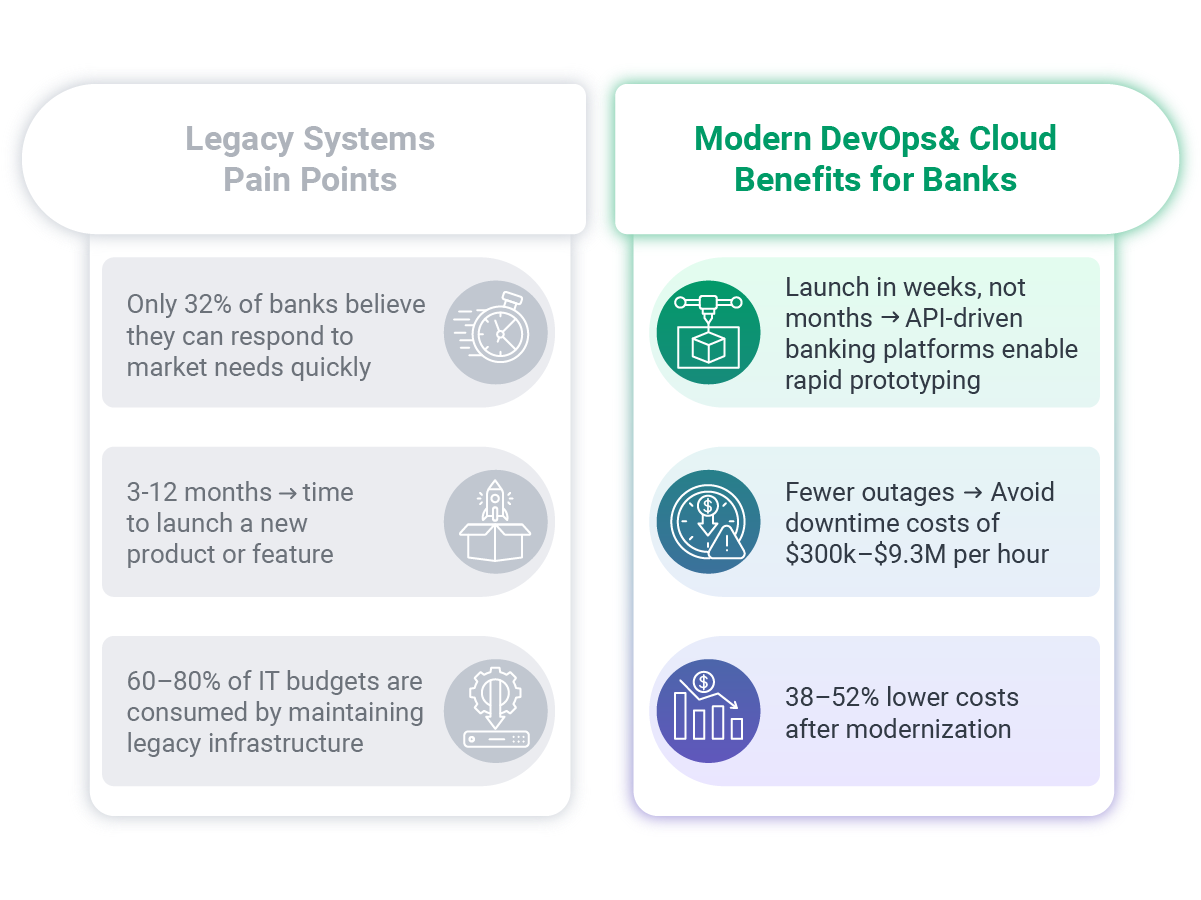
The banking industry invests billions in technology annually – with IT spending reaching 10.6% of revenues across the sector – yet only 32% of banks believe they can respond to market needs in the required time. On average, banks take over 3 months to launch a new product in an existing market, while fintech startups accomplish similar launches in weeks.
DevOps in banking offers a solution to this innovation gap. By combining development and operations teams, automating infrastructure, and implementing continuous integration practices, financial institutions can achieve the speed and agility of modern tech companies without compromising the security, compliance, and reliability that banking operations demand.
