sessions together. Multiple activities can be managed and tracked easily by users, which allows an app to be flexible and highly efficient.
Machine Learning & Smartbots. AI is no longer an innovative and extra functionality for fintech apps; it is a necessity. Users are growing used to highly-personalized experiences and their expectations are high, as 61% of mobile banking customers said they would switch banks if their bank offered a poor experience, according to Business Insider.
AI has evolved from an experimental technology to an operational necessity in fintech. The AI in fintech market reached $30 billion in 2025 and is projected to grow to $83.1 billion by 2030. Generative AI in banking is expected to expand from $1.29 billion in 2024 to $21.57 billion by 2034. In 2025, AI-powered chatbots handled 78% of consumer service inquiries in digital banking, while AI adoption across financial institutions is expected to increase by 52% by 2026.
Users now expect highly-personalized experiences powered by AI, with 32% of U.S. consumers reporting they switched banks in 2025 due to poor digital service experiences. Big fintech players like JP Morgan Chase, Bank of America, and Wells Fargo use AI-powered solutions to provide personalized user experiences, predictive financial insights, fraud detection, and risk analytics—making AI integration essential for customer retention and competitive advantage
Big fintech players, like JP Morgan Chase, Bank of America, and Wells Fargo use smartbot solutions to improve their customer services across many parts of their apps. For big finance companies, smart chatbots might be the answer to providing more personalized user experiences and thus bettering customer retention.
What’s Next in User Features?
Voice Integration. Fintech services are beginning to introduce voice recognition as tools for two-way authentication, payments, and even for users to voice their concerns. Most frequently, fintech apps choose to utilize voice assistants, like Siri, Google, and Bixby for users to access the app without actually opening it. Some banks, like Santander, allow customers to conduct money transfers, inquire about transactions, and report stolen cards using voice recognition.
Crypto and Blockchain. Blockchain technology is rapidly emerging and could be a feature for some fintech apps to adopt. Issues like payment anomalies with vendors or cash flow administration are certainly prime for blockchain technology, and digital wallets and other bookkeeping methods can benefit from these solutions as well.
That said, Blockchain may not be the right technology for every type of fintech app, and choosing this technology entails extensive research about the needs of your app and its users.
Top Features on the Admin Side
We often give a lot of thought to how an app will look on the user side, but we must also consider what functions administrators need to communicate with users, secure user safety, and accept payments.

It is necessary for any fintech app to have an admin panel, which allows owners to manage the app’s data to power user-related functions, handle transactions, and track KPIs. An admin panel can also help companies gain valuable insights about users and utilize this data to identify problem areas, boost user conversion and retention rates, and increase the app’s quality. The most popular features for fintech companies on the admin side consist of the following:
- Admin authentication with encryption
- Secure hosting with multiple failover redundancy
- Access to banking data and real-time transfers to an escrow account
- A payment gateway
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system
- User Management (including extras like credit score checking)
- User analytics and KPI trackers
- Third-party integrations
- Chatbox to communicate with users and provide support
This section covers some non-obvious yet critical admin capabilities to consider during fintech app development.
- Core Admin Capabilities:
- Secure admin authentication with multi-factor verification
- User management, including credit scoring and account oversight
- Real-time access to banking data and transaction monitoring
- Payment gateway and escrow account management
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) integration
- User analytics and KPI tracking dashboards
- Third-party service integrations
- Support chatbox for user communication - Critical Security Controls:
- Granular role-based access control (not just admin vs. employee)
- Single sign-on integration and audit logs of all admin actions
- Automated compliance checks against regulatory guidelines
- Emergency controls: freeze accounts, rollback changes, disable compromised credentials - Risk Management:
- Real-time monitoring of threats and bad actor patterns
- Automated security certificate and protocol updates
- Transaction anomaly detection and blocking
Security Features
Fintech apps must demonstrate strong security to protect users’ data and financial information. Despite your best efforts, it is not possible to prevent 100% of cyberattacks and data breaches from hitting your app. Even large financial institutions like JPMorgan, Chase, and Equifax spend millions of dollars on cybersecurity.. However, it is within your power to protect users’ data to the best of your ability. To uphold your app to the highest level of security, we recommend the following:
Two-Factor Authentication
To improve your app’s security and go beyond the basic authentication method that consists of having simply a username and a password, two-factor authentication (2FA) is used as a top solution. The most commonly used 2FA method is a one-time code via SMS or email sent to users to login. Another popular method that is widely used by apps is a push notification that allows users to authenticate themselves with the push of a button.