However, implementing DevOps in financial services presents unique challenges. Banks must navigate complex regulatory requirements, maintain zero-tolerance policies for downtime, and integrate with legacy systems that power critical operations.
This guide addresses these banking-specific challenges with real-world implementations, proven frameworks, and practical insights for successfully transforming financial services operations through DevOps.
The Banking Industry's DevOps Challenge
Financial institutions face a unique set of operational challenges that make traditional IT approaches increasingly inadequate.
Unlike technology companies that can iterate quickly and tolerate occasional downtime, banks must balance the need for innovation with stringent regulatory requirements, zero-tolerance policies for system failures, and integration with legacy infrastructure that often dates back decades.
Legacy Infrastructure Constraints
Many banks operate on core systems that were built 20-30 years ago, designed for a world where batch processing overnight was acceptable and real-time transactions were rare. These monolithic systems resist modern development practices, requiring extensive manual testing, lengthy change approval processes, and deployment windows that span months rather than days.
Legacy approaches require 6-12 months to launch new card products or features such as virtual cards or buy-now-pay-later options due to rigid code bases and manual configurations.
Meanwhile, modern API-driven platforms support rapid prototyping, enabling new product launches in weeks and instant integration with digital wallets like Apple Pay and Google Pay.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Banking operations must comply with an extensive framework of regulations, including SOX, PCI DSS, FDIC, and various data protection standards. These requirements create additional layers of validation, documentation, and approval processes that traditional development methodologies struggle to accommodate efficiently.
Every code change must be traceable, every deployment must be auditable, and every system modification must demonstrate compliance with applicable regulations. Without proper automation and integrated compliance checking, these requirements can add weeks to development cycles.
Cost Pressures and Hidden Expenses
Legacy technology incurs high hidden costs, with maintenance, hardware, and per-change fees consuming 60-80% of IT budgets. Financial institutions consistently underestimate the true total cost of ownership of legacy systems by 70-80%, with the average bank discovering their actual IT costs are 3.4 times higher than initially budgeted when all factors are considered.
The stakes for system reliability couldn't be higher. Downtime in banking systems costs between $300,000 to $9.3 million per hour, with annual costs for the financial sector reaching hundreds of millions of dollars.

Real-World Example: Legacy System Crisis
Our team recently worked with a mid-sized bank facing an urgent deadline: their SaaS core banking system was reaching end-of-life, with vendor support ending in months. Rather than purchasing an expensive replacement, they chose to build modern cloud infrastructure from scratch.
We architected and deployed their entire AWS infrastructure, implementing comprehensive monitoring and automated deployment processes. The project was delivered ahead of schedule, giving the bank modern, scalable cloud capabilities with full regulatory compliance. Read More.
DevOps Fundamentals for Banking
DevOps in banking requires adapting core development and operations principles to meet the unique demands of financial services.
While the fundamental concepts remain consistent (automation, collaboration, and continuous improvement) their implementation must account for regulatory compliance, security requirements, and the zero-tolerance approach to system failures that characterizes banking operations.