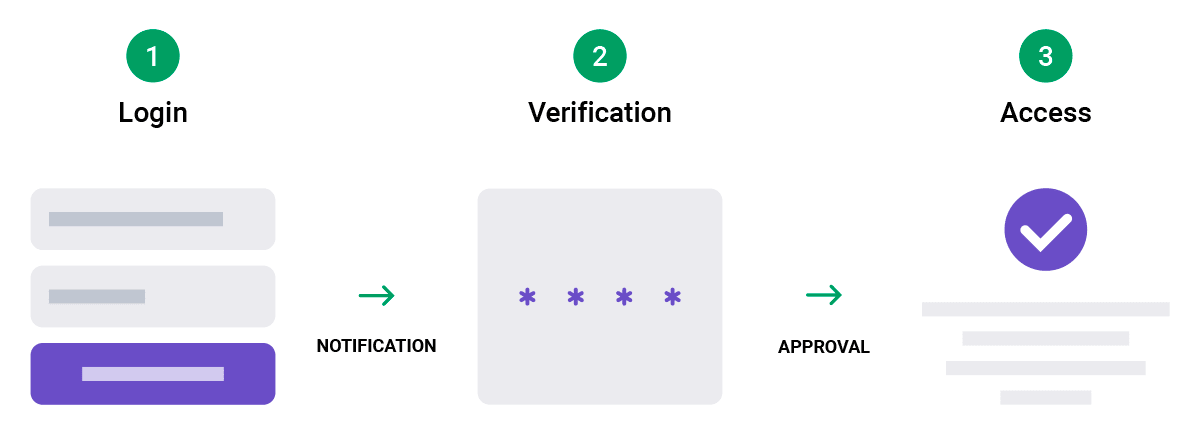
Tokenization & Encryption
Replace sensitive data (like credit card numbers) with random tokens stored in encrypted vaults. End-to-end encryption protects user data including names, addresses, SSNs, and financial information.
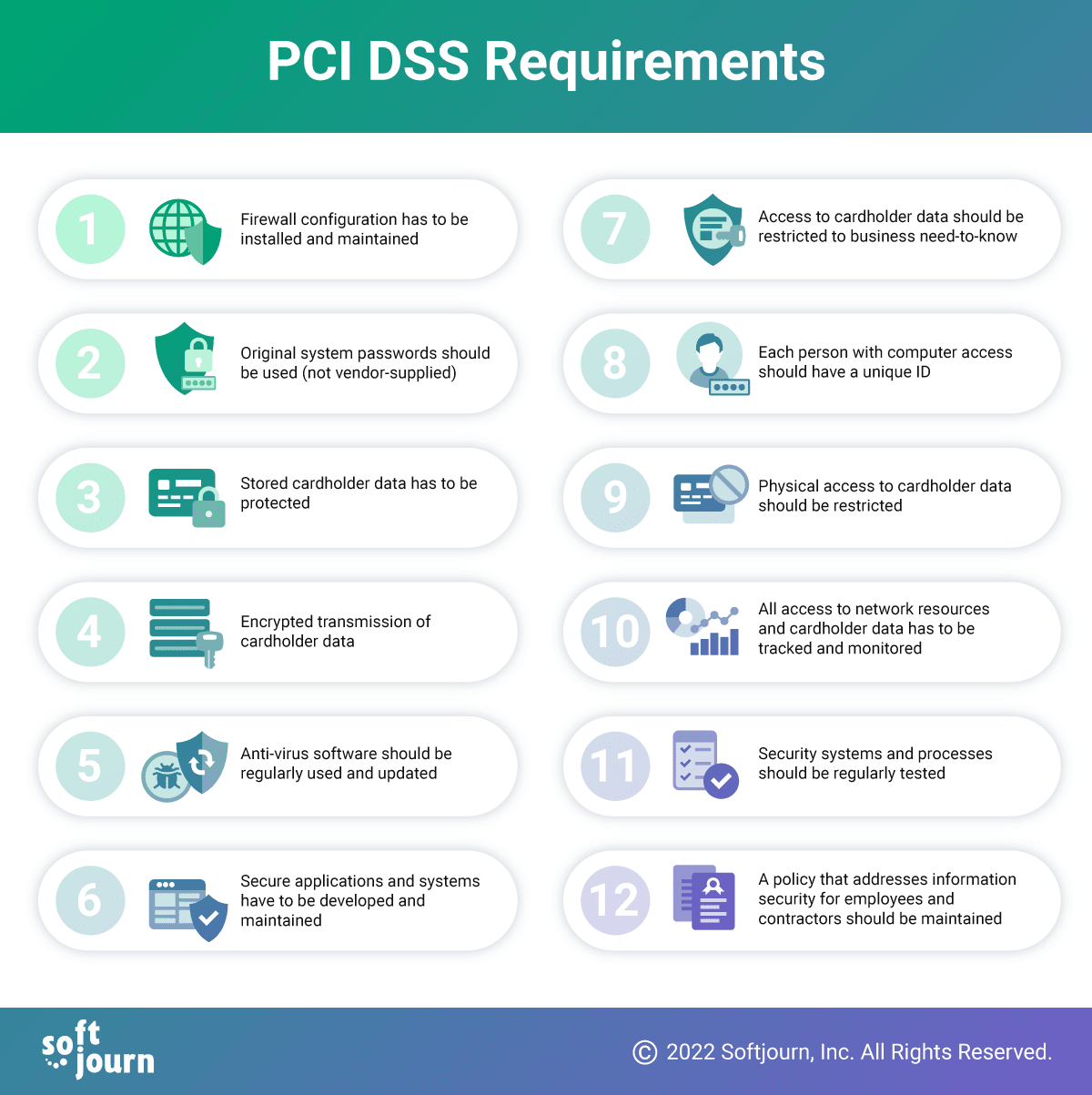
PCI DSS Compliance
For apps processing card payments, compliance is essential. While rigorous, it helps identify threats, avoid breaches, and build trust. Non-compliance can result in fines, increased fees, or loss of card processing ability. For all fintech apps that receive or process card payments, we highly recommend that they comply with the PCI DSS standard.
Positive outcomes associated with PCI compliance include identifying ongoing threats and vulnerabilities, avoiding data breaches, and gaining a certification that will put the company’s name in a reputable and stable position. However, the consequences of failing to comply with PCI DSS can consist of large fines, increased fees, and even the termination of the ability to process credit cards.
Fintech app owners should strive to log any user activity from every user at all times, monitor all transactions and stop hazardous ones. The app’s system should continuously record every user’s:
- Transactions and other actions
- User ID or account in the platform
- IP address
- Geolocation
- Device data
- Any other important information
These logs should be easily accessible during a potential ‘post-mortem analysis’ when an incident must be reviewed from all angles. Logs are crucial for properly conducting incident reports, which usually include the complete timeline, root cause analysis, and incident details.
It is also essential to have security precautions in place for stopping breaches, and a payment blocking feature is a good place to start. Payment blocking essentially halts any transaction that the system deems highly unusual or suspicious. Transactions can be rated as low, medium or high risk, through your own ranking system or in conjunction with a 3rd party’s system. In the case of a high-risk transaction, the system will decline the transaction and send an alert to inspect those log actions.