Core Principles Adapted for Financial Services
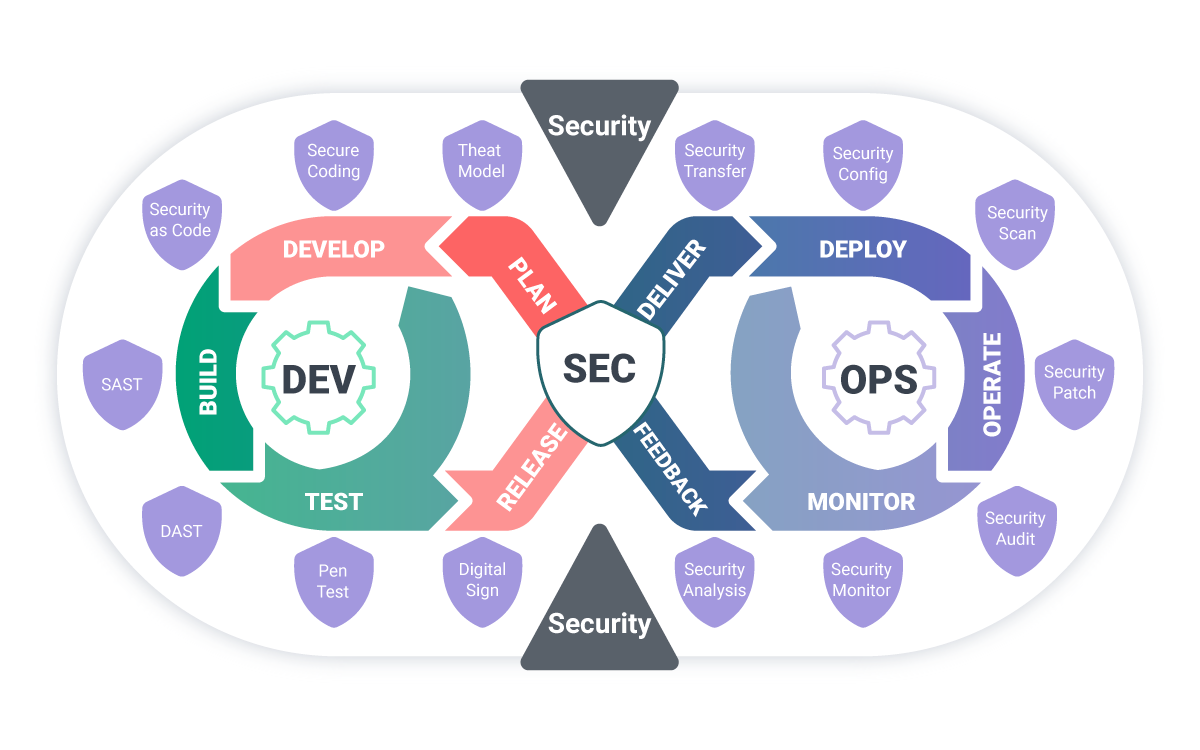
Security-First Development: Unlike general DevOps practices where security might be integrated later in the process, banking DevOps requires security considerations from the initial design phase. Every automation script, deployment pipeline, and infrastructure component must incorporate security controls and compliance verification as integral elements, not afterthoughts.
Compliance as Code: Traditional compliance involves manual documentation and periodic audits. Banking DevOps transforms compliance into automated processes where regulatory requirements are coded into deployment pipelines, infrastructure provisioning, and monitoring systems. This approach ensures consistent compliance across all environments while reducing manual oversight requirements.
Controlled Automation: While DevOps emphasizes automation, banking environments require carefully controlled automation with extensive logging, rollback capabilities, and human approval gates for critical systems. The goal is to automate routine operations while maintaining oversight and control over changes that could impact customer transactions or regulatory compliance.
Key Differences in Banking DevOps from General DevOps
Implementing banking DevOps differs significantly from DevOps at regular tech companies due to:
Change Management: Technology companies often embrace the "move fast and break things" philosophy, but banking requires controlled change management with extensive testing, documentation, and approval processes. DevOps in banking accelerates these processes through automation rather than eliminating necessary controls.
Deployment Strategies: While web applications can tolerate brief downtime during deployments, banking systems require zero-downtime deployment strategies, such as blue-green deployments, canary releases, and rolling updates, that ensure continuous service availability.
Data Handling: Banking DevOps must incorporate specialized data protection measures, encryption at rest and in transit, and audit trails for all data access. Development and testing environments require data masking and synthetic data generation to protect customer information while enabling effective testing.

Essential Toolchain for Banking DevOps
A banking-focused DevOps toolchain emphasizes security, auditability, and compliance integration:
Infrastructure as Code: Tools like Terraform and Ansible enable reproducible, auditable infrastructure deployments while maintaining version control and change tracking essential for regulatory compliance.
CI/CD with Security Integration: Continuous integration pipelines incorporate security scanning, compliance checking, and automated testing specific to financial services requirements. Every code change undergoes security analysis before deployment approval.