End-to-End Encryption
The FinTech industry has privacy standards with strict requirements for user data protection. One such requirement is the use of encryption to ensure data is protected against eavesdropping, data leaks, and data tampering.
End-to-End (E2E) Encryption is used to encrypt your users’ personal information, such as names, addresses, social security numbers, and their financial data, like credit card numbers and payment histories, as well as other sensitive information that users provide in your app.
3DS
Both businesses and consumers gain an extra layer of authentication with 3D Secure (3DS), which was developed by Visa in 2001. 3DS is a tool used to combat cyber threats involving card-related fraud, theft, and data breaches.
3DS protects customers by verifying their identity before payment authorization to shield the card from unauthorized usage, by using a three-domain model. For business owners, 3DS transfers the liability of fraudulent transactions to issuers and helps them meet security regulations.
HSM
Using HSM (Hardware Security Module) for data encryption may be the safest and most reliable option to prevent and mitigate risks of fraud, plus it meets the data security requirements defined by PCI. HSM is used to encrypt sensitive cardholder data and minimize the impact of threats and fraud.
An HSM is a device based on cryptographic hardware, responsible for the protection and security of sensitive information and critical assets. An HSM generates and stores cryptographic keys associated with digital certificates. The keys are used for encryption, decryption and authentication of digital signatures in operations used for fast and secure processing of information, such as online transactions and payments.
How Much Does It Cost to Build a Fintech App?
The average cost of developing a fintech solution mobile application varies greatly, depending on a broad range of factors, from the complexity of your app to your development team’s hourly rate. Generally, the starting cost for fintech app development is somewhere between $25,000 to $150,000. When shopping around for your app development, consider these factors that can drive up costs:
- UI/UX Design: The cost of UI/UX design can vary widely. If you require a custom, sophisticated design with a superior user experience, the cost will be higher. This includes interactive elements, custom animations, and a design that aligns with your brand identity.
- App Complexity and Features: More features mean more complexity, which drives up costs. Features like real-time analytics, advanced user profiles, or complex financial charts require more development time and expertise.
- Platform Choice (iOS, Android, Cross-platform): Developing for multiple platforms can increase costs, especially if you're building native apps for each platform. Cross-platform solutions like React Native or Flutter can be more cost-effective but may have limitations in terms of performance and integration with device-specific features.
- Web App and Backend API Development: Creating a web version of your fintech app or developing a robust backend API adds to the overall cost. This includes the setup of servers, databases, APIs, and integration with other services.
- Payment Processing and Subscriptions: Integrating payment gateways and managing recurring subscriptions through a mobile app require significant security and compliance measures, which can increase app development costs.
- Encryption and Compliance (like HIPAA): Compliance with regulations like HIPAA or adhering to bank-level encryption standards adds complexity and necessitates expert knowledge, impacting the budget.
- API Integrations: The cost will vary based on the number and complexity of third-party services your app integrates with. Common integrations include SMS gateways, calendar services, or map services.
- Machine Learning Capabilities: Incorporating AI or machine learning for features like predictive analytics, personalized financial advice, or fraud detection requires specialized skills and can significantly increase costs.
- User Authentication Methods: The complexity of the sign-up and authentication process (like integrating Google or Facebook login) can affect the cost. More sophisticated authentication methods, such as biometric checks, will increase development expenses.
- Ongoing Maintenance and Support: Post-launch, your app will require regular updates, bug fixes, and possibly the addition of new features. Ongoing maintenance is a recurrent cost and is crucial for the app's long-term success.
- Geographical Location of the Development Team: The cost can also be influenced by the location of your development team. Developers in North America and Western Europe typically charge more than those in Eastern Europe or Asia.
- Project Timeline: A tighter deadline can increase costs as it may require more resources or overtime work to meet the schedule.