Monitoring and Observability: Banking systems require comprehensive monitoring that tracks not only performance metrics but also compliance indicators, security events, and audit trails. Tools must provide real-time alerting for any anomalies that could indicate security breaches or compliance violations.
Secret Management: Secure handling of API keys, database credentials, and encryption keys requires specialized tools that provide automated rotation, access logging, and integration with existing banking security infrastructure.
The successful implementation of these fundamentals creates a foundation for DevOps practices that accelerate development cycles while maintaining the security, compliance, and reliability standards that banking operations demand.
Cloud Banking and DevOps Integration
The convergence of cloud computing and DevOps practices has become essential for modern banking operations.
Cloud banking platforms enable financial institutions to leverage scalable infrastructure, automated deployments, and cost-effective operations while maintaining the security and compliance standards required for financial services.
Cloud-Native Banking Platforms
Modern banking increasingly relies on cloud-native architectures that support rapid scaling, global deployment, and integration with third-party financial services.
Cloud banking solutions provide the foundation for DevOps implementations by offering infrastructure as code, automated scaling, and managed services that reduce operational overhead.
Cloud-based core banking systems enable banks to deploy new features and services without the constraints of legacy infrastructure. These platforms support microservices architectures, containerized applications, and API-first designs that align naturally with DevOps practices and continuous delivery methodologies.

Hybrid Cloud Strategies for Banks
Most financial institutions adopt hybrid cloud approaches that balance regulatory requirements with operational flexibility. Critical customer data and core banking functions often remain in private clouds or on-premises environments, while development, testing, and non-critical workloads leverage public cloud resources.
This hybrid approach allows banks to implement DevOps practices across different environments while maintaining compliance with data residency requirements and regulatory frameworks. Successful implementations use consistent tooling and processes across hybrid environments to ensure seamless operations and deployment workflows.
Container Orchestration for Financial Applications
Container technologies like Kubernetes have become central to banking DevOps implementations, enabling consistent deployment across different environments and efficient resource utilization.
Containers provide the isolation and security controls necessary for banking applications while supporting the automation and scalability that DevOps practices require.
Financial institutions use container orchestration to manage complex application deployments, implement blue-green deployment strategies, and ensure consistent configuration across development, testing, and production environments.

Real-World Example: Cost Optimization Through DevOps Practices
Cloud banking implementations can achieve significant cost reductions through intelligent DevOps practices and continuous optimization.
Our team recently helped an expense management company reduce their AWS costs by nearly 40%, saving over $25,000 annually.
The optimization involved analyzing system load patterns, implementing auto-scaling during low-demand periods, and selecting optimal service subscription models over expensive on-demand options.
By establishing dedicated monitoring for resource consumption and eliminating unnecessary resources like test databases running during weekends, the client achieved a four-fold reduction in resource usage while maintaining performance. Read More.
Implementation Framework
Successfully implementing DevOps in banking requires a structured approach that balances the need for rapid transformation with the careful controls and compliance requirements essential to financial services.
This framework provides a proven methodology for introducing DevOps practices while maintaining operational stability and regulatory compliance.