- Custom Analytics and Reporting Tools: If you need custom analytics to track user behavior or financial trends, this will require additional development work.
- Security Audits and Testing: Rigorous testing and security audits are essential in fintech, but they also add to the development cost. This includes penetration testing, vulnerability assessments, and compliance checks.
- Scalability Considerations: If you anticipate a high number of users right from the start, the app needs to be scalable, which may require a more robust architecture and cloud services, impacting the initial development cost.
- A significant decision that impacts the cost of fintech app development is whether to build the app with an in-house team or to outsource the project. Each approach has its implications on the overall budget and project execution:
- In-House Development:
- App Cost Implications: Developing in-house usually involves higher initial costs. This includes salaries, benefits, and the necessary tools and technology. However, having an in-house team can mean better control over the project and potentially lower long-term costs due to the ongoing nature of app maintenance and updates.
- Expertise and Training: In-house development requires you to have or hire staff with specific skills in fintech app development. Training existing staff for such specialized skills can also add to the cost.
- Project Management: You'll need robust project management to oversee the development process. This includes managing timelines, coordinating different departments, and ensuring quality control.
- Outsourcing Fintech Development:
- Cost Efficiency: One of the primary benefits of outsourcing is its cost-effectiveness. By choosing to outsource, you can significantly reduce overhead costs associated with hiring full-time staff, such as salaries, benefits, and workspace. Outsourcing agencies often operate in regions with lower labor costs, which can lead to substantial savings without compromising on quality.
- Access to Specialized Expertise in fintech mobile app development: Outsourcing connects you with a global talent pool, providing access to specialized skills that might be scarce or expensive in your local market. These experts bring a wealth of experience in fintech-specific areas such as regulatory compliance, cybersecurity, blockchain technology, and advanced analytics. Their specialized knowledge can greatly enhance the quality and innovation of your fintech app.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Outsourcing offers unmatched flexibility in managing your workforce. It allows you to scale your development team according to project demands without the long-term commitments associated with in-house hiring. This adaptability is particularly beneficial in the dynamic fintech sector, where market demands and technology trends can shift rapidly.
- Efficient Project Management and Time Savings: Outsourcing companies bring streamlined processes and sophisticated project management tools, which can significantly expedite the development timeline. They are adept at handling complex projects, ensuring timely delivery while maintaining high standards of quality.
- Focus on Core Business Functions: By outsourcing app development, your internal team can focus on core business activities such as strategy, marketing, and customer engagement. This division of labor allows for a more efficient allocation of resources and can accelerate overall business growth.
- Risk Mitigation: Professional outsourcing firms have extensive experience in managing the risks associated with app development, including adherence to regulatory standards and data security. Their expertise in these areas can provide peace of mind and reduce the burden of risk management on your internal team.
- Continuous Support and Maintenance: Outsourcing firms often provide ongoing support and maintenance post-launch, ensuring that the app remains up-to-date with the latest technological advancements and security protocols. This long-term support is crucial for the app's durability and relevance in the market.
While outsourcing does require careful management of communication and quality control, the advantages it offers in terms of cost savings, access to expertise, and flexibility make it a highly attractive option for fintech app development. Choosing the right outsourcing app development company can lead to a fruitful collaboration, resulting in a high-quality app that meets both your budget and your business objectives.
How Softjourn Can Help You Build a Fintech App
To provide users with a reliable and fast app experience, your application should be developed using the latest programming languages, libraries, and frameworks. To position yourself well on the market, we recommend turning to a trusted software development partner. If you are looking to take the next step toward developing your app, Softjourn is here to help.
We have deep knowledge of the ins and outs of the financial software development industry and have been helping to make our clients’ ideas successful since 2001. Our R&D teams have expert knowledge and have been trusted for years by many top fintech companies.
No matter where you are on your app development journey, we can help your project succeed. We would be happy to schedule a call with you and provide project time and cost estimates tailored to your project.