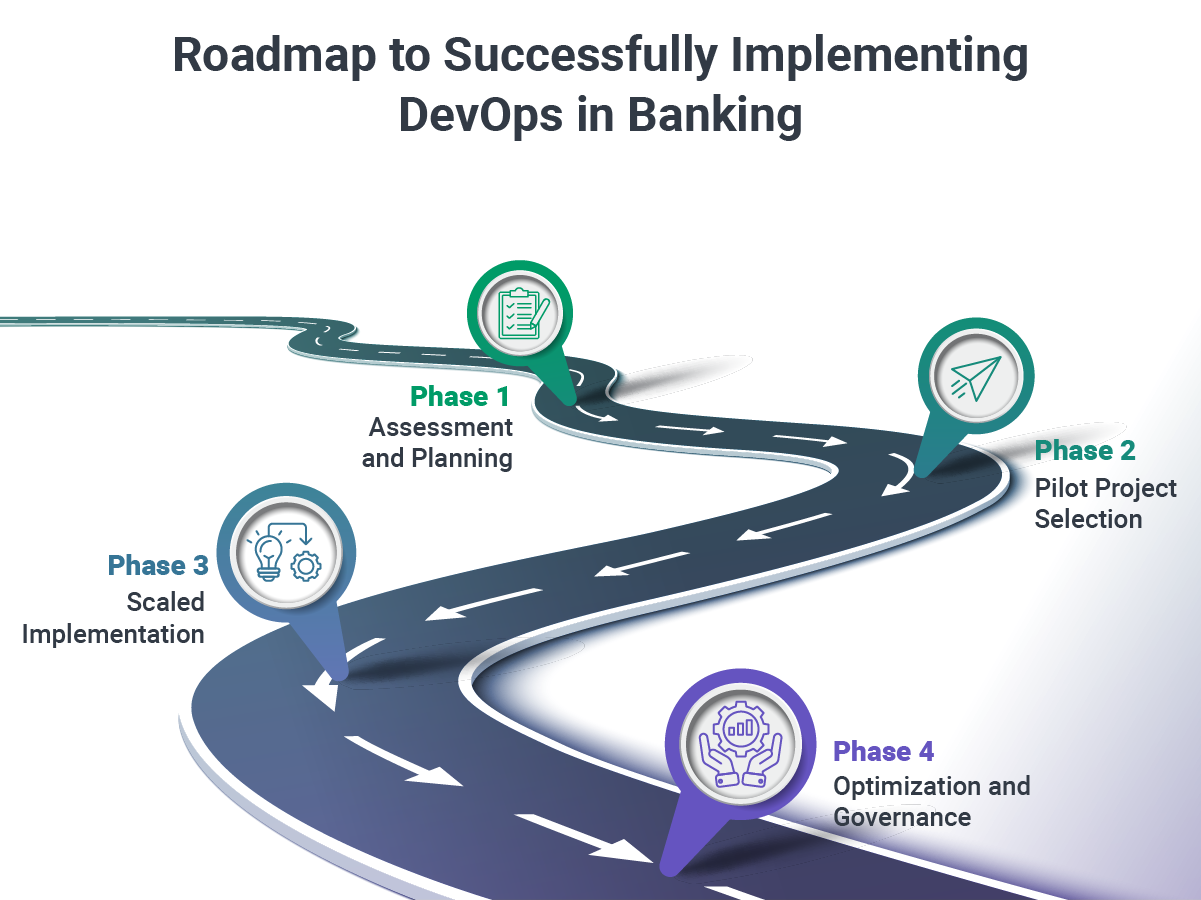
Phase 1: Assessment and Planning
The foundation of any banking DevOps transformation begins with a comprehensive assessment of existing systems, processes, and organizational readiness. This phase involves mapping current development workflows, identifying legacy system dependencies, and evaluating regulatory compliance requirements that will influence the implementation approach.
Key activities include conducting infrastructure audits, documenting existing deployment processes, assessing team skills and organizational culture, and establishing baseline metrics for performance, security, and compliance. This assessment creates the roadmap for transformation while identifying potential risks and mitigation strategies.
Phase 2: Pilot Project Selection
Banking DevOps implementations succeed through careful pilot project selection that demonstrates value while minimizing risk to critical operations. Ideal pilot projects involve non-customer-facing systems, have limited regulatory requirements, and can showcase measurable improvements in deployment speed, system reliability, or operational efficiency.
The pilot phase focuses on establishing foundational DevOps practices: implementing infrastructure as code, creating automated testing frameworks, establishing CI/CD pipelines, and integrating security scanning into development workflows. Success in the pilot phase builds organizational confidence and provides lessons learned for broader implementation.
Phase 3: Scaled Implementation
Scaling DevOps practices across banking operations requires systematic expansion that maintains quality while accelerating adoption. This phase involves extending successful pilot practices to additional systems, training development and operations teams on new processes, and integrating DevOps workflows with existing compliance and risk management frameworks.
Critical scaling activities include standardizing toolchains across teams, implementing organization-wide monitoring and alerting systems, establishing shared infrastructure and deployment pipelines, and creating governance frameworks that ensure consistency while enabling team autonomy.
Phase 4: Optimization and Governance
Mature banking DevOps implementations require ongoing optimization and governance to maintain effectiveness while adapting to changing regulatory requirements and business needs. This phase focuses on continuous improvement of processes, optimization of cloud costs and resource utilization, and evolution of practices based on operational experience and changing technology landscape.

Real-World Example: Engineering Process Transformation
Our team recently partnered with a bank during a major transformation initiative to address fragmented workflows and limited process maturity across multiple vendor systems. We introduced structured development practices, including full SDLC with peer reviews, disaster recovery plans, and automated QA processes.
The implementation included building secure AWS infrastructure with multi-environment isolation and automated deployments.
The structured practices we established became part of the client's permanent framework, demonstrating how systematic DevOps implementation can create lasting organizational improvement while maintaining banking compliance standards. Read More.
Compliance and Security in Banking DevOps
Security and regulatory compliance represent the most critical aspects of DevOps implementation in banking environments.
Unlike other industries where security can be layered on later, financial services require security-first approaches that integrate compliance verification, audit trails, and regulatory requirements directly into development and deployment workflows.
Automated Compliance Checking
DevOps in modern banking transforms compliance from manual documentation exercises into automated processes integrated throughout the development lifecycle. Compliance as code ensures that regulatory requirements for PCI DSS, PSD2, FDIC, and other frameworks are automatically verified at every stage of development and deployment.
Automated compliance checking includes code analysis for security vulnerabilities, infrastructure validation against regulatory standards, and deployment verification that ensures production systems meet compliance requirements before going live. This approach reduces compliance overhead while providing more consistent and reliable adherence to regulatory frameworks.
Security Scanning in CI/CD Pipelines
When used for financial institutions, DevOps pipelines integrate multiple layers of security scanning that examine code, dependencies, containers, and infrastructure configurations before any deployment proceeds. Static application security testing, dynamic analysis, and infrastructure security scanning become automatic gates in the deployment process.
These security integrations ensure that vulnerabilities are identified and addressed during development rather than discovered in production environments. Automated security scanning provides continuous protection while enabling the rapid deployment cycles that DevOps practices enable.

Audit Trails and Documentation
Financial services regulations require comprehensive audit trails that document every change, access, and deployment across all systems. DevOps implementations in most banks automatically generate and maintain these audit records through integrated logging, change tracking, and access monitoring.
Every infrastructure modification, code deployment, and system access is logged with full traceability, providing the documentation necessary for regulatory audits while supporting operational troubleshooting and security incident response.
Zero-Trust Architecture Principles
Banking DevOps implementations increasingly adopt zero-trust security models that verify every access request, encrypt all communications, and maintain strict access controls across all systems and environments. This approach aligns with the security-first requirements of financial services while supporting the automation and integration that DevOps practices require.

Real-World Example: PCI DSS Compliance With Cloud Migration
Our team recently supported UPC (Ukrainian Processing Center), a major financial institution, in their migration to AWS while maintaining critical PCI DSS compliance requirements. The project involved migrating existing on-premise infrastructure to cloud-based systems due to new regulatory requirements for Open Banking and API services.
We implemented a phased migration strategy using AWS serverless architecture to ensure both security and compliance. The approach included infrastructure as code through Terraform, environment isolation within a single AWS account for security, and centralized management that simplified oversight while meeting audit requirements.
The migration enhanced the client's performance, scalability, and security while reducing operational costs through serverless technologies. Read More.
Common Pitfalls and Solutions
Banking DevOps implementations face predictable challenges that can derail transformation efforts if not properly anticipated and addressed. Understanding these common pitfalls and their solutions enables financial institutions to avoid costly mistakes and accelerate successful adoption.
Underestimating Migration Complexity
One of the most frequent mistakes is underestimating the complexity of migrating from legacy systems to modern platforms. Banks often focus on technical migration aspects while overlooking operational dependencies, compliance requirements, and team training needs.
Solution: Implement phased migration strategies that address technical, operational, and organizational changes systematically. Begin with a comprehensive assessment of existing systems, dependencies, and compliance requirements before attempting any migration activities.
Inadequate Security Integration
Many banking DevOps implementations fail because security considerations are treated as separate concerns rather than integrated throughout the development and deployment lifecycle. This approach creates vulnerabilities and compliance gaps that can compromise entire implementations.
Solution: Adopt security-first DevOps practices that integrate security scanning, compliance checking, and audit requirements into every stage of development and deployment. Treat security as an enabler of DevOps rather than an impediment.
Insufficient Change Management
Banking organizations often underestimate the cultural and process changes required for successful DevOps adoption. Technical implementations succeed while organizational adoption fails due to inadequate change management and team training.
Solution: Invest equally in organizational change management and technical implementation. Provide comprehensive training, establish clear communication channels, and celebrate early wins to build organizational momentum for DevOps adoption.

Real-World Example: Complex Platform Migration
Our team recently supported PEX, a financial services company, through a complex migration from Windows to Linux infrastructure while adopting containerization and transitioning automation tools across hybrid cloud environments.
The migration achieved significant licensing cost savings, reduced server maintenance time from 90 minutes to 15 minutes per server, and enhanced operational resilience through containerized services.
This demonstrates how systematic execution and focus on both technical and operational requirements enable successful DevOps transformations in banking environments. Read More.

The Future of DevOps in Banking
The evolution of DevOps in banking continues to accelerate as financial institutions recognize the competitive advantages of modern development and operations practices. Several emerging trends will shape how banks implement and optimize DevOps practices in the coming years:
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Two massive transformations are reshaping banking simultaneously: artificial intelligence is revolutionizing how banks operate, while DevOps is fundamentally changing how they build and deploy technology.
As Chris Couch, Head of Invoice-to-Cash Business Development at Flywire, notes at a recent PYMNTS’ conference: "AI is an inflection point in technology, it is like the invention of internet or the iPhone, and CFOs are realizing that not being involved in it is going to leave you behind."
When AI meets DevOps in banking, the results are transformative. Intelligent automation can predict infrastructure failures before they occur, automatically optimize cloud costs based on usage patterns, and identify security threats in real-time across deployment pipelines. Machine learning algorithms analyze system performance data to recommend optimal scaling strategies, while AI-driven compliance monitoring ensures regulatory adherence without manual oversight.
This convergence enables banks to move from reactive operations to truly predictive systems that anticipate problems, optimize resources automatically, and maintain security and compliance through intelligent automation rather than manual processes.

Regulatory Evolution and Automation
Regulatory frameworks continue to evolve toward greater emphasis on digital services, open banking, and real-time payment systems. DevOps practices will become essential for banks to rapidly adapt to new regulatory requirements while maintaining compliance with existing frameworks.
Automated compliance checking, policy-as-code implementations, and regulatory change management will transition from competitive advantages to essential capabilities for financial institutions operating in dynamic regulatory environments.
Edge Computing and Distributed Operations
The growth of mobile banking, IoT devices, and real-time payment systems drives demand for edge computing capabilities that bring processing closer to end users. DevOps practices in banking must evolve to support distributed architectures that maintain security, compliance, and operational consistency across diverse deployment environments.
Final Word
DevOps in banking represents a fundamental shift toward operational excellence that enables financial institutions to compete effectively in digital markets while maintaining the security, compliance, and reliability standards essential to banking operations.
The financial institutions that successfully implement banking-specific DevOps practices achieve faster time-to-market, reduced operational costs, and the agility to respond quickly to market opportunities and regulatory changes.
The path forward requires commitment to both technical excellence and organizational change, supported by proven frameworks and experienced teams who understand the unique requirements of financial services.

Ready to Transform Your Banking Operations?
Contact us to learn how our DevOps expertise can help optimize your financial services infrastructure and accelerate your digital transformation.
The combination of cloud banking infrastructure and DevOps practices creates opportunities for financial institutions to reduce operational costs while improving system reliability, security, and scalability - essential advantages in today's competitive banking environment.



















